
Vanguard 1 is an American satellite that was the fourth artificial Earth-orbiting satellite to be successfully launched, following Sputnik 1, Sputnik 2, and Explorer 1. It was launched 17 March 1958. Vanguard 1 was the first satellite to have solar electric power. Although communications with the satellite were lost in 1964, it remains the oldest human-made object still in orbit, together with the upper stage of its launch vehicle.
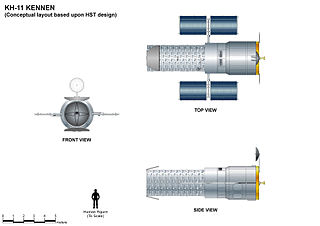
The KH-11 KENNEN is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and so offer real-time optical observations.

Shavit 2 is a small lift launch vehicle produced by Israel from 1982 onwards, to launch satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched on 19 September 1988, making Israel the eighth nation to have an orbital launch capability after the USSR, United States, France, Japan, People's Republic of China, United Kingdom, and India.

Vanguard 2 is an Earth-orbiting satellite launched 17 February 1959 at 15:55:02 GMT, aboard a Vanguard SLV-4 rocket as part of the United States Navy's Project Vanguard. The satellite was designed to measure cloud cover distribution over the daylight portion of its orbit, for a period of 19 days, and to provide information on the density of the atmosphere for the lifetime of its orbit. As the first weather satellite and one of the first orbital space missions, the launch of Vanguard 2 was an important milestone in the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Vanguard 2 remains in orbit.

Ofeq, also spelled Offek or Ofek is the designation of a series of Israeli reconnaissance satellites first launched in 1988. Most Ofeq satellites have been carried on top of Shavit 2 launch vehicles from Palmachim Airbase in Israel, on the Mediterranean coast. The low Earth orbit satellites complete one Earth orbit every 90 minutes. The satellite launches made Israel the eighth nation to gain an indigenous launch capability. Both the satellites and the launchers were designed and manufactured by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) with Elbit Systems' El-Op division supplying the optical payload.

The Israel Space Agency is a governmental body, a part of Israel's Ministry of Science and Technology, that coordinates all Israeli space research programs with scientific and commercial goals.

KH-9, commonly known as Big Bird or KeyHole-9, was a series of photographic reconnaissance satellites launched by the United States between 1971 and 1986. Of twenty launch attempts by the National Reconnaissance Office, all but one were successful. Photographic film aboard the KH-9 was sent back to Earth in recoverable film return capsules for processing and interpretation. The highest ground resolution achieved by the main cameras of the satellite was 2 ft (0.61 m). Another source says "images in the "better-than-one-foot" category" for the last "Gambit" missions.

TecSAR-1, also known as TechSAR, Polaris and Ofeq-8, is an Israeli reconnaissance satellite, equipped with a synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) developed by Elta Systems. It was successfully launched at 03:45 UTC on 21 January 2008, by PSLV C-10 launch vehicle, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India.
The Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) was a constellation of polar orbiting weather satellites funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) with the intent of improving the accuracy and detail of weather analysis and forecasting. The spacecraft were provided by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center oversaw the manufacture, integration and test of the NASA-provided TIROS satellites. The first polar-orbiting weather satellite launched as part of the POES constellation was the Television Infrared Observation Satellite-N (TIROS-N), which was launched on 13 October 1978. The final spacecraft, NOAA-19, was launched on 6 February 2009. The ESA-provided MetOp satellite operated by EUMETSAT utilize POES-heritage instruments for the purpose of data continuity. The Joint Polar Satellite System, which was launched on 18 November 2017, is the successor to the POES Program.
Kosmos 8, also known as DS-K-8 No.1 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 18 was a technology demonstration satellite which was launched by the Soviet Union in 1962. It was the eighth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the third spacecraft launched as part of the DS programme to successfully reach orbit, after Kosmos 1 and Kosmos 6. Its primary mission was to demonstrate the technologies of SIGINT for future Soviet military satellites.
Ofeq-9, also known as Ofek 9, is part of the Ofeq family of reconnaissance satellites designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israeli Ministry of Defense.

DISCOVERE 34, also known as CORONA 9027, was a United States optical reconnaissance satellite which was launched on 5 November 1961. It was the ninth of ten CORONA KH-2 satellites, based on the Agena B.
The Earth Remote Observation System-A was part of the EROS family of Israeli commercial Earth observation satellites, designed and manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI). This was the first satellite in the series. The satellite was owned and operated by ImageSat International, ImageSat International N.V. (ISI) headquartered at Limassol, Cyprus, and incorporated in the Netherlands Antilles, Cayman Islands.
AMOS-4 is an Israeli commercial communications satellite, operated by Spacecom Satellite Communications, Tel Aviv-based, part of the AMOS series of satellites.
Ofeq-10, also known as Ofek-10, is part of the Ofeq family of reconnaissance satellites designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israeli Ministry of Defense.

Landsat 9 is an Earth observation satellite launched on 27 September 2021 from Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Space Force Base on an Atlas V 401 launch vehicle. NASA is in charge of building, launching, and testing the satellite, while the United States Geological Survey (USGS) operates the satellite, and manages and distributes the data archive. It is the ninth satellite in the Landsat program, but Landsat 6 failed to reach orbit. The Critical Design Review (CDR) was completed by NASA in April 2018, and Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems (NGIS) was given the go-ahead to manufacture the satellite.
Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) is an initiative created by NASA to attract and retain students in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines. The program is managed by the Launch Services Program (LSP) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Explorer 24 was a NASA satellite designed for atmospheric studies. Explorer 24 was launched on 21 November 1964 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Lompoc, California, with a Scout X-4. Explorer 24 was launched along with its successor satellite, Explorer 25.










