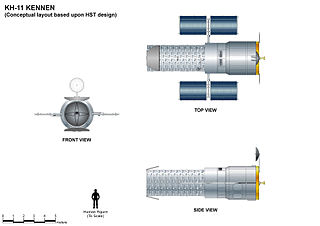
The KH-11 KENNEN is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and so offer real-time optical observations.

Shavit 2 is a small lift launch vehicle produced by Israel from 1982 onwards, to launch satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched on 19 September 1988, making Israel the eighth nation to have an orbital launch capability after the USSR, United States, France, Japan, People's Republic of China, United Kingdom, and India.

Israel Aerospace Industries or IAI (תע"א) is Israel's major aerospace and aviation manufacturer, producing aerial and astronautic systems for both military and civilian usage. It has 15,000 employees as of 2018. IAI is completely state-owned by the government of Israel.

Ofeq, also spelled Offek or Ofek is the designation of a series of Israeli reconnaissance satellites first launched in 1988. Most Ofeq satellites have been carried on top of Shavit 2 launch vehicles from Palmachim Airbase in Israel, on the Mediterranean coast. The low Earth orbit satellites complete one Earth orbit every 90 minutes. The satellite launches made Israel the eighth nation to gain an indigenous launch capability. Both the satellites and the launchers were designed and manufactured by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) with Elbit Systems' El-Op division supplying the optical payload.

Earth Resources Observation Satellite (EROS) is a series of Israeli commercial Earth observation satellites, designed and manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI), with optical payload supplied by El-Op. The satellites are owned and operated by ImageSat International N.V. (ISI), a company founded in 1997, as a Joint venture between IAI, El-Op and Core Software Technology (CST). EROS A was launched on December 5, 2000 and EROS B on April 25, 2006.

United Launch Alliance (ULA), legally United Launch Alliance, LLC, is an American spacecraft launch service provider that has manufactured and operated a number of rocket vehicles that are capable of launching spacecraft into orbits around Earth and to other bodies in the Solar System and beyond. The company, which is a joint venture between Lockheed Martin Space and Boeing Defense, Space & Security, was formed in December 2006. Launch customers of the United Launch Alliance include the Department of Defense (DoD), NASA, and other organizations.

The Israel Space Agency is a governmental body, a part of Israel's Ministry of Science and Technology, that coordinates all Israeli space research programs with scientific and commercial goals.
The Palmachim Airbase is an Israeli military facility and spaceport located near the cities of Rishon LeZion and Yavne on the Mediterranean coast. It is named after nearby Kibbutz Palmachim.
AMOS-1, then INTELSAT 24, is a commercial communications satellite which was operated by Spacecom as AMOS-1, for Affordable Modular Optimized Satellite and formed part of the AMOS series of satellites. It was the first Israeli civilian communications satellite, and was initially positioned at 4° West longitude in geostationary orbit. Then in September 2011, it was moved to 31° East.

Ofeq-7 is part of the Ofeq family of Earth observation satellites designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israel Ministry of Defense.

TecSAR-1, also known as TechSAR, Polaris and Ofeq-8, is an Israeli reconnaissance satellite, equipped with a synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) developed by Elta Systems. It was successfully launched at 03:45 UTC on 21 January 2008, by PSLV C-10 launch vehicle, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India.
Shavit 2 was the first Israeli sounding rocket, launched on 5 July 1961 for meteorological research.
Ofeq-9, also known as Ofek 9, is part of the Ofeq family of reconnaissance satellites designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israeli Ministry of Defense.

Several new rockets and spaceports began operations in 2016.
The Earth Remote Observation System-A was part of the EROS family of Israeli commercial Earth observation satellites, designed and manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI). This was the first satellite in the series. The satellite was owned and operated by ImageSat International, ImageSat International N.V. (ISI) headquartered at Limassol, Cyprus, and incorporated in the Netherlands Antilles, Cayman Islands.

The Earth Remote Observation System-B (EROS-B) is the second satellite launched in a series of the EROS family of Israeli commercial Earth observation satellites, designed and manufactured by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI). It is owned and operated by ImageSat International N.V. (ISI), in the Netherlands Antilles, Cayman Islands, with offices in Limassol, Cyprus, and in Tel Aviv, Israel.
Ofeq-11, also known as Ofek 11, is part of the Ofeq family of reconnaissance satellites designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israeli Ministry of Defense.
Ofek-16, also known as Ofeq-16, is an Israeli electro-optical reconnaissance satellite. It is part of the Ofeq family, designed and built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israeli Ministry of Defence.
The Mohammed VI satellites are a series of two Moroccan Earth observation and reconnaissance satellites, namely Mohammed VI-A and Mohammed VI-B, developed and built by Airbus Defence and Space and Thales Alenia Space based upon the Astrosat-1000 satellite bus. They are Morocco's first optical imaging satellites, and are operated by Morocco's Ministry of Defense, with an expected service life of 5 years. They are named after Mohammed VI, the King of Morocco.







