
Beta Aquarii is a single star in the constellation of Aquarius. It has the official name Sadalsuud and the Bayer designation β Aquarii, abbreviated Beta Aqr or β Aqr. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, this component is located at a distance of approximately 540 light years (165 parsecs) from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 6.5 km/s. The star serves as an IAU radial velocity standard.

98 Aquarii is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 98 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation, although it also bears the Bayer designation b1 Aquarii. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.97. The distance to this star, 163 light-years, is known from parallax measurements made with the Hipparcos spacecraft.

Eta Aquarii, Latinized from η Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.04. The distance to this star, as determined by parallax measurements, is about 168 light-years. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of –8 km/s. Eta Aquarii is near the radiant of a meteor shower named after it.

Tau2 Aquarii, Latinized from τ2 Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.0. Because the star lies near the ecliptic it is subject to occultations by the Moon. The star is located at a distance of approximately 318 light years from the Sun based on parallax.

91 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation for a triple star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It also bears the Bayer designation Psi1 Aquarii. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.248. Parallax measurements yield an estimated distance of around 150 light-years from Earth. An extrasolar planet is known to orbit the main star.

Psi3 Aquarii, Latinized from ψ3 Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a visual binary star system in the constellation of Aquarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.98, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of roughly 262 light-years.

Iota Aquarii, Latinised from ι Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of +4.279. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to this star is around 175 light-years. The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −10 km/s.

Sigma Aquarii, Latinized from σ Aquarii, is a double star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius, positioned about 1.3° to the south of the ecliptic. Due to its proximity to the ecliptic, this star is subject to occultation by the Moon. It has a white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.81. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to this star is approximately 175 light-years. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +11 km/s.

Rho Aquarii, Latinized from ρ Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.34. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is at a distance of roughly 870 light-years from Earth. It is drifting closer with a radial velocity of –9 km/s. The proximity of this star to the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations.

3 Aquarii is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 3 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the Bayer designation k Aquarii and the variable star designation EN Aquarii. With a mean apparent visual magnitude of 4.429, it is visible to the naked eye in dark skies. It has an annual parallax shift of 5.57 milliarcseconds with a 5% margin of error, which translates to a physical distance of around 590 light-years from Earth.
104 Aquarii (abbreviated 104 Aqr) is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 104 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation, although it also bears the Bayer designation A2 Aquarii. Based on an annual parallax shift of only 3.89 ± 0.25 milliarcseconds, the distance to this star is about 840 light-years (260 parsecs). At that range, the brightness of the star in the V-band is reduced by 0.10 magnitudes as a result of extinction caused by intervening gas and dust.

106 Aquarii, abbreviated 106 Aqr, is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 106 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation, and it also bears the Bayer designation i1 Aquarii. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.2, making it bright enough to be viewed from the suburbs according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale. An annual parallax shift of 8.61 milliarcseconds yields an estimated distance of around 380 light-years from Earth.

38 Aquarii is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 38 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation; its Bayer designation is e Aquarii. It is a faint star but visible to the naked eye, with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.43. Based on parallax measurements, it is around 450 light-years away; it is 0.28 degree south of the ecliptic.
44 Aquarii is a single star located 336 light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 44 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, yellow-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.75. This body is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +7.4 km/s.

74 Aquarii is a triple star system in the constellation of Aquarius. 74 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation and it also bears the variable star designation HI Aquarii. The combined apparent visual magnitude is 5.8, although it is very slightly variable, and it is located at a distance of 590 light-years from Earth.
82 Aquarii is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 82 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.15, which, according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, means it is a faint star that requires dark rural skies to view. The annual parallax shift of 82 Aquarii is 3.6764±0.1715 mas, which equates to a distance of roughly 890 light-years from Earth. Because this star is positioned near the ecliptic, it is subject to lunar eclipses.
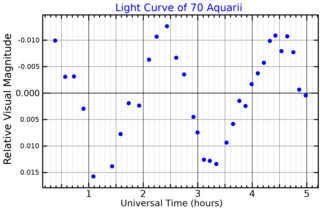
70 Aquarii is a variable star located 425 light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It has the variable star designation FM Aquarii; 70 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation. It is near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye, appearing as a dim, yellow-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 6.19. This star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of –5.8 km/s.
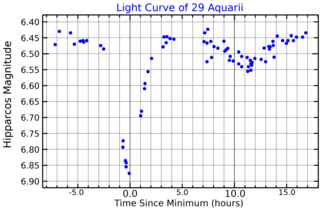
29 Aquarii is a binary star system located around 590 light years away from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 29 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation; the system also bears the variable star designation DX Aquarii. It is a challenge to view with the naked eye, appearing as a dim star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 6.39. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of about +15 km/s.
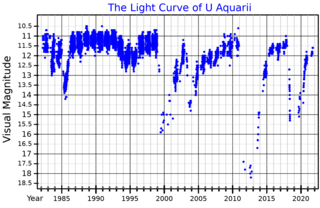
U Aquarii, abbreviated U Aqr, is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is invisible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude that ranges from 10.6 down to as low as 15.9. Based on parallax measurements, the distance to this star is approximately 38 kly (12 kpc). In 1990, W. A. Lawson and associates provided a distance estimate of 43 kly (13.2 kpc) based on the assumption of a bolometric magnitude of −5. It appears to lie several kiloparsecs below the galactic plane, and thus may belong to an old stellar population.

EP Aquarii is a semiregular variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. At its peak brightness, visual magnitude 6.37, it might be faintly visible to the unaided eye under ideal observing conditions. A cool red giant on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), its visible light brightness varies by about 1/2 magnitude over a period of 55 days. EP Aquarii has a complex circumstellar envelope (CSE), which has been the subject of numerous studies.








