
Sigma Sagittarii, Latinized from σ Sagittarii; formally named Nunki, is the second-brightest star in the constellation of Sagittarius. It has an apparent magnitude of +2.05, making it readily visible to the naked eye. The distance to this star, determined using parallax measurements from the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, yields a value of approximately 228 light-years from the Sun.

Gamma Virginis, officially named Porrima, is a binary star system in the constellation of Virgo. It consists of two almost identical main sequence stars at a distance of about 38 light-years.

Pi Sagittarii is a triple star system in the zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +2.89, bright enough to be readily seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, it is roughly 510 light-years from the Sun.

Gamma Aquarii, or γ Aquarii, is a binary star system in the constellation of Aquarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.849, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. Based upon parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, this star is located at a distance of approximately 164 light-years from the Sun. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −16 km/s. In 1998, Olin J. Eggen included this star as a candidate member of the Hyades Supercluster.

Beta Aquarii is a single yellow supergiant star in the constellation of Aquarius. It has the official name Sadalsuud and the Bayer designation β Aquarii, abbreviated Beta Aqr or β Aqr. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, this component is located at a distance of approximately 540 light years (165 parsecs) from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 6.5 km/s. The star serves as an IAU radial velocity standard.

Epsilon Aquarii, Latinized from ε Aquarii, is a binary star in the equatorial zodiac constellation of Aquarius, located near the western constellation border with Capricornus. It has the proper name Albali, now formally recognized by the IAU. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.77, and has an absolute magnitude of −0.46. Based upon parallax measurements taken by the Gaia spacecraft, it is located at a distance of approximately 244 light-years (75 pc) from Earth. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −20 km/s.

Xi Aquarii is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.7. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this system lies at a distance of around 179 light-years from the Sun.

Zeta Sagittarii is a triple star system and the third-brightest star in the constellation of Sagittarius after Kaus Australis and Nunki. Based upon parallax measurements, it is about 88 light-years from the Sun.

Phi Sagittarii, Latinized from φ Sagittarii, is an interferometric binary star in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.17, it is the ninth-brightest star in the constellation and is readily visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements place it at a distance of roughly 239 light-years from the Earth. It is receding with a radial velocity of +21.5 km/s.

Iota Andromedae is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has the Flamsteed designation 17 Andromedae, while Iota Andromedae is the Bayer designation as Latinized from ι Andromedae. This object is visible to the naked eye at night as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.29. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located approximately 500 light years distant from the Sun.

Zeta Aquarii is the Bayer designation for a triple star system, the central star of the "water jar" asterism in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. The combined apparent visual magnitude of this system is 3.65, which is readily visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of around 92 light-years from Earth.

Eta Aquarii, Latinized from η Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.04. The distance to this star, as determined by parallax measurements, is about 168 light-years. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of –8 km/s. Eta Aquarii is near the radiant of a meteor shower named after it.

Iota Aquarii, Latinised from ι Aquarii, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of +4.279. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to this star is around 175 light-years. The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −10 km/s.

Pi Arietis, Latinized from π Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Aries. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this system is approximately 800 light-years distant from Earth and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.21. This is bright enough to be faintly seen with the naked eye.

38 Aquarii is a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 38 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation; its Bayer designation is e Aquarii. It is a faint star but visible to the naked eye, with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.43. Based on parallax measurements, it is around 450 light-years away; it is 0.28 degree south of the ecliptic.
5 Aquarii is a single star in the zodiac constellation of Aquarius, located about 830 light years away from the Sun, based on parallax. 5 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.55. This object is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −3 km/s.
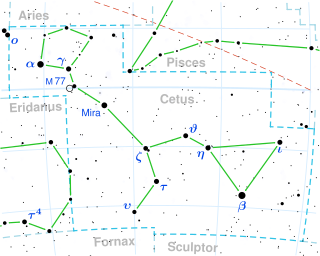
Eta Ceti is a star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It has the traditional name Deneb Algenubi or Algenudi. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is +3.4, making it the fourth-brightest star in this otherwise relatively faint constellation. The distance to this star can be measured directly using the parallax technique, yielding a value of 120.5 light-years.
Theta Ceti, Latinized from θ Ceti, is a solitary, orange-hued star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.60. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 20m04 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 113 light-years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.28 due to interstellar dust.

Omega Piscium is a star approximately 106 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Pisces. It has a spectral type of F4IV, meaning it is a subgiant/dwarf star, and it has a temperature of 6,600 kelvins. It may or may not be a close binary star system. Variations in its spectrum were once interpreted as giving it an orbital period of 2.16 days, but this claim was later debunked as false. It is 20 times brighter than the Sun and is 1.8 times greater in mass, if it is a single star.










