Theta Ursae Minoris, Latinized from θ Ursae Minoris, is a suspected binary star system that is visible to the naked eye in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is roughly 860 light years from Earth with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.0. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −25 km/s.

Lambda Ursae Minoris is a star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is an M-type red giant with an apparent magnitude of +6.38, making it very faintly visible to the naked eye under the best observing conditions. It is approximately 880 light years from Earth.

Chi Aquarii, Latinized from χ Aquarii, is the Bayer designation of a star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. The distance to this star, based upon parallax measurements with a 7% margin of error, is roughly 610 light-years. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 5.

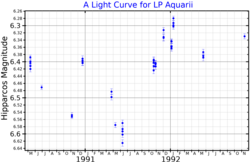
3 Aquarii is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 3 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the Bayer designation k Aquarii and the variable star designation EN Aquarii. With a mean apparent visual magnitude of 4.429, it is visible to the naked eye in dark skies. It has an annual parallax shift of 5.57 milliarcseconds with a 5% margin of error, which translates to a physical distance of around 590 light-years from Earth.

74 Aquarii is a triple star system in the constellation of Aquarius. 74 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation and it also bears the variable star designation HI Aquarii. The combined apparent visual magnitude is 5.8, although it is very slightly variable, and it is located at a distance of 590 light-years from Earth.
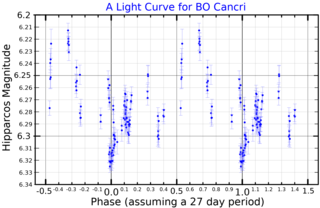
53 Cancri is a variable star in the zodiac constellation Cancer, located around 960 light years from the Sun. It has the variable star designation BO Cancri; 53 Cancri is the Flamsteed designation. This object is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude around 6. It is around 960 light years away.

CS Camelopardalis is a binary star in reflection nebula VdB 14, in the constellation Camelopardalis. It is a 4th magnitude star, and is visible to the naked eye under good observing conditions.
HD 1606 is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda, positioned a few degrees to the northeast of the bright star Alpheratz. It has a blue-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.87. Although it is suspected of variability, none has been conclusively found. The star is located at a distance of approximately 580 light-years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +4 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −0.5.

V385 Andromedae is a variable star in the constellation Andromeda, about 360 parsecs (1,200 ly) away. It is a red giant over a hundred times larger than the sun. It has an apparent magnitude around 6.4, just about visible to the naked eye in ideal conditions.

14 Aquarii is red giant star. 14 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the variable star designation IW Aquarii. It is a semiregular variable with an amplitude of a tenth of a magnitude, and shows variations on a timescale of just one day. At its brightest, magnitude 6.44, it could be faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal observing conditions.
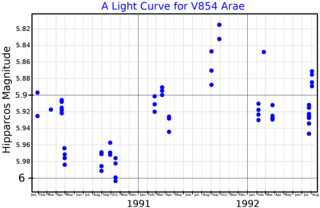
HD 155035 is a star in the constellation Ara, the Altar. It is located at a distance of approximately 1,450 light-years from Earth and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.92, making it is faintly visible to the naked eye. This is a red giant star with a stellar classification of M1.5 III.

1 Camelopardalis is a double star system in the constellation Camelopardalis. Its combined apparent magnitude is 5.56 and it is approximately 800 parsecs (2,600 ly) away. It is faintly visible to the naked eye under good observing conditions.

Delta2 Gruis, Latinized from δ2 Gruis, is a solitary, red-hued star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.88 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located around 330 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +3 km/s.
98 Herculis is a single star located approximately 590 light years from the Sun in the northern constellation Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. The brightness of the star is diminished by an extinction of 0.19 due to interstellar dust. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −19 km/s.

5 Lacertae is a spectroscopic binary in the constellation Lacerta. Its apparent magnitude is 4.36.

17 Persei is a single star in the northern constellation of Perseus, located about 420 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.53. This object is moving further from the Earth at a heliocentric radial velocity of +13 km/s.

V1073 Scorpii is a variable star in the constellation Scorpius. It has a non-Greek Bayer designation of k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +4.87. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920 ly (896 pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −6.8

10 Persei is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Perseus. Its apparent magnitude is 6.26 although it is slightly variable.

W Coronae Borealis is a Mira-type long period variable star in the constellation Corona Borealis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 7.8 and 14.3 over a period of 238 days.

U Microscopii is a Mira variable star in the constellation Microscopium. It ranges from magnitude 7 to 14.4 over a period of 334 days. The Astronomical Society of Southern Africa in 2003 reported that observations of U Microscopii were very urgently needed as data on its light curve was incomplete.