
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations further east, south or north. The term does not describe a single communion or religious denomination. Eastern Christianity is a category distinguished from Western Christianity, which is composed of those Christian traditions and churches that originally developed further west.

Patriarchate is an ecclesiological term in Christianity, designating the office and jurisdiction of an ecclesiastical patriarch. According to Christian tradition three patriarchates were established by the apostles as apostolic sees in the 1st century: Rome, Antioch, and Alexandria. Constantinople was added in the 4th century and Jerusalem in the 5th century. Eventually, together, these five were recognised as the pentarchy by the Council of Chalcedon in 451.

The Syriac Orthodox Church, also known as West Syriac Church or West Syrian Church, officially known as the Syriac Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East, and informally as the Jacobite Church, is an Oriental Orthodox church that branched from the Church of Antioch. The bishop of Antioch, known as the patriarch, heads the church and possesses apostolic succession through Saint Peter, according to sacred tradition. The church upholds Miaphysite doctrine in Christology, and employs the Liturgy of Saint James, associated with James the Just. Classical Syriac is the official and liturgical language of the church.

The Syriac Catholic Church is an Eastern Catholic Christian jurisdiction originating in the Levant that uses the West Syriac Rite liturgy and has many practices and rites in common with the Syriac Orthodox Church. Being one of the twenty-three Eastern Catholic Churches, the Syriac Catholic Church is a self-governed sui iuris particular church, while it is in full communion with the Holy See and with the entirety of the Roman Catholic Church.
A catholicos is the head of certain churches in some Eastern Christian traditions. The title implies autocephaly and, in some cases, it is the title of the head of an autonomous church. The word comes from ancient Greek καθολικός, derived from καθ' ὅλου from κατά and ὅλος, meaning "concerning the whole, universal, general"; it originally designated a financial or civil office in the Roman Empire.
Non-Chalcedonian Christianity comprises the branches of Christianity that do not accept theological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon, the Fourth Ecumenical Council, held in 451. Non-Chalcedonian denominations reject the Christological Definition of Chalcedon, for varying reasons. Non-Chalcedonian Christianity thus stands in contrast to Chalcedonian Christianity.

Alphabetical list of Eastern Christianity-related articles on English Wikipedia

The vast majority of Christians in Iraq are indigenous Assyrians who descend from ancient Assyria, and are considered to be one of the oldest continuous Christian communities in the world. They primarily adhere to the Syriac Christian tradition and rites and speak Northeastern Neo-Aramaic dialects, although Turoyo is also present on a smaller scale. Some are also known by the name of their religious denomination as well as their ethnic identity, such as Chaldo-Assyrians, Chaldean Catholics or Syriacs. Non-Assyrian Iraqi Christians include Arab Christians and Armenians, and a very small minority of Kurdish, Shabaks and Iraqi Turkmen Christians. Regardless of religious affiliation Assyrians Christians in Iraq and surrounding countries are one genetically homogeneous people and are of different origins than other groups in the country, with a distinct history of their own harking back to ancient Assyria and Mesopotamia.

Christianity in Turkey has a long history dating back to the early origins of Christianity in Asia Minor during the 1st century AD. In modern times the percentage of Christians in Turkey has declined from 20-25% in 1914, to about 2% in 1927, to 0.2–0.4% today Sources estimate that the Christian population in Turkey ranges between 180,000 and 370,000. However, the exact number remains unclear due to the absence of a religious census in the country. The percentage of Christians in Turkey fell mainly as a result of the late Ottoman genocides: the Armenian genocide, Greek genocide, and Assyrian genocide, the population exchange between Greece and Turkey, the emigration of Christians that began in the late 19th century and gained pace in the first quarter of the 20th century, and due to events such as the 1942 Varlık Vergisi tax levied on non-Muslim citizens in Turkey and the 1955 Istanbul pogrom against Greek and Armenian Christians. Exact numbers are difficult to estimate, as many Turkish former Muslim converts to Christianity often hide their Christian faith for fear of familial pressure, religious discrimination, and persecution.

Christianity, which originated in the Middle East during the 1st century AD, is a significant minority religion within the region, characterized by the diversity of its beliefs and traditions, compared to Christianity in other parts of the Old World. Today, Christians make up approximately 5% of the Middle Eastern population, down from 13% in the early 20th century. Cyprus is the only Christian majority country in the Middle East, with Christians forming between 76% and 78% of the country's total population, most of them adhering to Eastern Orthodox Christianity. Lebanon has the second highest proportion of Christians in the Middle East, around 40%, predominantly Maronites. After Lebanon, Egypt has the next largest proportion of Christians, at around 10% of its total population. Copts, numbering around 10 million, constitute the single largest Christian community in the Middle East.
Oriental Orthodoxy is the communion of Eastern Christian Churches that recognize only three ecumenical councils—the First Council of Nicaea, the First Council of Constantinople and the Council of Ephesus. They reject the dogmatic definitions of the Council of Chalcedon. Hence, these Churches are also called Old Oriental Churches or Non-Chalcedonian Churches.

The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 50 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches adhere to the Nicene Christian tradition. Oriental Orthodoxy is one of the oldest branches in Christianity.

In the period of its greatest expansion, in the tenth century, the Syriac Orthodox Church had around 20 metropolitan dioceses and a little over a hundred suffragan dioceses. By the seventeenth century, only 20 dioceses remained, reduced in the twentieth century to 10. The seat of Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch was at Mardin before the First World War, and thereafter in Deir Zaʿfaran, from 1932 in Homs, and finally from 1959 in Damascus.

Oriental Orthodoxy in Egypt represents Christians in Egypt who are adherents of Oriental Orthodoxy. In demographic terms, Oriental Orthodox Christians constitute the majority of Christians in Egypt.
Syriac Orthodox Archdiocese of Baghdad is an archdiocese of the Syriac Orthodox Church, centered in Baghdad, capital city of Iraq. The diocese originated during the early medieval period. It is attested between the 9th and the 13th centuries, but later declined, to be renewed again, thus existing up to the modern times. The diocese was probably established soon after Baghdad became the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate in the 770s. Eight Syriac Orthodox bishops of Baghdad from the medieval period are mentioned in the narratives of Michael the Syrian, Bar Hebraeus and other sources. Current Archbishop is Severius Jamil Hawa.

Christianity in Cyprus is the largest religion in the country, making up 78% of the island's population. The largest Christian denomination is the Greek Orthodox Church, while the rest are smaller communities of Anglicans, Roman Catholics, Latin Christians, Maronites, Armenian Apostolics, and Greek Evangelicals.

Oriental Orthodoxy in Germany is part of the Oriental Orthodox Christian tradition. Before the beginning of the 20th century, the presence of Oriental Orthodox Christianity in Germany was minor, mainly represented by Armenian communities. It was gradually increasing in the second half of the century with immigration, mainly from the region of Middle East. Today, it is a growing community, well integrated into German society.
Eastern Orthodoxy in Iraq refers to adherents, communities and institutions of Eastern Orthodox Christianity in Iraq. Within the ecclesiastical order of the Eastern Orthodox Church, territory of Iraq traditionally belongs to patrimonial jurisdiction of the Eastern Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East. The Patriarchate has a diocese in Iraq, the Eastern Orthodox Archdiocese of Baghdad, headed since 2014 by Metropolitan Ghattas Hazim.

Oriental Orthodoxy in North America represents adherents, religious communities, institutions and organizations of Oriental Orthodox Christianity in North America, including the United States, Canada, Mexico and other North American states. Oriental Orthodox Christians in North America are traditionally organized in accordance with their patrimonial ecclesiastical jurisdictions, with each community having its own structure of dioceses and parishes. Most Oriental Orthodox Christians in North America belong to Armenian, Coptic, Ethiopian, Eritrean, Indian, Syriac and some other communities, representing religious majority or minority within a particular community. Oriental Orthodox jurisdictions are organized within the Standing Conference of Oriental Orthodox Churches.
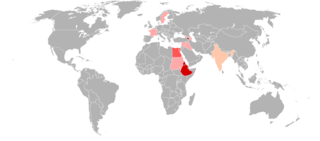
Oriental Orthodox Churches are the churches descended from those that rejected the Council of Chalcedon in 451. Despite the similar name, they are therefore a different branch of Christianity from the Eastern Orthodox. Oriental Orthodoxy consists of several autocephalous and autonomous jurisdictions holding a single set of beliefs and united in full communion. However, they each have their own separate rites, and there are significant differences between their respective practices. Thus, there is more internal diversity of practice among the Oriental Orthodox than among the Eastern Orthodox.















