Related Research Articles

A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material such as coal, oil, and natural gas, formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. Fossil fuels may be burned to provide heat for use directly, to power engines, or to generate electricity. Some fossil fuels are refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and propane before burning. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing organic molecules created by photosynthesis. The conversion from these materials to high-carbon fossil fuels typically require a geological process of millions of years.

Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biology, and geography to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.

Udupi is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Udupi is situated about 55 km (34 mi) north of the educational, commercial and industrial hub of Mangalore and about 422 km (262 mi) west of state capital Bangalore by road.

Udupi district is an administrative subdivision in the Karnataka state of India, with the district headquarters in the city of Udupi. It is situated in the Canara old north malabar coastal region, there are seven taluks, 233 villages and 21 towns in Udupi district. The three northern tehsils of Udupi, Kundapur and Karkala, were partitioned from Dakshina Kannada district to form Udupi district on 25 August 1997. Moodabidri was officially declared as new tehsil (taluk), separated from Karkala with effect from 11 January 2018.
Global strategic petroleum reserves (GSPR) refer to crude oil inventories held by the government of a particular country, as well as private industry, to safeguard the economy and help maintain national security during an energy crisis. Strategic reserves are intended to be used to cover short-term supply disruptions.
The economy of South India after independence in 1947 conformed to a socialist framework, with strict governmental control over private sector participation, foreign trade and foreign direct investment (FDI). Through 1960–1990, South Indian economies experienced mixed economic growth. In the 1960s, Kerala achieved above-average economic growth, while Andhra Pradesh's economy declined during this period. Similarly, Kerala experienced an economic decline in the 1970s while the economies of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka consistently exceeded national average growth rates after 1970. South India first started to overtake the rest of India economically in the 1980s. Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka were noted by some to be more reform-oriented in terms of economic policy when compared to other Indian states. Over the last decade South India has grown at 8% annually. Future economic growth will be shackled by a relatively low proportion of the active age population to the number of dependents. Today, South India has about 20% of India's population, and contributes about 31% of India's GDP; it is projected to contribute 35% by 2030.

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level.
The energy policy of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22.
Hindustan Construction Company Limited(HCC) is an Indian multinational engineering and construction company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The company was founded by Industrialist Seth Walchand Hirachand in 1926.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero, to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution, limit climate change, and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition, but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.
Hydrocarbon economy is a term referencing the global hydrocarbon industry and its relationship to world markets. Energy used mostly comes from three hydrocarbons: petroleum, coal, and natural gas. Hydrocarbon economy is often used when talking about possible alternatives like the hydrogen economy.

Ghana generates electric power from hydropower, fossil-fuel, and renewable energy sources such as wind and solar energy. Electricity generation is one of the key factors in order to achieve the development of the Ghanaian national economy, with aggressive and rapid industrialization; Ghana's national electric energy consumption was 265 kilowatt hours per each one in 2009.

Industrial and commercial activities dominate Mangalore's economy. Mangalore is the only city in the state of Karnataka to have all modes of transport — air, road, rail and sea — as well as being one of only five cities in India to have both a major port and an international airport. Around 75% of India's coffee, timber and cashew nuts exports are handled by the New Mangalore Port. Mangalore International Airport is one of only two international airports in Karnataka; the other being Bangalore's Kempegowda International Airport. Mangalore is the fastest growing non-metropolitan area in South India and the second largest business centre in Karnataka. The city has some of the tallest buildings in South India, with many more under construction.

POSCO India Private Limited is an Indian subsidiary of Korean conglomerate POSCO.
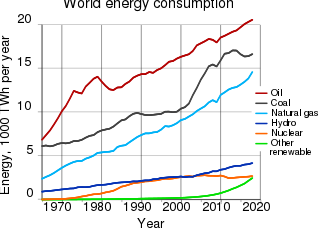
The environmental impact of the energy industry is significant, as energy and natural resource consumption are closely related. Producing, transporting, or consuming energy all have an environmental impact. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources. Scientific consensus on some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are considered to be increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, causing a warming effect, global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect, increasing concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.

The environmental impact of the petroleum industry is extensive and expansive due to petroleum having many uses. Crude oil and natural gas are primary energy and raw material sources that enable numerous aspects of modern daily life and the world economy. Their supply has grown quickly over the last 150 years to meet the demands of the rapidly increasing human population, creativity, knowledge, and consumerism.
The Strategic Petroleum Reserve is an emergency fuel store of oil maintained by the People's Republic of China National Development and Reform Commission. China does not officially report its volume, but as of 2016 the SPR was estimated to hold approximately 400 million barrels in total, out of a capacity of around 500 million barrels.

Indian Oil Corporation Limited is an Indian Multinational oil and gas company under the ownership of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India. Headquartered in New Delhi, it is a public sector undertaking whose operations are overseen by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. Indian Oil is ranked 94th on the Fortune Global 500 list of the world's biggest corporations as of 2022. It is the largest government owned oil producer in the country both in terms of capacity and revenue.It has consolidated refining capacity of 80.55MMTPA which it intends to increase to 107MMTPA by 2024-25. As of 31 March 2021, Indian Oil's employee strength is 31,648, out of which 17,762 are executives and 13,876 non-executives, while 2,776 are women, comprising 8.77% of the total workforce.

Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserves Limited (ISPRL) is an Indian company responsible for maintaining the country's strategic petroleum reserves. ISPRL is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Oil Industry Development Board (OIDB), which functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
The petroleum industry in India dates back to 1889 when the first oil deposits in the country were discovered near the town of Digboi in the state of Assam. The natural gas industry in India began in the 1960s with the discovery of gas fields in Assam and Maharashtra. As on 31 March 2018, India had estimated crude oil reserves of 594.49 million metric tonnes (Mt) and natural gas reserves of 1339.57 billion cubic metres of natural gas (BCM).
References
- ↑ "Pin Code of Padur in Udupi, Karnataka". Maps of India. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ↑ "Saudi Aramco to store 4.6 mn barrels of oil in India's Padur reserve". Business Today. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ↑ "Abu Dhabi National Oil Company to fill up half of Padur strategic crude oil storage". The Economic Times. 12 February 2019. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ↑ "'House panel suggests government to construct small caverns for crude storage' - LiveMint". www.livemint.com. Retrieved 14 September 2023.