Related Research Articles
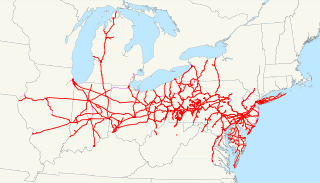
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was so named because it was established in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.

The Metroliners were extra-fare high speed trains between Washington, D.C. and New York City which operated from 1969 to 2006. They were briefly first operated by Penn Central Transportation, then by Amtrak for 35 years.

Amtrak's 195-mile (314 km) Keystone Service provides frequent regional passenger train service between the Harrisburg Transportation Center in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania and 30th Street Station in Philadelphia, running along the Philadelphia to Harrisburg Main Line. Most trains continue along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) to Pennsylvania Station in New York.

MARC Train Service, previously known as Maryland Rail Commuter, is a commuter rail system comprising three lines in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. MARC is administered by the Maryland Transit Administration (MTA), a Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT) agency, and is operated under contract by Bombardier Transportation Services USA Corporation (BTS) and Amtrak over tracks owned by CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Amtrak.

The Northeast Corridor Line is a commuter rail service operated by NJ Transit between the Trenton Transit Center and New York Penn Station on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor in the United States. The service is the successor to Pennsylvania Railroad commuter trains between Trenton and New York, and is NJ Transit's busiest commuter rail service. After arrival at New York Penn Station, some trains load passengers and return to New Jersey, while others continue east to Sunnyside Yard for storage. Most servicing is done at the Morrisville Yard, at the west end of the line. The Northeast Corridor Line is colored red on NJ Transit system maps and its symbol is the State House. The Princeton Branch is a shuttle service connecting to the line. Connecting SEPTA Trenton Line service between Philadelphia and Trenton is listed in the timetable.

Suburban Station is an art deco office building and underground commuter rail station in Penn Center, Philadelphia. Its official SEPTA address is 16th Street and JFK Boulevard. The station is owned and operated by SEPTA and is one of the three core Center City stations on SEPTA Regional Rail. The station was built by the Pennsylvania Railroad to replace the original Broad Street Station and opened on September 28, 1930.

The New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road (NC&F) was opened in 1831, was the first railroad in Delaware and one of the first in the United States. About half of the route was abandoned in 1859; the rest became part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) route into the Delmarva Peninsula and is still used by Norfolk Southern Railway. The abandoned segment from Porter, Delaware, to Frenchtown, Maryland, the New Castle and Frenchtown Railroad Right-of-Way, was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.

The Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B) was an American railroad that operated from 1836 to 1881. Formed as a result of the merger of four small lines dating from the earliest days of American railroading in the late 1820s and early 1830s, it was purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) in 1881, becoming part of their main line in 1902.

West Baltimore is a regional rail station located in the western part of the City of Baltimore, Maryland along the Northeast Corridor and is served by MARC Penn Line trains. It is positioned on an elevated grade above and between the nearby parallel West Mulberry and West Franklin Streets at 400 North Smallwood Street. Three large surface lots are available for commuters. The station is not handicapped accessible, with four low-level side platforms next to the outer tracks, but MTA Maryland plans to later renovate the outdoor station with accessible platforms and entrances.

The Millstone and New Brunswick Railroad (M&NB) was chartered in the mid-19th century as a seven-mile long branch line from New Brunswick, New Jersey to East Millstone, New Jersey. Construction was completed and the line began operation on December 19, 1854. In 1871, under the order of the company's president Martin Howell, the M&NB signed a 999-year lease with the United Jersey Railroad Company, which would later become part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) known as the "Millstone Branch." In 1915, the company was dissolved and became part of the United Jersey Railroad Company.

The Butler Branch is a historic railroad line that operated in Indiana, USA. It ran between the city of Logansport on the Wabash River in north central Indiana and the namesake town of Butler near the Ohio border in northeastern Indiana.

The Pope's Creek Subdivision is a CSX Transportation railroad line in Maryland, running from Bowie to Morgantown where the Morgantown Generating Station is located and the Chalk Point Generating Station.

Bowie State is a regional rail station on the Northeast Corridor, located adjacent to the campus of Bowie State University in Bowie, Maryland. It is served by MARC Penn Line commuter rail trains. The station is located on a three-track section of the Northeast Corridor, with two side platforms next to the outer tracks.

The Bowie Railroad Buildings comprise three small frame structures at the former Bowie train station, located at the junction of what is now the Northeast Corridor and the Pope's Creek Subdivision in the town center of Bowie, Maryland. The complex includes a single-story freight depot, a two-story interlocking tower, and an open passenger shed. The station was served by passenger trains from 1872 until 1989, when it was replaced by Bowie State station nearby. The buildings were restored in 1992 as the Bowie Railroad Museum and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1998.

The Paoli/Thorndale Line, commonly known as the Main Line, is a SEPTA Regional Rail service running from Center City Philadelphia to Thorndale in Chester County. It operates on Amtrak's Philadelphia to Harrisburg Main Line, which in turn was once the Main Line of the Pennsylvania Railroad and is now part of the Keystone Corridor, a federally-designated high-speed rail corridor.

Long Bridge is the common name used for a series of three bridges connecting Washington, D.C. to Arlington, Virginia over the Potomac River. The first was built in 1808 for foot, horse and stagecoach traffic. Bridges in the vicinity were repaired and replaced several times in the 19th century. The current bridge was built in 1904 and substantially modified in 1942 and has only been used for railroad traffic. It is owned by CSX Transportation and is used by CSX freight trains, Amtrak intercity trains, and Virginia Railway Express commuter trains. Norfolk Southern Railway has trackage rights on the bridge but does not exercise those rights. In 2019 Virginia announced that it would help fund and build a new rail bridge parallel to the existing one to double its capacity, following the plans that have been studied by the District Department of Transportation (DDOT) and Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) since 2011.
County Yard is a rail yard in New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA, along the Northeast Corridor (NEC). Originally developed by the Pennsylvania Railroad, it is owned by Amtrak. The New Jersey Transit Rail Operations (NJT) Jersey Avenue Station, served by its Northeast Corridor Line, is just south of the yard. In 2014, NJT began a project to upgrade the yard and build a "train haven" and re-inspection station. County Yard will be able to store 132 rail cars. The Delco Lead, south along NEC, would be expanded to five additional tracks able to park 312 rail cars and a service and inspection facility would be built to return equipment to service.
Lanham station was a regional rail station on the Northeast Corridor, located just outside the Capital Beltway off Route 450 in Lanham, Maryland. It was served by the predecessor of today's MARC Penn Line, until August 1982.

The Raritan River Bridge is a rail bridge over the Raritan River, in New Brunswick and Highland Park in Middlesex County, New Jersey, U.S. The arch bridge carries the Northeast Corridor (NEC) at MP 30.92. It used by Amtrak, including Northeast Regional service, and New Jersey Transit's Northeast Corridor Line. It also crosses over New Jersey Route 18 and the East Coast Greenway.
The New Portage Branch was a rail line which ran between the New Portage Tunnel and Duncansville, Pennsylvania.
References
- ↑ "PRRTHS History". National Society. Pennsylvania Railroad Technical and Historical Society. October 28, 2008. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- 1 2 "Mission and Membership". National Society. Pennsylvania Railroad Technical and Historical Society. October 28, 2008. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- ↑ "Railroad Historical Societies". RailModel Journal. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- ↑ "RailPace Interlocking". RailPace Newsmagazine. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- ↑ "PRR listings". Model Railroader. Retrieved December 9, 2008.