
Erbium is a chemical element with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element, originally found in the gadolinite mine in Ytterby, Sweden, which is the source of the element's name.

An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiberoptic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links.

In the field of optics, transparency is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale, the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite property of translucency is opacity.
A diode-pumped solid-state laser (DPSSL) is a solid-state laser made by pumping a solid gain medium, for example, a ruby or a neodymium-doped YAG crystal, with a laser diode.
Chalcogenide glass is a glass containing one or more chalcogens. Such glasses are covalently bonded materials and may be classified as covalent network solids. Polonium is also a chalcogen but is not used because of its strong radioactivity. Chalcogenide materials behave rather differently from oxides, in particular their lower band gaps contribute to very dissimilar optical and electrical properties.

Bioglass 45S5 or calcium sodium phosphosilicate, is a bioactive glass specifically composed of 45 wt% SiO2, 24.5 wt% CaO, 24.5 wt% Na2O, and 6.0 wt% P2O5. Typical applications of Bioglass 45S5 include: bone grafting biomaterials, repair of periodontal defects, cranial and maxillofacial repair, wound care, blood loss control, stimulation of vascular regeneration, and nerve repair.

Bioactive glasses are a group of surface reactive glass-ceramic biomaterials and include the original bioactive glass, Bioglass. The biocompatibility and bioactivity of these glasses has led them to be used as implant devices in the human body to repair and replace diseased or damaged bones. Most bioactive glasses are silicate based glasses that are degradable in body fluids and can act as a vehicle for delivering ions beneficial for healing. Bioactive glass is differentiated from other synthetic bone grafting biomaterials, in that it is the only one with anti-infective and angiogenic properties.
ZBLAN is the most stable, and consequently the most used, fluoride glass, a subcategory of the heavy metal fluoride glass (HMFG) group. Typically its composition is 53% ZrF4, 20% BaF2, 4% LaF3, 3% AlF3 and 20% NaF. ZBLAN is not a single material but rather has a spectrum of compositions, many of which are still untried. The biggest library in the world of ZBLAN glass compositions is currently owned by Le Verre Fluore, the oldest company working on HMFG technology. Other current ZBLAN fiber manufacturers are Thorlabs and KDD Fiberlabs. Hafnium fluoride is chemically similar to zirconium fluoride, and is sometimes used in place of it.
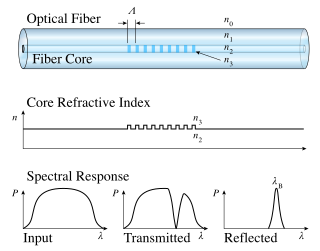
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector.

A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers, called laser diodes.

An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light guides, and liquid waveguides.
A fiber laser is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing. Fiber nonlinearities, such as stimulated Raman scattering or four-wave mixing can also provide gain and thus serve as gain media for a fiber laser.
Photodarkening is an optical effect observed in the interaction of laser radiation with amorphous media (glasses) in optical fibers. Until now, such creation of color centers was reported only in glass fibers. Photodarkening limits the density of excitations in fiber lasers and amplifiers. The experimental results suggest that operating at a saturated regime helps to reduce photodarkening.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for optical communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
Phosphate glass is a class of optical glasses composed of metaphosphates of various metals. Instead of SiO2 in silicate glasses, the glass forming substrate is P2O5.
A dopant is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When doped into crystalline substances, the dopant's atoms get incorporated into its crystal lattice. The crystalline materials are frequently either crystals of a semiconductor such as silicon and germanium for use in solid-state electronics, or transparent crystals for use in the production of various laser types; however, in some cases of the latter, noncrystalline substances such as glass can also be doped with impurities.

Lead bismuthate is a superconductor with the formula Pb(BiO3)2. has only been discovered in recent years in the laboratory as it is not naturally occurring. Lead bismuthate forms a pentavalent structure, significantly different from the regular ionic interactions of sodium bismuthate, but similar to that of strontium bismuthate. In the structure, six oxygen atoms are coordinated octahedrally to both the bismuth and lead atoms. The bismuth and oxygen atoms form negatively charged layers by creating repeating octahedral geometries. The positively charged lead atoms are then disbursed within the layers, forming a hexagonal unit cell, with a lead atom in each of the corners. The density of the crystal is 9.18 g/cm3. The formula weight is 233.99 g/mol. The volume of the crystal structure unit is 169.26 A3. Lattice parameters (a) is 5.321 angstroms.
An erbium-doped waveguide amplifier is a type of an optical amplifier enhanced with erbium. It is a close relative of an EDFA, erbium-doped fiber amplifier, and in fact EDWA's basic operating principles are identical to those of the EDFA. Both of them can be used to amplify infrared light at wavelengths in optical communication bands between 1500 and 1600 nm. However, whereas an EDFA is made using a free-standing fiber, an EDWA is typically produced on a planar substrate, sometimes in ways that are very similar to the methods used in electronic integrated circuit manufacturing. Therefore, the main advantage of EDWAs over EDFAs lies in their potential to be intimately integrated with other optical components on the same planar substrate and thus making EDFAs unnecessary.
John Ballato is an American materials scientist, entrepreneur, and academic. He holds the J. E. Sirrine Endowed Chair of Optical Fiber and is a professor of materials science and engineering, electrical and computer engineering, as well as physics and astronomy at Clemson University. He has received many international recognitions for his research on optical and optoelectronic materials, particularly as relates to optical fiber.










