
The Spirochaetales are an order of spirochete bacteria. Some species within this order are known to causes syphilis, Lyme disease, relapsing fever, and other illnesses.

In taxonomy, the Thermoplasmata are a class of the Euryarchaeota.

Thermoplasmataceae is a family of archaeans in the order Thermoplasmatales. It contains only one genus, Thermoplasma. All species within Thermoplasmataceae are thermoacidophiles, and they grow at a temperature of 60 °C and pH 2. They were isolated from hydrothermal vents, fumaroles and similar environments.

Thermoplasmatales is an order of archaeans in the class Thermoplasmata. All are acidophiles, growing optimally at pH below 2. Picrophilus is currently the most acidophilic of all known organisms, being capable of growing at a pH of -0.06. Many of these organisms do not contain a cell wall, although this is not true in the case of Picrophilus. Most members of the Thermotoplasmata are thermophilic.
In taxonomy, Picrophilus is an archaean genus of the family Picrophilaceae.
The Desulfurococcales is an order of the Thermoprotei, part of the kingdom Archaea. The order encompasses some genera which are all thermophilic, autotrophs which utilise chemical energy, typically by reducing sulfur compounds using hydrogen. Desulfurococcales cells are either regular or irregular coccus in shape, with forms of either discs or dishes. These cells can be single, in pairs, in short chains, or in aciniform formation.

Sulfolobales is an order of archaeans in the class Thermoprotei.

In taxonomy, the Ferroplasmaceae are a family of the Thermoplasmatales.
In taxonomy, the Methanocaldococcaceae are a family of microbes within the order Methanococcales. It contains two genera, the type genus Methanocaldococcus and Methanotorris. These species are coccoid in form, neutrophilic to slightly acidophilic, and predominantly motile, and they have a very short generation period, from 25 to 45 minutes under optimal conditions. They produce energy exclusively through the reduction of carbon dioxide with hydrogen. Some species have been found in marine hydrothermal vents.
Methanospirillaceae are a family of microbes within Methanomicrobiales.
The Pyrodictiaceae are a family of disc-shaped anaerobic microorganisms belonging to the order Desulfurococcales, in the domain Archaea. Members of this family are distinguished from the other family (Desulfurococcaceae) in the order Desulfurococcales by having an optimal growth temperature above 100 °C, rather than below 100 °C.

In taxonomy, Acidianus is a genus of the Sulfolobaceae.
Sulfurisphaera is a genus of the Sulfolobaceae.
Halobaculum is a genus of the Halorubraceae.
In taxonomy, Methanocorpusculum is a genus of microbes within the family Methanocorpusculaceae. The species within Methanocorpusculum were first isolated from biodisgester wastewater and activated sludge from anaerobic digestors. In nature, they live in freshwater environments. Unlike most other methanogenic archaea, they do not require high temperatures or extreme salt concentrations to live and grow.
In taxonomy, Methanospirillum is a genus of microbes within the family Methanospirillaceae. All its species are methanogenic archaea. The cells are bar-shaped and form filaments. Most produce energy via the reduction of carbon dioxide with hydrogen, but some species can also use formate as a substrate. They are Gram-negative and move using archaella on the sides of the cells. They are strictly anaerobic, and they are found in wetland soil and anaerobic water treatment systems.
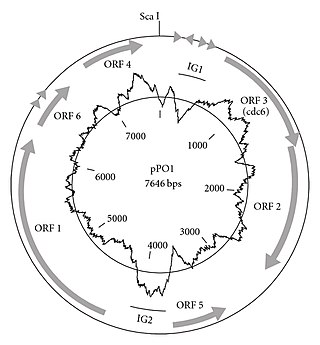
Picrophilus oshimae is a species of Archaea described in 1996. Picrophilus oshimae was found in a fumarole in Hokkaido, Japan. The hot spring the fumarole was located in had a pH of 2.2.
Laceyella is a Gram-positive, thermophilic, spore-forming and aerobic bacterial genus from the family of Thermoactinomycetaceae. The genus Laceyella is namened after the English microbiologist John Lacey.

Haloferacaceae is a family of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the order Haloferacales. The type genus of this family is Haloferax. Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order Haloferacales.
Halorubraceae is a family of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the order Haloferacales. The type genus of this family is Halorubrum. Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order Haloferacales.







