
Rodhocetus is an extinct genus of protocetid early whale known from the Lutetian of Pakistan. The best-known protocetid, Rodhocetus is known from two partial skeletons that taken together give a complete image of an Eocene whale that had short limbs with long hands and feet that were probably webbed and a sacrum that was immobile with four partially fused sacral vertebrae. It is one of several extinct whale genera that possess land mammal characteristics, thus demonstrating the evolutionary transition from land to sea.
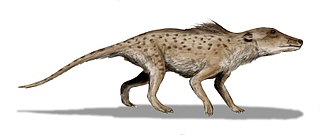
Pakicetidae is an extinct family of Archaeoceti that lived during the Early Eocene in Pakistan.

Basilosaurus is a genus of large, predatory, prehistoric archaeocete whale from the late Eocene, approximately 41.3 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). First described in 1834, it was the first archaeocete and prehistoric whale known to science. Fossils attributed to the type species B. cetoides were discovered in the United States. They were originally thought to be of a giant reptile, hence the suffix "-saurus", Ancient Greek for "lizard". The animal was later found to be an early marine mammal, which prompted attempts at renaming the creature, which failed as the rules of zoological nomenclature dictate using the original name given. Fossils were later found of the second species, B. isis, in 1904 in Egypt, Western Sahara, Morocco, Jordan, Tunisia, and Pakistan. Fossils have also been unearthed in the southeastern United States and Peru.

Basilosauridae is a family of extinct cetaceans. They lived during the middle to the early late Eocene and are known from all continents, including Antarctica. They were probably the first fully aquatic cetaceans. The group is noted to be a paraphyletic assemblage of stem group whales from which the monophyletic Neoceti are derived.

Dorudon ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside Basilosaurus 40.4 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with D. atrox measuring 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighing 1–2.2 metric tons. Dorudon lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand, and Western Sahara.

Archaeoceti, or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene. Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia 53 to 45 mya, resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation 36 to 35 mya.

Zygorhiza ("Yoke-Root") is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale known from the Late Eocene of Louisiana, Alabama, and Mississippi, United States, and the Bartonian to the late Eocene of New Zealand . Specimens reported from Europe are considered Dorudontinae incertae sedis.
Pachycetus is a genus of basilosaurine basilosaurid from Middle Eocene (Bartonian) of the eastern United States, and Ukraine.

Georgiacetus is an extinct genus of ancient whale known from the Eocene period of the United States. Fossils are known from Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi and protocetid fossils from the right time frame, but not yet confirmed as Georgiacetus, have been found in Texas and South Carolina.

Cynthiacetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale that lived during the Late Eocene Specimens have been found in the southeastern United States and Peru.

Remingtonocetidae is a diverse family of early aquatic mammals of the order Cetacea. The family is named after paleocetologist Remington Kellogg.
Takracetus was a primitive cetacean that lived approximately 45 million years ago. The type specimen is a partial skull though the literature mentions a second more complete specimen.
Chrysocetus is a genus of extinct early whale known from Late Eocene-aged fossils of the eastern United States and western Africa.
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America.
Pontogeneus is a genus of extinct cetacean known from fossils recovered from Late Eocene sediments of the southeastern United States.
Natchitochia is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the Middle Eocene Cook Mountain Formation in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana.
Carolinacetus is an extinct protocetid early whale found in the Bartonian Tupelo Bay Formation in Berkeley County, South Carolina.
Eocetus is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the early late Eocene Giushi Formation in Gebel Mokattam, outside Cairo, Egypt. The specimen was first named by Fraas as Mesocetus schweinfurthi. However, the name Mesocetus was previously used causing a change to the species name to Eocetus schweinfurthi. Since the genus was first described in the early 20th century, several other specimens, mostly isolated vertebrae, have been attributed to Eocetus, but the taxonomic status of these widely distributed specimens remain disputed.
Basilotritus is a genus of basilosaurid early whale known from the early late Middle Eocene Kiev Formation of the Ukraine, Stockletten Formation of Germany, Tongeren Formation of the Netherlands, Giushi Formation of Egypt and the United States.









