
Trachodon is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur based on teeth from the Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana, U.S. It is a historically important genus with a convoluted taxonomy that has been all but abandoned by modern dinosaur paleontologists.
Physeter is a genus of toothed whales. There is only one living species in this genus: the sperm whale. Some extremely poorly known fossil species have also been assigned to the same genus including Physeter antiquus from the Pliocene of France, and Physeter vetus from the Quaternary of the U.S. state of Georgia. Physeter vetus is very likely an invalid species, as the few teeth that were used to identify this species appear to be identical to those of another toothed whale, Orycterocetus quadratidens.

Joseph Mellick Leidy was an American paleontologist, parasitologist and anatomist.

Basilosaurus is a genus of large, predatory, prehistoric archaeocete whale from the late Eocene, approximately 41.3 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). First described in 1834, it was the first archaeocete and prehistoric whale known to science. Fossils attributed to the type species B. cetoides were discovered in the United States. They were originally thought to be of a giant reptile, hence the suffix "-saurus", Ancient Greek for "lizard". The animal was later found to be an early marine mammal, prompting attempts at renaming the creature, which failed as the rules of zoological nomenclature dictate using the original name given. Fossils were later found of the second species, B. isis, in 1904 in Egypt, Western Sahara, Morocco, Jordan, Tunisia, and Pakistan. Fossils have also been unearthed in the southeastern United States and Peru.

Basilosauridae is a family of extinct cetaceans. They lived during the middle to the early late Eocene and are known from all continents, including Antarctica. They were probably the first fully aquatic cetaceans. The group is noted to be a paraphyletic assemblage of stem group whales from which the monophyletic Neoceti are derived.

Uintatherium is an extinct genus of herbivorous dinoceratan mammal that lived during the Eocene epoch. Two species are currently recognized: U. anceps from the United States during the Early to Middle Eocene and U. insperatus of Middle to Late Eocene China.

Dorudon ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside Basilosaurus 40.4 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with D. atrox measuring 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighing 1–2.2 metric tons. Dorudon lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand and Western Sahara.
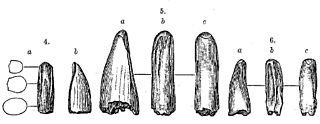
Aublysodon is a genus of carnivorous dinosaurs known only from the Judith River Formation in Montana, which has been dated to the late Campanian age of the late Cretaceous period. The only currently recognized species, Aublysodon mirandus, was named by paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1868. It is sometimes considered dubious now, because the type specimen consists only of an isolated premaxillary (front) tooth. Although this specimen is now lost, similar teeth have been found in many US states, western Canada, and Asia. These teeth almost certainly belong to juvenile tyrannosaurine tyrannosaurids, but most have not been identified to species level. However, it is likely that the type tooth belongs to one of the species in the genus Daspletosaurus, which was present in contemporary formations, and which matches specific details of the original tooth. The synapomorphies alleged to distinguish the Aublysodontinae, especially lack of serrations on premaxillary teeth could have been caused by tooth wear in life, postmortem abrasion, or digestion. Most other "aublysodontine"-type teeth may be from ontogenetic stages or sexual morphs of other tyrannosaurids.

Hyaenodon ("hyena-tooth") is an extinct genus of carnivorous placental mammals from extinct tribe Hyaenodontini within extinct subfamily Hyaenodontinae, that lived in Eurasia and North America from the middle Eocene, throughout the Oligocene, to the early Miocene.

Archaeoceti, or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene. Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia 53 to 45 mya, resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation 36 to 35 mya.

Cetotherium is an extinct genus of baleen whales from the family Cetotheriidae.

Archaeotherium is an extinct genus of entelodont artiodactyl endemic to North America during the Eocene and Oligocene epochs. Archaeotherium fossils are most common in the White River Formation of the Great Plains, but it has also been found in the John Day Basin of Oregon and the Trans-Pecos area of Texas.

Protosphyraena is a fossil genus of swordfish-like marine fish, that thrived worldwide during the Cretaceous period (Albian-Maastrichtian). Fossil remains of this taxon are mainly discovered in North America and Europe, and potential specimens are also known from Asia, Africa and Australia. Its fossils are best known from the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk Formation of Kansas.

Zygorhiza ("Yoke-Root") is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale known from the Late Eocene of Louisiana, Alabama, and Mississippi, United States, and the Bartonian to the late Eocene of New Zealand . Specimens reported from Europe are considered Dorudontinae incertae sedis.

Arthur Remington Kellogg was an American naturalist and a director of the United States National Museum. His work focused on marine mammals.

Georgiacetus is an extinct genus of ancient whale known from the Eocene period of the United States. Fossils are known from Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi and protocetid fossils from the right time frame, but not yet confirmed as Georgiacetus, have been found in Texas and South Carolina.

Remingtonocetidae is a diverse family of early aquatic mammals of the order Cetacea. The family is named after paleocetologist Remington Kellogg.
Takracetus was a primitive cetacean that lived approximately 45 million years ago. The type specimen is a partial skull though the literature mentions a second more complete specimen.
Pontogeneus is a genus of extinct cetacean known from fossils recovered from the Late Eocene sediments of the southeastern United States.

The Bridger Formation is a geologic formation in southwestern Wyoming. It preserves fossils dating back to the Bridgerian and Uintan stages of the Paleogene Period. The formation was named by American geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden for Fort Bridger, which had itself been named for mountain man Jim Bridger. The Bridger Wilderness covers much of the Bridger Formation's area.
















