Pakicetidae is an extinct family of Archaeoceti that lived during the Early Eocene in Pakistan. Unlike modern cetaceans, they had well developed limbs and were capable of walking.

Ambulocetus is a genus of early amphibious cetacean from the Kuldana Formation in Pakistan, roughly 48 or 47 million years ago during the Early Eocene (Lutetian). It contains one species, Ambulocetus natans, known solely from a near-complete skeleton. Ambulocetus is among the best-studied of Eocene cetaceans, and serves as an instrumental find in the study of cetacean evolution and their transition from land to sea, as it was the first cetacean discovered to preserve a suite of adaptations consistent with an amphibious lifestyle. Ambulocetus is classified in the group Archaeoceti—the ancient forerunners of modern cetaceans whose members span the transition from land to sea—and in the family Ambulocetidae, which includes Himalayacetus and Gandakasia.

Dorudon ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside Basilosaurus 40.4 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with D. atrox measuring 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighing 1–2.2 metric tons. Dorudon lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand and Western Sahara.

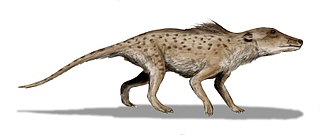
Pakicetus is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Indian Subcontinent during the Ypresian period, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like mammal, about 1–2 m long, and lived in and around water where it ate fish and other animals. The name Pakicetus comes from the fact that the first fossils of this extinct amphibious whale were discovered in Pakistan. The vast majority of paleontologists regard it as the most basal whale, representing a transitional stage between land mammals and whales. It belongs to the even-toed ungulates with the closest living non-cetacean relative being the hippopotamus.
Ishatherium is an extinct genus of ungulate from the early Eocene of the Subathu formation in northwestern India.
Lammidhania is an extinct genus of anthracobunids, which lived from the early to middle Eocene period. Its fossil remains were discovered in 1940 in the Chorlakki locality of the Punjab province of Pakistan.
Himalayacetus is an extinct genus of carnivorous aquatic mammal of the family Ambulocetidae. The holotype was found in Himachal Pradesh, India, in what was the remnants of the ancient Tethys Ocean during the Early Eocene. This makes Himalayacetus the oldest archaeocete known, extending the fossil record of whales some 3.5 million years.
Nalacetus is an extinct pakicetid early whale, fossils of which have been found in Lutetian red beds in Punjab, Pakistan. Nalacetus lived in a fresh water environment, was amphibious, and carnivorous. It was considered monophyletic by Cooper, Thewissen & Hussain 2009. It was said to be wolf-sized and one of the earliest forms of the order Cetacea.
Gandakasia is an extinct genus of ambulocetid from Pakistan, that lived in the Eocene epoch. It probably caught its prey near rivers or streams.

Ichthyolestes is an extinct genus of archaic cetacean that was endemic to Indo-Pakistan during the Lutetian stage. To date, this monotypic genus is only represented by Ichthyolestes pinfoldi.

Remingtonocetidae is a diverse family of early aquatic mammals of the order Cetacea. The family is named after paleocetologist Remington Kellogg.
Gaviacetus is an extinct archaeocete whale that lived approximately 45 million years ago. Gaviacetus was named for its characteristic narrow rostrum and the fast pursuit predation suggested by its unfused sacral vertebrae.
Dermotherium is a genus of fossil mammals closely related to the living colugos, a small group of gliding mammals from Southeast Asia. Two species are recognized: D. major from the Late Eocene of Thailand, based on a single fragment of the lower jaw, and D. chimaera from the Late Oligocene of Thailand, known from three fragments of the lower jaw and two isolated upper molars. In addition, a single isolated upper molar from the Early Oligocene of Pakistan has been tentatively assigned to D. chimaera. All sites where fossils of Dermotherium have been found were probably forested environments and the fossil species were probably forest dwellers like living colugos, but whether they had the gliding adaptations of the living species is unknown.
Indraloris is a fossil primate from the Miocene of India and Pakistan in the family Sivaladapidae. Two species are now recognized: I. himalayensis from Haritalyangar, India and I. kamlialensis from the Pothohar Plateau, Pakistan. Other material from the Potwar Plateau may represent an additional, unnamed species. Body mass estimates range from about 2 kg (4.4 lb) for the smaller I. kamlialensis to over 4 kg (8.8 lb) for the larger I. himalayensis.

Kala Chitta Range is a mountain range in the Attock District of Punjab, Pakistan. Kala- Chitta are Punjabi words meaning Kala the Black and Chitta means white. The range thrusts eastward across the Potohar plateau towards Rawalpindi.
Babiacetus is an extinct genus of early cetacean that lived during the late Lutetian middle Eocene of India . It was named after its type locality, the Harudi Formation in the Babia Hills, Kutch District, Gujarat, India.
Sivaladapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the middle Miocene.
Sectisodon is an extinct genus of hyainailourid hyaenodont mammal of the subfamily Hyainailourinae from early Oligocene to early Miocene deposits in Egypt and Uganda.
Sivapardus is an extinct, little-known genus of feline with only one species assigned to it, Sivapardus punjabiensis. It was described in 1969 by the paleontologist Abu Bakr based on a partial mandible from the Upper Siwaliks in Pakistan; the locality it was found at is estimated to be from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene. S. punjabiensis was a large cat with a short and broad snout that may have lived on open grasslands.
The Kuldana Formation is a fossil-bearing geological formation of Lutetian age which crops out in northern Pakistan. The abundant fossil remains were deposited by rivers and estuaries crossing an arid to semi-arid environment, between several marine transgressions. Its fossil fauna is best known for the early cetaceans Indohyus, Pakicetus and Ambulocetus, that helped to shed a new light on the evolution of whales, but it also features a large number of early ungulates, rodents and primates.







