Related Research Articles

In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.

Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers with amide backbones, usually linking aliphatic or semi-aromatic groups.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is also an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word acid in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word anhydride. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called acetic anhydride.Mixed (or unsymmetrical) acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride").
A fabric softener or fabric conditioner is a conditioner applied to laundry after it has been washed in a washing machine. A similar, more dilute preparation meant to be applied to dry fabric is known as a wrinkle releaser.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.
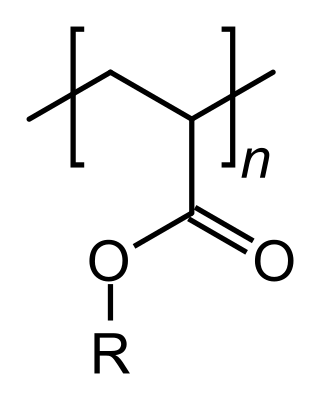
An acrylate polymer is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.
In chemistry, aminolysis (/am·i·nol·y·sis/) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule is lysed by reacting with ammonia or an amine. The case where the reaction involves ammonia may be more specifically referred to as ammonolysis.
Polyester resins are synthetic resins formed by the reaction of dibasic organic acids and polyhydric alcohols. Maleic anhydride is a commonly used raw material with diacid functionality in unsaturated polyester resins. Unsaturated polyester resins are used in sheet moulding compound, bulk moulding compound and the toner of laser printers. Wall panels fabricated from polyester resins reinforced with fiberglass—so-called fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP)—are typically used in restaurants, kitchens, restrooms and other areas that require washable low-maintenance walls. They are also used extensively in cured-in-place pipe applications. Departments of Transportation in the USA also specify them for use as overlays on roads and bridges. In this application they are known AS Polyester Concrete Overlays (PCO). These are usually based on isophthalic acid and cut with styrene at high levels—usually up to 50%. Polyesters are also used in anchor bolt adhesives though epoxy based materials are also used. Many companies have and continue to introduce styrene free systems mainly due to odor issues, but also over concerns that styrene is a potential carcinogen. Drinking water applications also prefer styrene free. Most polyester resins are viscous, pale coloured liquids consisting of a solution of a polyester in a reactive diluent which is usually styrene, but can also include vinyl toluene and various acrylates.
Nylon 66 is a type of polyamide or nylon. It, and nylon 6, are the two most common for textile and plastic industries. Nylon 66 is made of two monomers each containing 6 carbon atoms, hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid, which give nylon 66 its name. Aside from its superior physical characteristics, nylon 66 is attractive because its precursors are inexpensive.
Biodegradable polymers are a special class of polymer that breaks down after its intended purpose by bacterial decomposition process to result in natural byproducts such as gases (CO2, N2), water, biomass, and inorganic salts. These polymers are found both naturally and synthetically made, and largely consist of ester, amide, and ether functional groups. Their properties and breakdown mechanism are determined by their exact structure. These polymers are often synthesized by condensation reactions, ring opening polymerization, and metal catalysts. There are vast examples and applications of biodegradable polymers.
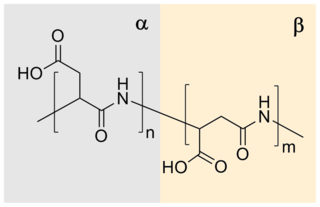
Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble condensation polymer based on the amino acid aspartic acid. It is a biodegradable replacement for water softeners and related applications. PASA can be chemically crosslinked with a wide variety of methods to yield PASA hydrogels. The resulting hydrogels are pH-sensitive such that under acidic conditions, they shrink, while the swelling capacity increases under alkaline conditions.

DMTMM is an organic triazine derivative commonly used for activation of carboxylic acids, particularly for amide synthesis. Amide coupling is one of the most common reactions in organic chemistry and DMTMM is one reagent used for that reaction. The mechanism of DMTMM coupling is similar to other common amide coupling reactions involving activated carboxylic acids. Its precursor, 2-chloro-4,6,-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine (CDMT), has also been used for amide coupling. DMTMM has also been used to synthesize other carboxylic functional groups such as esters and anhydrides. DMTMM is usually used in the chloride form but the tetrafluoroborate salt is also commercially available.

α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds are organic compounds with the general structure (O=CR)−Cα=Cβ-R. Such compounds include enones and enals, but also carboxylic acids and the corresponding esters and amides. In these compounds, the carbonyl group is conjugated with an alkene. Unlike the case for carbonyls without a flanking alkene group, α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are susceptible to attack by nucleophiles at the β-carbon. This pattern of reactivity is called vinylogous. Examples of unsaturated carbonyls are acrolein (propenal), mesityl oxide, acrylic acid, and maleic acid. Unsaturated carbonyls can be prepared in the laboratory in an aldol reaction and in the Perkin reaction.
References
- ↑ Winnacker, Malte; Rieger, Bernhard (22 November 2016). "Poly(ester amide)s: recent insights into synthesis, stability and biomedical applications". Polymer Chemistry. 7 (46): 7039–7046. doi: 10.1039/C6PY01783E .
- 1 2 3 Höfer, Rainer (11 November 2022). Renewable Resources for Surface Coatings, Inks and Adhesives. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-83916-130-8.

