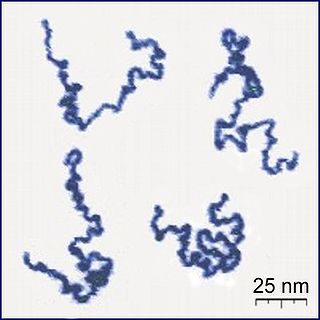
A polymer is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules linked together into chains of repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals.

Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to air and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, with the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene is naturally transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging, containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called epoxy. The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane.

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer reactions are absent and the rate of chain initiation is also much larger than the rate of chain propagation. The result is that the polymer chains grow at a more constant rate than seen in traditional chain polymerization and their lengths remain very similar. Living polymerization is a popular method for synthesizing block copolymers since the polymer can be synthesized in stages, each stage containing a different monomer. Additional advantages are predetermined molar mass and control over end-groups.
In polymer chemistry, emulsion polymerization is a type of radical polymerization that usually starts with an emulsion incorporating water, monomers, and surfactants. The most common type of emulsion polymerization is an oil-in-water emulsion, in which droplets of monomer are emulsified in a continuous phase of water. Water-soluble polymers, such as certain polyvinyl alcohols or hydroxyethyl celluloses, can also be used to act as emulsifiers/stabilizers. The name "emulsion polymerization" is a misnomer that arises from a historical misconception. Rather than occurring in emulsion droplets, polymerization takes place in the latex/colloid particles that form spontaneously in the first few minutes of the process. These latex particles are typically 100 nm in size, and are made of many individual polymer chains. The particles are prevented from coagulating with each other because each particle is surrounded by the surfactant ('soap'); the charge on the surfactant repels other particles electrostatically. When water-soluble polymers are used as stabilizers instead of soap, the repulsion between particles arises because these water-soluble polymers form a 'hairy layer' around a particle that repels other particles, because pushing particles together would involve compressing these chains.

Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (CH2CHCN)n. Almost all PAN resins are copolymers with acrylonitrile as the main monomer. PAN is used to produce large variety of products including ultra filtration membranes, hollow fibers for reverse osmosis, fibers for textiles, and oxidized PAN fibers. PAN fibers are the chemical precursor of very high-quality carbon fiber. PAN is first thermally oxidized in air at 230 °C to form an oxidized PAN fiber and then carbonized above 1000 °C in inert atmosphere to make carbon fibers found in a variety of both high-tech and common daily applications such as civil and military aircraft primary and secondary structures, missiles, solid propellant rocket motors, pressure vessels, fishing rods, tennis rackets and bicycle frames. It is a component repeat unit in several important copolymers, such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic.

Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) describe families of synthetic rubbers derived from styrene and butadiene. These materials have good abrasion resistance and good aging stability when protected by additives. In 2012, more than 5.4 million tonnes of SBR were processed worldwide. About 50% of car tires are made from various types of SBR. The styrene/butadiene ratio influences the properties of the polymer: with high styrene content, the rubbers are harder and less rubbery. SBR is not to be confused with the thermoplastic elastomer, styrene-butadiene block copolymer, although being derived from the same monomers.

In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called bipolymers. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called terpolymers and quaterpolymers, respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material.
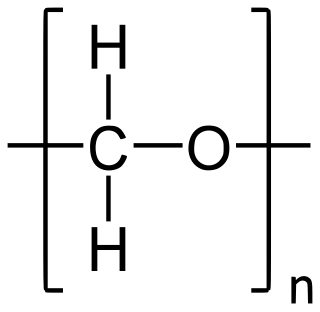
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, polyacetal, and polyformaldehyde, is an engineering thermoplastic used in precision parts requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. Short-chained POM is also better known as paraformaldehyde (PFA). As with many other synthetic polymers, polyoxymethylenes are produced by different chemical firms with slightly different formulas and sold variously by such names as Delrin, Kocetal, Ultraform, Celcon, Ramtal, Duracon, Kepital, Polypenco, Tenac and Hostaform.
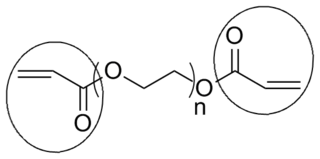
End groups are an important aspect of polymer synthesis and characterization. In polymer chemistry, they are functional groups that are at the very ends of a macromolecule or oligomer (IUPAC). In polymer synthesis, like condensation polymerization and free-radical types of polymerization, end-groups are commonly used and can be analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to determine the average length of the polymer. Other methods for characterization of polymers where end-groups are used are mass spectrometry and vibrational spectrometry, like infrared and raman spectroscopy. These groups are important for the analysis of polymers and for grafting to and from a polymer chain to create a new copolymer. One example of an end group is in the polymer poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate where the end-groups are circled.
In polymer chemistry, free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks. Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms, usually involving separate initiator molecules. Following its generation, the initiating free radical adds (nonradical) monomer units, thereby growing the polymer chain.

Hot-melt adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is a form of thermoplastic adhesive that is commonly sold as solid cylindrical sticks of various diameters designed to be applied using a hot glue gun. The gun uses a continuous-duty heating element to melt the plastic glue, which the user pushes through the gun either with a mechanical trigger mechanism on the gun, or with direct finger pressure. The glue squeezed out of the heated nozzle is initially hot enough to burn and even blister skin. The glue is sticky when hot, and solidifies in a few seconds to one minute. Hot-melt adhesives can also be applied by dipping or spraying, and are popular with hobbyists and crafters both for affixing and as an inexpensive alternative to resin casting.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.
Polyanhydrides are a class of biodegradable polymers characterized by anhydride bonds that connect repeat units of the polymer backbone chain. Their main application is in the medical device and pharmaceutical industry. In vivo, polyanhydrides degrade into non-toxic diacid monomers that can be metabolized and eliminated from the body. Owing to their safe degradation products, polyanhydrides are considered to be biocompatible.
Solution polymerization is a method of industrial polymerization. In this procedure, a monomer is dissolved in a non-reactive solvent that contains a catalyst or initiator.

Styrene acrylonitrile resin (SAN) is a copolymer plastic consisting of styrene and acrylonitrile. It is widely used in place of polystyrene owing to its greater thermal resistance. The chains of between 70 and 80% by weight styrene and 20 to 30% acrylonitrile. Larger acrylonitrile content improves mechanical properties and chemical resistance, but also adds a yellow tint to the normally transparent plastic.
INEOS Styrolution is a global styrenics supplier and is headquartered in Germany. It is a subcompany of INEOS and provides styrenics applications for many everyday products across a broad range of industries, including automotive, electronics, household, construction, healthcare, packaging and toys/sports/leisure.

In polymer chemistry, graft polymers are segmented copolymers with a linear backbone of one composite and randomly distributed branches of another composite. The picture labeled "graft polymer" shows how grafted chains of species B are covalently bonded to polymer species A. Although the side chains are structurally distinct from the main chain, the individual grafted chains may be homopolymers or copolymers. Graft polymers have been synthesized for many decades and are especially used as impact resistant materials, thermoplastic elastomers, compatibilizers, or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys. One of the better-known examples of a graft polymer is a component used in high impact polystyrene, consisting of a polystyrene backbone with polybutadiene grafted chains.

















