
Endocrinology is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology.

Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes.

Zollinger–Ellison syndrome is a rare disease in which tumors cause the stomach to produce too much acid, resulting in peptic ulcers. Symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.

Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest.

Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands or as response to external stimuli. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium excreted from the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis.

Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms, with an estimated prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%.

Primary hyperparathyroidism is a medical condition where the parathyroid gland produce excess amounts of parathyroid hormone (PTH). The symptoms of the condition relate to the resulting elevated serum calcium (hypercalcemia), which can cause digestive symptoms, kidney stones, psychiatric abnormalities, and bone disease.

Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 is one of a group of disorders, the multiple endocrine neoplasias, that affect the endocrine system through development of neoplastic lesions in pituitary, parathyroid gland and pancreas. Individuals suffering from this disorder are prone to developing multiple endocrine and nonendocrine tumors. It was first described by Paul Wermer in 1954.

Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 is a group of medical disorders associated with tumors of the endocrine system. The tumors may be benign or malignant (cancer). They generally occur in endocrine organs, but may also occur in endocrine tissues of organs not classically thought of as endocrine. MEN2 is a sub-type of MEN and itself has sub-types, as discussed below. Variants in MEN2A have been associated with Hirschsprung disease. Screening for this condition can begin as young as eight years old for pheochromocytoma.
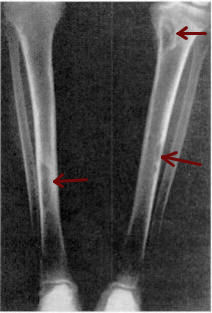
Osteitis fibrosa cystica is a skeletal disorder resulting in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue, and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. Osteitis fibrosis cystica (OFC), also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, and von Recklinghausen's disease of bone, is caused by hyperparathyroidism, which is a surplus of parathyroid hormone from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream, causing both elevated blood calcium levels, and the structural changes which weaken the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.

Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy is a form of osteodystrophy, and is classified as the phenotype of pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1A; this is a condition in which the body does not respond to parathyroid hormone.
Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a rare autosomal dominant genetic condition associated primarily with resistance to the parathyroid hormone. Those with the condition have a low serum calcium and high phosphate, but the parathyroid hormone level (PTH) is inappropriately high. Its pathogenesis has been linked to dysfunctional G proteins. Pseudohypoparathyroidism is a very rare disorder, with estimated prevalence between 0.3 and 1.1 cases per 100,000 population depending on geographic location.

Tertiary hyperparathyroidism is a condition involving the overproduction of the hormone, parathyroid hormone, produced by the parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are involved in monitoring and regulating blood calcium levels and respond by either producing or ceasing to produce parathyroid hormone.
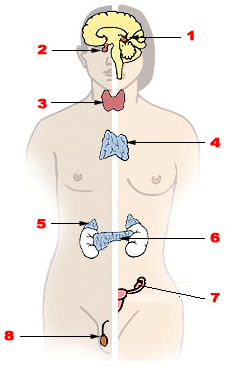
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.

Menin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEN1 gene. Menin is a putative tumor suppressor associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 and has autosomal dominant inheritance. Variations in the MEN1 gene can cause pituitary adenomas, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, gastrinoma, and adrenocortical cancers.

The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a Class C G-protein coupled receptor which senses extracellular levels of calcium ions. It is primarily expressed in the parathyroid gland, the renal tubules of the kidney and the brain. In the parathyroid gland, it controls calcium homeostasis by regulating the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH). In the kidney it has an inhibitory effect on the reabsorption of calcium, potassium, sodium, and water depending on which segment of the tubule is being activated.

Adrenal gland disorders are conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal glands. Your body produces too much or too little of one or more hormones when you have an adrenal gland dysfunction. The type of issue you have and the degree to which it affects your body's hormone levels determine the symptoms.

Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1), is a subtype of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome. It causes the dysfunction of multiple endocrine glands due to autoimmunity. It is a genetic disorder, inherited in autosomal recessive fashion due to a defect in the AIRE gene , which is located on chromosome 21 and normally confers immune tolerance.
Michael A. Levine is an American physician, scientist, academic, and author. He is an emeritus Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.














