A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce, or infrequently encountered. This designation may be applied to either a plant or animal taxon, and is distinct from the term endangered or threatened. Designation of a rare species may be made by an official body, such as a national government, state, or province. The term more commonly appears without reference to specific criteria. The International Union for Conservation of Nature does not normally make such designations, but may use the term in scientific discussion. [1]
Rarity rests on a specific species being represented by a small number of organisms worldwide, usually fewer than 10,000. However, a species having a very narrow endemic range or fragmented habitat also influences the concept. [2] [3] Almost 75% of known species can be classified as "rare". [4]
Rare species are species with small populations. Many will move into the endangered or vulnerable category if the negative factors affecting them continue to operate. Well-known examples of rare species - because these are large terrestrial animals - include the Himalayan brown bear, Fennec fox, Wild Asiatic buffalo, or the Hornbill.
They are not endangered yet, but classified as "at risk", [5] [6] although the frontier between these categories is increasingly difficult to draw given the general paucity of data on rare species. This is especially the case in the ocean where many 'rare' species not seen for decades may well have gone extinct unnoticed, if they are not already on the verge of extinction like the Mexican Vaquita. [7]
A species may be endangered or vulnerable, but not considered rare if it has a large, dispersed population. IUCN uses the term "rare" as a designation for species found in isolated geographical locations. Rare species are generally considered threatened because a small population size is less likely to recover from ecological disasters.
Rare plants can be classified based on the size and distribution of their populations. Some species may be rare because they consist of only a few individuals, are confined to a limited geographic area, or both. Certain rare plants are found sparsely distributed across a wide area. Others might have a large number of individuals that are concentrated in a very small area, such as a single county or canyon. The rarest plants typically have both a small number of individuals and a very limited geographic range.
Assessments of the status of rare plants are conducted using the best available data and consider various factors, including:
A rare plant's legal status can be observed through the USDA's Plants Database.
| Common name | Scientific name | Image | Last sighting | International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Threatened Species category and criteria | Present estimated wildlife population | Present estimated captive population | Present estimated total population | Endemic geographic location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern white rhinoceros | Ceratotherium simum cottoni | | N/A | Critically Endangered (Possibly Extinct in the Wild) A2abcd; C1+2a(i,ii); D | 0 | 2 | 2 | 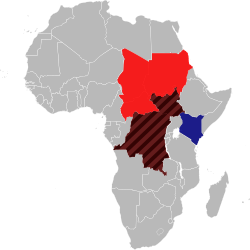 |
| Barbary lion | Panthera leo leo |  | N/A | Extinct in the Wild | 0 | 98 | 98 | Belfast Zoo, Ireland Rabat Zoo, Morocco Keystone Safari, United States |
| Yangtze giant softshell turtle | Rafetus swinhoei | | N/A | Critically Endangered A2acd; D | 2 | 1 | 3 |  |
| Ivory-billed woodpecker | Campephilus principalis principalis |  | 8 April 2022 | Critically Endangered D | 1-50 | 0 | 1-50 |  |
| Fernandina Island Galápagos tortoise | Chelonoidis niger phantasticus | | N/A | Critically Endangered (Possibly Extinct) D | 0-5 | 1 | 1-6 |  |
| Northern Sumatran rhinoceros | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis lasiotis |  | 1993 | Critically Endangered A2abd; C1+2a(i) | 0-9 | 0 | 0-9 | Tamanthi Wildlife Sanctuary, Myanmar |
| Vaquita | Phocoena sinus |  | May 2024 | Critically Endangered A2a; C1+2a(ii); D; E | 6-10 | 0 | 6-10 |  |
| Baishanzu fir | Abies beshanzuensis | N/A | Critically Endangered D | 3 | 1-9 | 4-12 |  | |
| Bornean rhinoceros | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis harrissoni | | N/A | Critically Endangered A2cd+3cd+4cd; C2a(i); D | 0-14 | 1 | 1-15 | |
| Wood's cycad | Encephalartos woodii |  | N/A | Extinct in the Wild | 0 | 1-36 | 1-36 | Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden, South Africa |
| Loneliest palm | Hyophorbe amaricaulis |  | N/A | Critically Endangered | ??? | 1 | 1 | Curepipe Botanic Gardens, Mauritius |
| Hainan black crested gibbon | Nomascus hainanus |  | 2023 | Critically Endangered A2acd; B1ab(iii); D | 36-37 | 0 | 36-37 |  |
| Gobi bear | Ursus arctos gobiensis | | 12 April 2023 | Critically Endangered | 30-40 | 0 | 30-40 |  |
| Māui dolphin | Cephalorhynchus hectori maui | | 28 January 2023 | Critically Endangered A2cd+4cd; C2a(i,ii); D | 48-64 | 0 | 48-64 |  |
| Colossal squid | Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni | 2015 | Least Concern | ??? | 0 | ??? |  | |
| Indonesian Javan rhinoceros | Rhinoceros sondaicus sondaicus | | 17 March 2023 | Critically Endangered D | 76-80 | 0 | 76-80 |  |
| Western Sumatran rhinoceros | Dicerorhinus sumatrensis sumatrensis | | N/A | Critically Endangered A2cd+3cd+4cd; C2a(i); D | 30-80 | 7-8 | 37-88 |  |
| Ornate Ground snake | Erythrolamprus ornatus | 2012 | Critically Endangered D | 18-100 | 0 | 18-100 | Maria Islands Nature Reserve, Saint Lucia | |
| Saola | Pseudoryx nghetinhensis |  | August 2013 | Critically Endangered A2acd+3cd+4acd; C2a(i) | 20-100 | 0 | 20-100 |  |
| Alagoas curassow | Mitu mitu |  | N/A | Extinct in the Wild | 0 | 50-100 | 50-100 |  |
| Horrid ground-weaver | Nothophantes horridus | | N/A | Critically Endangered A3c | 1-99 | 1-9 | 2-108 |
|
| Cat Ba langur | Trachypithecus poliocephalus | | 8 November 2022 | Critically Endangered D | 130-150 | 0 | 130-150 |  |
| Siau scops owl | Otus siaoensis |  | 2017 | Critically Endangered D | 50-200 | 0 | 50-200 | Siau Island, Indonesia |
| South China tiger | Panthera tigris amoyensis |  | N/A | Critically Endangered (Possibly Extinct in the Wild) | 0 | 150-200 | 150-200 |  |
| Devils Hole pupfish | Cyprinodon diabolis | | N/A | Critically Endangered B1ab(v)+2ab(v); C2a(ii) | 100-200 | 1-9 | 101-209 | Devils Hole, Death Valley National Park, United States of America |
| Loa water frog | Telmatobius dankoi | N/A | Critically Endangered B1ab(iii)+2ab(iii) | 1-9 | 214 | 215-223 | Small streams along the Loa River southwest of Calama, Chile | |
| Bleeding toad | Leptophryne cruentata | | 2003 | Critically Endangered C2a(i) | 1-249 | 0 | 1-249 | |
| Black-naped pheasent pigeon | Otidiphaps insularis | September 2022 | Critically Endangered | 50-249 | 0 | 50-249 | Fergusson Island, Papua New Guinea | |
| Ganges shark | Glyphis gangeticus | | February 2016 | Critically Endangered A2cd; C2a(i) | 1-249 | 0 | 1-249 | 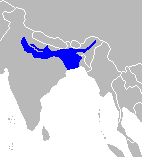 |
| Pink-headed duck | Rhodonessa caryophyllacea | | June 1935 | Critically Endangered | 1-49 | 0 | ??? |  |
| New Guinea big-eared bat | Pharotis imogene | March 2014 | Critically Endangered D | 49-249 | 0 | 49-249 |  | |
| Wimmer's shrew | Crocidura wimmeri | 1988 | Critically Endangered B1ab(iii) | 5-250 | 0 | 5-250 | 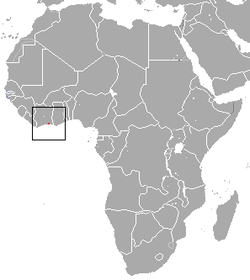 | |
| Archer's lark | Heteromirafra archeri | 2003 | Critically Endangered A3bc; C2a(i) | 50-250 | 0 | 50-250 |  | |
| Spix's Macaw | Cyanopsitta spixii | | N/A | Extinct in the Wild | 0 | 200-300 | 200-300 |  |
| Kākāpō | Strigops habroptilus |  | N/A | Critically Endangered A2be | 0 | 250-300 | 250-300 | |
| Gurney's pitta | Hydrornis gurneyi |  | 2016 | Critically Endangered A3c | 50-300 | 0-5 | 55-305 |
|
| Cross River gorilla | Gorilla gorilla diehli | | N/A | Critically Endangered C2a(i) | 250-300 | 1-9 | 251-309 |  |
| Philippine eagle | Pithecophaga jefferyi | | N/A | Critically Endangered A2cd; C2a(ii) | 250-300 | 10-20 | 260-320 |  |
| Amur leopard | Panthera pardus orientalis | | N/A | Critically Endangered C2a(ii); D | 60-125 | 217 | 277-342 |  |
| North Atlantic right whale | Eubalaena glacialis | | 22 August 2023 | Critically Endangered C2a(ii) | 350-400 | 0 | 350-400 | 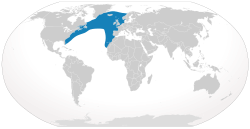 |
| Black softshell turtle | Nilssonia nigricans |  | N/A | Critically Endangered A4cd | 1-499 | 50-100 | 51-599 |
|
| California condor | Gymnogyps californianus |  | N/A | Critically Endangered C2a(i); D | 300-350 | 150-200 | 450-550 | 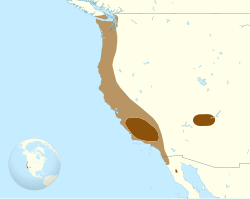 |
| Cumberlandian combshell | Epioblasma brevidens | | N/A | Critically Endangered A1ce | 200–1,000 | ? | 200-1,000 | 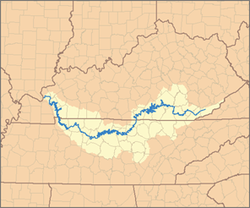 |
| De Winton's golden mole | Cryptochloris wintoni | N/A | Critically Endangered (Possibly Extinct) B1ab(iii)+2ab(iii) | 1-999 | 1-9 | 2-1,008 |  | |
| Lord Howe Island stick insect | Dryococelus australis | | N/A | Critically Endangered D | 1-49 | 500–1,000 | 501-1,049 | Ball's Pyramid, Australia |
| Wild Bactrian camel | Camelus ferus | | N/A | Critically Endangered A3de+4ade | 1,000-1,500 | 100-200 | 1,100-1,700 |  |
| Key tree-cactus | Pilosocereus robinii |  | N/A | Extinct in the Wild | 0 | 200–2,000 | 200-2,000 |
|
| Central rock rat | Zyzomys pedunculatus | | N/A | Critically Endangered A2abce | 500–2,000 | 1-9 | 501-2,009 |  |
| Eastern lowland gorilla | Gorilla beringei graueri | | N/A | Critically Endangered A4bcd | 3,800-5,000 | 1-19 | 3,801-5,019 |  |