This aims to be a complete list of the articles on real estate.
Owner-occupancy or home-ownership is a form of housing tenure in which a person, called the owner-occupier, owner-occupant, or home owner, owns the home in which they live. The home can be a house, such as a single-family house, an apartment, condominium, or a housing cooperative. In addition to providing housing, owner-occupancy also functions as a real estate investment.
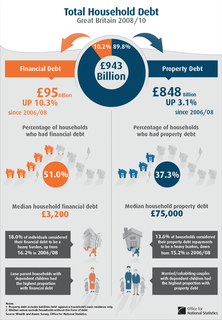
Household debt is defined as the combined debt of all people in a household. It includes consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent European economic crises of 2007–2012. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries.

Real estate economics is the application of economic techniques to real estate markets. It tries to describe, explain, and predict patterns of prices, supply, and demand. The closely related field of housing economics is narrower in scope, concentrating on residential real estate markets, while the research on real estate trends focuses on the business and structural changes affecting the industry. Both draw on partial equilibrium analysis, urban economics, spatial economics, basic and extensive research, surveys, and finance.

Second mortgages, commonly referred to as junior liens, are loans secured by a property in addition to the primary mortgage. Depending on the time at which the second mortgage is originated, the loan can be structured as either a standalone second mortgage or piggyback second mortgage. Whilst a standalone second mortgage is opened subsequent to the primary loan, those with a piggyback loan structure are originated simultaneously with the primary mortgage. With regard to the method in which funds are withdrawn, second mortgages can be arranged as home equity loans or home equity lines of credit. Home equity loans are granted for the full amount at the time of loan origination in contrast to home equity lines of credit which permit the homeowner access to a predetermined amount which is repaid during the repayment period.

The United States housing bubble was a real estate bubble affecting over half of the U.S. states. It was the impetus for the subprime mortgage crisis. Housing prices peaked in early 2006, started to decline in 2006 and 2007, and reached new lows in 2012. On December 30, 2008, the Case–Shiller home price index reported its largest price drop in its history. The credit crisis resulting from the bursting of the housing bubble is an important cause of the Great Recession in the United States.
A housing bubble is one of several types of asset price bubbles which periodically occur in the market. The basic concept of a housing bubble is the same as for other asset bubbles, consisting of two main phases. First there is a period where house prices increase dramatically, driven more and more by speculation. In the second phase, house prices fall dramatically. Housing bubbles tend to be among the asset bubbles with the largest effect on the real economy, because they are credit-fueled, because a large number of households participate and not just investors, and because the wealth effect from housing tends to be larger than for other types of financial assets.

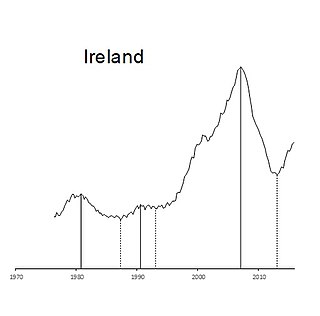
The Irish property bubble was the speculative excess element of a long-term price increase of real estate in the Republic of Ireland from the early 2000s to 2007, a period known as the later part of the Celtic Tiger. In 2006, the prices peaked at the top of the bubble, with a combination of increased speculative construction and rapidly rising prices; in 2007 the prices first stabilised and then started to fall until 2010 following the shock effect of the Great Recession. By the second quarter of 2010, house prices in Ireland had fallen by 35% compared with the second quarter of 2007, and the number of housing loans approved fell by 73%.
Capitalization rate is a real estate valuation measure used to compare different real estate investments. Although there are many variations, a cap rate is often calculated as the ratio between the net operating income produced by an asset and current market value.

Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a median household income or below as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on affordable housing refers to mortgages and number of forms that exist along a continuum – from emergency shelters, to transitional housing, to non-market rental, to formal and informal rental, indigenous housing, and ending with affordable home ownership.
Real estate investing involves the purchase, ownership, management, rental and/or sale of real estate for profit. Improvement of realty property as part of a real estate investment strategy is generally considered to be a sub-specialty of real estate investing called real estate development. Real estate is an asset form with limited liquidity relative to other investments. It is also capital intensive and is highly cash flow dependent. If these factors are not well understood and managed by the investor, real estate becomes a risky investment.

Robert James Shiller is an American economist, academic, and best-selling author. As of 2019, he serves as a Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University and is a fellow at the Yale School of Management's International Center for Finance. Shiller has been a research associate of the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) since 1980, was vice president of the American Economic Association in 2005, its president-elect for 2016, and president of the Eastern Economic Association for 2006–2007. He is also the co‑founder and chief economist of the investment management firm MacroMarkets LLC.
United States housing prices experienced a major market correction after the housing bubble that peaked in early 2006. Prices of real estate then adjusted downwards in late 2006, causing a loss of market liquidity and subprime defaults

Observers and analysts have attributed the reasons for the 2001–2006 housing bubble and its 2007–10 collapse in the United States to "everyone from home buyers to Wall Street, mortgage brokers to Alan Greenspan". Other factors that are named include "Mortgage underwriters, investment banks, rating agencies, and investors", "low mortgage interest rates, low short-term interest rates, relaxed standards for mortgage loans, and irrational exuberance" Politicians in both the Democratic and Republican political parties have been cited for "pushing to keep derivatives unregulated" and "with rare exceptions" giving Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac "unwavering support".
Karl Edwin "Chip" Case was Professor of Economics Emeritus at Wellesley College in Wellesley, Massachusetts, United States, where he held the Coman and Hepburn Chair in Economics and taught for 34 years. He was a Senior Fellow at the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University and was President of the Boston Economic Club 2011-12. Professor Case was also a founding partner in the real estate research firm of Fiserv Case Shiller Weiss, Inc., which created the S&P Case Shiller Index of home prices. He served as a member of the Board of Directors of the Depositors Insurance Fund of Massachusetts. He was a member of the Standard and Poor’s Index Advisory Committee, the Academic Advisory Board of the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston and the Board of Advisors of the Rappaport Institute for Greater Boston at Harvard University. He served as a member of the Boards of Directors of the Mortgage Guaranty Insurance Corporation (MGIC), Century Bank, The Lincoln Institute of Land Policy, and the American Real Estate and Urban Economics Association. He was also an Associate Editor of The Journal of Economic Perspectives and The Journal of Economics Education.
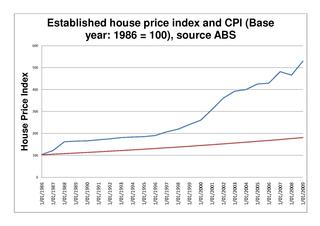
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.

The 2005 Chinese property bubble was a real estate bubble in residential and commercial real estate in China. The New York Times reported that the bubble started to deflate in 2011, while observing increased complaints that members of the middle-class were unable to afford homes in large cities. The deflation of the property bubble is seen as one of the primary causes for China's declining economic growth in 2013.
Real estate in China is developed and managed by public, private, and state-owned red chip enterprises. In the years leading up to the 2008 financial crisis, the real estate sector in China was growing so rapidly that the government implemented a series of policies—including raising the required downpayment for some property purchases, and five 2007 interest rate increases—due to concerns of overheating. But after the crisis hit, these policies were quickly eliminated, and in some cases tightened. Beijing also launched a massive stimulus package to boost growth, and much of the stimulus wound up flowing into the property market and driving prices upward, resulting in investors increasingly looking abroad. By late 2014, the IMF warned that a real estate oversupply problem had arisen that threatened to cause detrimental effects to the Chinese economy, particularly in 2nd and 3rd tier cities. As of 2015, the market was experiencing low growth and the central government had eased prior measures to tighten interest rates, increase deposits and impose restrictions. By early 2016, the Chinese government introduced a series of measures to increase property purchases, including lower taxes on home sales, limiting land sales for new development projects, and the third in a series of mortgage down payment reductions.
Property investment calculator is a term used to define an application that provides fundamental financial analysis underpinning the purchase, ownership, management, rental and/or sale of real estate for profit. Property investment calculators are typically driven by mathematical finance models and converted into source code. Key concepts that drive property investment calculators include returns, cash flow, affordability of financing, investment strategy, equity and risk management.
The Canadian property bubble refers to a significant rise in Canadian real estate prices from 2002 to present which some observers have called a real estate bubble. From 2003 to 2018, Canada saw an increase in home and property prices of up to 337% in some cities.



















