Related Research Articles

Macau or Macao is a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China. With a population of about 710,000 people and a land area of 32.9 km2 (12.7 sq mi),it is the most densely populated region in the world.

劉 / 刘 is an East Asian surname. pinyin:Liú in Mandarin Chinese,Lau4 in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character 劉 originally meant 'battle axe',but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic text Hundred Family Surnames. Today,it is the 4th most common surname in mainland China as well as one of the most common surnames in the world.

The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region,commonly known as the Hong Kong Government or HKSAR Government,is the executive authorities of Hong Kong. It was formed on 1 July 1997 in accordance with the Sino-British Joint Declaration of 1983,an international treaty lodged at the United Nations. This government replaced the former British Hong Kong Government (1842–1997). The Chief Executive and the principal officials are appointed by the State Council of the People's Republic of China in accordance with the outcome of local processes. The Government Secretariat is headed by the Chief Secretary of Hong Kong,who is the most senior principal official of the Government. The Chief Secretary and the other secretaries jointly oversee the administration of Hong Kong,give advice to the Chief Executive as members of the Executive Council,and are accountable for their actions and policies to the Chief Executive and the Legislative Council.

Hong Kong Island is an island in the southern part of Hong Kong. The island,known originally and on road signs simply as "Hong Kong",had a population of 1,289,500 and a population density of 16,390 per square kilometre (42,400/sq mi),as of 2023. It is the second largest island in Hong Kong,with the largest being Lantau Island. Hong Kong Island forms one of the three areas of Hong Kong,with the other two being Kowloon and the New Territories.

Lantau Island is the largest island in Hong Kong,located west of Hong Kong Island and the Kowloon Peninsula,and is part of the New Territories. Administratively,most of Lantau Island is part of the Islands District of Hong Kong. A small northeastern portion of the island is located in the Tsuen Wan District.

Kowloon City is an area in New Kowloon,Hong Kong. It is part of Kowloon City District.

Sung Wong Toi is an important historic relic in Ma Tau Chung,Kowloon,Hong Kong. While its remaining portion is now located in the Sung Wong Toi Garden (宋皇臺花園) at the junction of Ma Tau Chung Road and Sung Wong Toi Road,it was originally a 45-metre-tall boulder standing on the top of Sacred Hill (聖山) in Ma Tau Chung above Kowloon Bay.

Mui Wo is a rural town on the eastern coast of Lantau Island in Hong Kong. The 2011 Census recorded 5,485 people living in Mui Wo and its environs.

The region of Hong Kong has been inhabited since the Old Stone Age,later becoming part of the Chinese Empire with its loose incorporation into the Qin dynasty. Starting out as a farming fishing village and salt production site,it became an important free port and eventually a major international financial center.
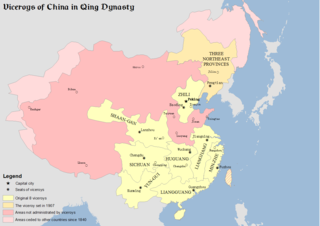
Zongdu were the managers supervising provincial governors in Ming and Qing China. One viceroy usually administered several provinces and was in charge of all affairs of military,food,wages,rivers,and provincial governors within their region of jurisdiction. Viceroys was appointed by and directly reported to the Emperor.

The grand chancellor,also translated as counselor-in-chief,chancellor,chief councillor,chief minister,imperial chancellor,lieutenant chancellor and prime minister,was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history,and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly,even during a particular dynasty.
Chang Hen Ge is a literary masterpiece from the Tang dynasty by the famous Chinese poet Bai Juyi (772–846). It retells the love story between Emperor Xuanzong of Tang and his favorite concubine Yang Guifei (719–756). This long narrative poem is dated from 809.
The Zhongshu Sheng,also known as the Palace Secretariat or Central Secretariat,was one of the departments of the Three Departments and Six Ministries government structure in imperial China from the Cao Wei (220–266) until the early Ming dynasty. As one of the Three Departments,the Zhongshu Sheng was primarily a policy-formulating agency responsible for proposing and drafting all imperial decrees,but its actual function varied at different times. The department traces its origins back to the Han dynasty.
The Three Departments and Six Ministries system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria,Korea and Vietnam.

The Constitutional and Mainland Affairs Bureau is a ministerial-level policy bureaux of the Government of Hong Kong responsible for the implementation of the Basic Law,including electoral matters and promotion of equal opportunities and privacy protection. The bureau also functions as the intermediary between the HKSAR Government and the Central People's Government and other Mainland authorities under the principles of "One Country,Two Systems",including the coordination of liaison between the HKSAR Government and Central authorities,promoting regional co-operation initiatives between Hong Kong and the Mainland,and overseeing the operation of offices of the HKSAR Government on the Mainland.

Kong Anguo,courtesy name Ziguo (子國),Kong Anguo was a Chinese classicist,philosopher,and politician of the Western Han dynasty of ancient China. A descendant of Confucius,he wrote the Shangshu Kongshi Zhuan,a compilation and commentary of the "Old Text" Shangshu. His work was lost,but a debated fourth-century forgery was officially recognized as a Confucian classic for over a millennium.

The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence,its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省),as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs. In addition,the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates,but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire.
The Menxia Sheng,sometimes translated as the Chancellery,was one of the departments of the Three Departments and Six Ministries government structure of imperial China. It advised the emperor and the Zhongshu Sheng,and reviewed edicts and commands. As the least important of the three departments,it existed in name only by the Song dynasty while its functions were delegated to the other two departments. In 1129,the Chancellery was merged with the Central Secretariat.
The Bureau of Military Affairs was the central government agency in charge of a state's military forces during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period,Liao dynasty,Song dynasty and Yuan dynasty. It was headed by the Shumishi.

The Qing dynasty (1644–1912) was the last imperial dynasty of China. The early Qing emperors adopted the bureaucratic structures and institutions from the preceding Ming dynasty but split rule between the Han and Manchus with some positions also given to Mongols. Like previous dynasties,the Qing recruited officials via the imperial examination system until the system was abolished in 1905. The Qing divided the positions into civil and military positions,each having nine grades or ranks,each subdivided into a and b categories. Civil appointments ranged from an attendant to the emperor or a grand secretary in the Forbidden City (highest) to being a prefectural tax collector,deputy jail warden,deputy police commissioner,or tax examiner. Military appointments ranged from being a field marshal or chamberlain of the imperial bodyguard to a third class sergeant,corporal or a first or second class private.
References
- Hucker, Charles O. (1985). A Dictionary of Official Titles in Imperial China. Stanford University Press. p. 151.