
The Polygonaceae are a family of flowering plants known informally as the knotweed family or smartweed—buckwheat family in the United States. The name is based on the genus Polygonum, and was first used by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu in 1789 in his book, Genera Plantarum. The name may refer to the many swollen nodes the stems of some species have, being derived from Greek [poly meaning 'many' and gony meaning 'knee' or 'joint']. Alternatively, it may have a different origin, meaning 'many seeds'.

Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks (petioles) of species and hybrids of Rheum in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The plant is a herbaceous perennial that grows from short, thick rhizomes. Historically, different plants have been called "rhubarb" in English. The large, triangular leaves contain high levels of oxalic acid and anthrone glycosides, making them inedible. The small flowers are grouped in large compound leafy greenish-white to rose-red inflorescences.

Alpine plants are plants that grow in an alpine climate, which occurs at high elevation and above the tree line. There are many different plant species and taxa that grow as a plant community in these alpine tundra. These include perennial grasses, sedges, forbs, cushion plants, mosses, and lichens. Alpine plants are adapted to the harsh conditions of the alpine environment, which include low temperatures, dryness, ultraviolet radiation, wind, drought, poor nutritional soil, and a short growing season.

Rheum palmatum is a species of flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae. It is commonly called Chinese rhubarb, ornamental rhubarb, Turkey rhubarb or East Indian rhubarb.

Rheum is a genus of about 60 herbaceous perennial plants in the family Polygonaceae. Species are native to eastern Europe, southern and eastern temperate Asia, with a few reaching into northern tropical Asia. Rheum is cultivated in Europe and North America. The genus includes the vegetable rhubarb. The species have large somewhat triangular shaped leaves with long, fleshy petioles. The flowers are small, greenish-white to rose-red, and grouped in large compound leafy inflorescences. Many rhubarb cultivars have been domesticated as medicinal plants and for human consumption. While the leaves are slightly toxic, the stalks are used in pies and other foods for their tart flavor.

In botany, the petiole is the stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem. It is able to twist the leaf to face the sun, producing a characteristic foliage arrangement, and also optimizing its exposure to sunlight. Outgrowths appearing on each side of the petiole in some species are called stipules. The terms petiolate and apetiolate are applied respectively to leaves with and without petioles.

Scutellaria lateriflora, is a hardy perennial herb of the mint family, Lamiaceae, native to North America.
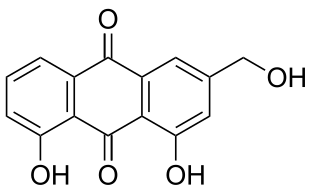
Aloe emodin is an anthraquinone and an isomer of emodin present in aloe latex, an exudate from the aloe plant. It has a strong stimulant-laxative action. Aloe emodin is not carcinogenic when applied to the skin, although it may increase the carcinogenicity of some kinds of radiation.
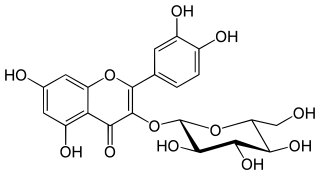
Isoquercetin, isoquercitrin or isotrifoliin is a flavonoid, a type of chemical compound. It is the 3-O-glucoside of quercetin. Isoquercitrin can be isolated from various plant species including Mangifera indica (mango) and Rheum nobile. It is also present in the leaves of Annona squamosa, Camellia sinensis (tea). and Vestia foetida

Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-O-galactoside of quercetin.

Rheum rhabarbarum is a species of flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae, native to a region stretching from southern Siberia to north and central China. It has been harvested from the wild for centuries for its root, which was harvested for use as a popular medicine in Europe and Asia. It was later cultivated for its root in England and Russia. It is considered to be one of the species involved in the development of culinary rhubarb, for which the scientific name R. rhabarbarum is sometimes (erroneously) used.

Rheum australe, synonym Rheum emodi, is a flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae. It is commonly known as Himalayan rhubarb, Indian rhubarb and Red-veined pie plant. It is a medicinal herb used in the Indian Unani system of medicine, and formerly in the European system of medicine where it was traded as Indian rhubarb. The plant is found in the sub-alpine and alpine Himalayas at an altitude of 4000 m.

Rhaponticum scariosum, common name giant scabiosa, is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant of the genus Rhaponticum of the family Asteraceae.

Rheum maximowiczii is a large herbaceous perennial plant species in the genus Rheum (rhubarbs) from the mountains of Central Asia where it grows in Kazakhstan, eastern Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and northeastern Afghanistan.

Rheum ribes, the Syrian rhubarb or currant-fruited rhubarb, or warty-leaved rhubarb, is an edible wild rhubarb species in the genus Rheum. It grows between 1000 and 4000 m on dunite rocks, among stones and slopes, and is now distributed in the temperate and subtropical regions of the world, chiefly in Western Asia to Afghanistan and Pakistan and also in ladakh(Kargil) region of India. The Syrian rhubarb is a partially commercial vegetable collected from wild patches in Eastern and Southern Anatolia, Northern Iraq and partly Northwestern Iran in early spring. Rheum ribes is considered as a valuable medicinal species in herbal medicine.

Rheum rhaponticum, the false rhubarb, rhapontic rhubarb or rhapontic, is a plant species in the genus Rheum found in the wild. It is the only Rheum species found only in Europe, and is now restricted to the Rila mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. It was introduced to other countries in Europe. It is considered to be one of the parents of the modern culinary rhubarb.

Teucrium gnaphalodes is a plant species in the genus Teucrium. It is endemic to the Iberian Peninsula and grows at altitudes between 200 and 1500 m. It flowers from March to July.

Iris hookeriana is a plant species in the genus Iris, it is also in the subgenus Iris and in the section Pseudoregelia. It is a rhizomatous perennial, from the Himalayan mountains of India and Pakistan. It has long pale green or yellow green leaves, long slender stem and fragrant blue, purple or lilac flowers, that are mottled with a darker colour. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions.
Rheum lhasaense is a plant from eastern Tibet belonging to the genus Rheum in family Polygonaceae. It is a mid-sized rhubarb species with triangular leaves and spherical fruit.

Rheum webbianum is a species of herbaceous perennial rhubarb-relative in the family Polygonaceae from the southwestern Himalayan region, known in (Indian) English as Indian rhubarb, Gilgiti rhubarb or small Himalayan rhubarb.





















