
Erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.

An entrenched river, or entrenched stream is a river or stream that flows in a narrow trench or valley cut into a plain or relatively level upland. Because of lateral erosion streams flowing over gentle slopes over a time develops meandering course. Meanders form where gradient is very gentle, for example in floodplain and delta. Meandering is the feature of the middle and final course of the river. But very deep and wide meanders can also be found cutting hard rocks. Such meanders are called incised or entrenched meanders. The exception is that entrenched meanders are formed during the upliftment of land where river is young. They widen and deepen over time and can be found as deep gorges or canyons in hard rock. In the case of an entrenched stream or river, it is often presumed that the watercourse has inherited its course by cutting down into bedrock from a pre-existing plain with little modification of the original course. The down-cutting of the river system could be the result not only of tectonic uplift but also of other factors such as river piracy, decrease of load, increase of runoff, extension of the drainage basin, or change in base level such as a fall in sea level. General, nongeneric terminology for either a river or stream that flows in a narrow trench or valley, for which evidence of a preexisting plain or relatively level upland can be either absent or present is either valley meander or meander valley with the latter term being preferred in literature.

Geomorphology is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features generated by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.

A braided river consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in British English usage, aits or eyots.

An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than 1 square kilometer (0.4 sq mi) to almost 20,000 square kilometers (7,700 sq mi).

A streambed or stream bed is the bottom of a stream or river (bathymetry) and is confined within a channel, or the banks of the waterway. Usually, the bed does not contain terrestrial (land) vegetation and instead supports different types of aquatic vegetation, depending on the type of streambed material and water velocity. Streambeds are what would be left once a stream is no longer in existence. The beds are usually well preserved even if they get buried because the banks and canyons made by the stream are typically hard, although soft sand and debris often fill the bed. Dry, buried streambeds can actually be underground water pockets. During times of rain, sandy streambeds can soak up and retain water, even during dry seasons, keeping the water table close enough to the surface to be obtainable by local people.
Denudation is the geological process in which moving water, ice, wind, and waves erode the Earth's surface, leading to a reduction in elevation and in relief of landforms and landscapes. Although the terms erosion and denudation are used interchangeably, erosion is the transport of soil and rocks from one location to another, and denudation is the sum of processes, including erosion, that result in the lowering of Earth's surface. Endogenous processes such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and tectonic uplift can expose continental crust to the exogenous processes of weathering, erosion, and mass wasting. The effects of denudation have been recorded for millennia but the mechanics behind it have been debated for the past 200 years and have only begun to be understood in the past few decades.
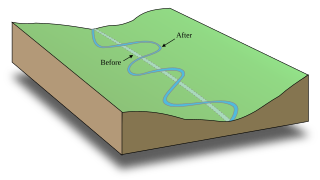
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain.

In geomorphology, a knickpoint or nickpoint is part of a river or channel where there is a sharp change in channel bed slope, such as a waterfall or lake. Knickpoints reflect different conditions and processes on the river, often caused by previous erosion due to glaciation or variance in lithology. In the cycle of erosion model, knickpoints advance one cycle upstream, or inland, replacing an older cycle. A knickpoint that occurs at the head of a channel is called a headcut. Headcuts resulting in headward erosion are hallmarks of unstable expanding drainage features such as actively eroding gullies.

Abrasion is a process of weathering that occurs when material being transported wears away at a surface over time, commonly happens in ice and glaciers. The primary process of abrasion is physical weathering. Its the process of friction caused by scuffing, scratching, wearing down, marring, and rubbing away of materials. The intensity of abrasion depends on the hardness, concentration, velocity and mass of the moving particles. Abrasion generally occurs in four ways: glaciation slowly grinds rocks picked up by ice against rock surfaces; solid objects transported in river channels make abrasive surface contact with the bed with ppl in it and walls; objects transported in waves breaking on coastlines; and by wind transporting sand or small stones against surface rocks. Abrasion is the natural scratching of bedrock by a continuous movement of snow or glacier downhill. This is caused by a force, friction, vibration, or internal deformation of the ice, and by sliding over the rocks and sediments at the base that causes the glacier to move.

A pediment, also known as a concave slope or waning slope, is a very gently sloping (0.5°–7°) inclined bedrock surface. It is typically a concave surface sloping down from the base of a steeper retreating desert cliff, escarpment, or surrounding a monadnock or inselberg, but may persist after the higher terrain has eroded away.

In sedimentary geology and fluvial geomorphology, avulsion is the rapid abandonment of a river channel and the formation of a new river channel. Avulsions occur as a result of channel slopes that are much less steep than the slope that the river could travel if it took a new course.

A bar in a river is an elevated region of sediment that has been deposited by the flow. Types of bars include mid-channel bars, point bars, and mouth bars. The locations of bars are determined by the geometry of the river and the flow through it. Bars reflect sediment supply conditions, and can show where sediment supply rate is greater than the transport capacity.

Stream power, originally derived by R. A. Bagnold in the 1960s, is the amount of energy the water in a river or stream is exerting on the sides and bottom of the river. Stream power is the result of multiplying the density of the water, the acceleration of the water due to gravity, the volume of water flowing through the river, and the slope of that water. There are many forms of the stream power formula with varying utilities, such as comparing rivers of various widths or quantifying the energy required to move sediment of a certain size. Stream power is closely related to other criteria such as stream competency and shear stress. Stream power is a valuable measurement for hydrologists and geomorphologists tackling sediment transport issues as well as for civil engineers, who use it in the planning and construction of roads, bridges, dams, and culverts.

An alluvial river is one in which the bed and banks are made up of mobile sediment and/or soil. Alluvial rivers are self-formed, meaning that their channels are shaped by the magnitude and frequency of the floods that they experience, and the ability of these floods to erode, deposit, and transport sediment. For this reason, alluvial rivers can assume a number of forms based on the properties of their banks; the flows they experience; the local riparian ecology; and the amount, size, and type of sediment that they carry.

A bedrock river is a river that has little to no alluvium mantling the bedrock over which it flows. However, most bedrock rivers are not pure forms; they are a combination of a bedrock channel and an alluvial channel. The way one can distinguish between bedrock rivers and alluvial rivers is through the extent of sediment cover.

In hydrology stream competency, also known as stream competence, is a measure of the maximum size of particles a stream can transport. The particles are made up of grain sizes ranging from large to small and include boulders, rocks, pebbles, sand, silt, and clay. These particles make up the bed load of the stream. Stream competence was originally simplified by the “sixth-power-law,” which states the mass of a particle that can be moved is proportional to the velocity of the river raised to the sixth power. This refers to the stream bed velocity which is difficult to measure or estimate due to the many factors that cause slight variances in stream velocities.
The term stream power law describes a semi-empirical family of equations used to predict the rate of erosion of a river into its bed. These combine equations describing conservation of water mass and momentum in streams with relations for channel hydraulic geometry and basin hydrology and an assumed dependency of erosion rate on either unit stream power or shear stress on the bed to produce a simplified description of erosion rate as a function of power laws of upstream drainage area, A, and channel slope, S:
Hillslope evolution is the changes in the erosion rates, erosion styles and form of slopes of hills and mountains over time.
Fluvial seismology is the application of seismological methods to understand river processes, such as discharge, erosion, and streambed evolution. Flowing water and the movement of sediments along the streambed generate elastic (seismic) waves that propagate into the surrounding Earth materials. Seismometers can record these signals, which can be analyzed to illuminate different fluvial processes such as turbulent water flow and bedload transport. Seismic methods have been used to observe discharge values that range from single-digits up through tens of thousands of cubic feet per second (cfs).



















