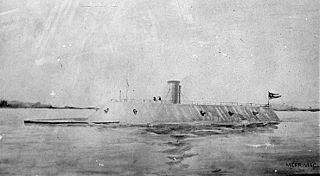
CSS Virginia was the first steam-powered ironclad warship built by the Confederate States Navy during the first year of the American Civil War; she was constructed as a casemate ironclad using the razéed original lower hull and engines of the scuttled steam frigate USS Merrimack. Virginia was one of the participants in the Battle of Hampton Roads, opposing the Union's USS Monitor in March 1862. The battle is chiefly significant in naval history as the first battle between ironclads.
CSS Scorpion was a Squib-class torpedo boat that served in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Armed with a single spar torpedo, she originally served guard duty on the James River after being built in late 1864. Along with the rest of the James River Squadron, Scorpion moved downriver on January 23, 1865, and participated in the Battle of Trent's Reach. After performing depth soundings near Union obstructions, Scorpion moved to get a lantern from the ironclad CSS Virginia II, but ran into a hawser and then ran aground. At 07:10 on the morning of January 24, Union fire struck the abandoned tender CSS Drewry, which then exploded. The force of the explosion swept Scorpion out of control downriver. An attempt to rescue her that night failed, and she was captured by Union forces.

CSS Texas was the third and last Columbia-class casemate ironclad built for the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. Not begun until 1864 and intended to become part of the James River Squadron, she saw no action before being captured by Union forces while still fitting out. CSS Texas was reputed to have been one of the very best-constructed Confederate ironclads, second only to CSS Mississippi.

The Battle of Hampton Roads, also referred to as the Battle of the Monitor and Merrimack or the Battle of Ironclads, was a naval battle during the American Civil War.

The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the American Civil War against the United States's Union Navy.

CSS Virginia II was a Confederate Navy steam-powered ironclad ram laid down in 1862 at the William Graves' shipyard in Richmond, Virginia. Acting Constructor William A. Graves, CSN, was the superintendent in charge of her construction. In order to conserve scarce iron plating, he ordered the ship's armored casemate shortened from the specifications given in John L. Porter's original building plans; in addition, the ship's iron-plating, while six inches thick on the casemate's forward face, was reduced to five inches on her port, starboard, and aft faces. Due to the shortening of her casemate, the number of her cannon were reduced to a single 11" smoothbore, a single 8" rifle, and two 6.4" rifles.

CSS Richmond was the name ship of her class of six casemate ironclads built for the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Completed during 1862 the ship was assigned to the James River Squadron where she mostly supported Confederate forces near Richmond, Virginia. She was burned in April 1865 to prevent her capture by Union forces.

The first USS Miami was a side-wheel steamer, double-ender gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.
The CSS Beaufort was an iron-hull gunboat that served in North Carolina and Virginia during the American Civil War. Originally launched as Caledonia at Wilmington, Delaware, in 1854, the ship was owned by James Cathcart Johnston. It saw use as a tugboat on the Dismal Swamp Canal. On July 9, 1861, Beaufort was commissioned into the navy of the state of North Carolina for use in the American Civil War. First serving on the North Carolina coast, Beaufort was present at the battles of Roanoke Island and Elizabeth City in February 1862. Escaping the Confederate defeat at Elizabeth City via the Dismal Swamp Canal, Beaufort reached Norfolk, Virginia, where she joined the James River Squadron.

CSS Fredericksburg was a casemate ironclad that served as part of the James River Squadron of the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Laid down in 1862 and Launched the following year, she did not see action until 1864 due to delays in receiving her armor and guns. After passing through the obstructions at Drewry's Bluff in May 1864, she participated in several minor actions on the James River and fought in the Battle of Chaffin's Farm from September 29 to October 1. On January 23 and 24, 1865, she was part of the Confederate fleet at the Battle of Trent's Reach, and was one of only two Confederate ships to make it past the obstructions at Trent's Reach. After the Confederate attack failed, Fredericksburg withdrew with the rest of the James River Squadron. On April 3, as the Confederates were abandoning Richmond, Fredericksburg and the other vessels of the James River Squadron were burned. Her wreck was located in the 1980s, buried under sediment.

William Augustin Webb (1824-1881) was an American sailor and Mexican–American War veteran who resigned his United States Navy commission after more than 20 years of service to join the Confederate States Navy in the American Civil War. Webb was decorated for his service as Captain of the CSS Teaser, part of the James River Squadron, during the Battle of Hampton Roads (1862).

The Battle of Drewry's Bluff, also known as the Battle of Fort Darling, or Fort Drewry, took place on May 15, 1862, in Chesterfield County, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. Four Union Navy warships, including the ironclads USS Monitor and Galena, and the United States Revenue Cutter Service's ironclad USRC Naugatuck steamed up the James River to test the defenses of Richmond, Virginia, the Confederate capital. They encountered submerged obstacles, and deadly accurate fire from the batteries of Fort Darling at Drewry's Bluff, which inflicted severe damage on Galena, forcing them to turn back.

USS Sangamon was a Passaic-class ironclad monitor constructed for the Union Navy during the second year of the American Civil War where she operated in the waterways of the Confederate States of America. She was later recommissioned and placed into service during the Spanish–American War.
The James River Squadron was formed shortly after the secession of Virginia during the American Civil War. The squadron was part of the Virginia Navy before being transferred to the Confederate States Navy. The squadron is most notable for its role in patrolling the James River, which was the main water approach to the Confederate capital, Richmond. It had two phases: early war, when it consisted mostly of wooden ships which ended with the Battle of Drewry's Bluff on May 15, 1862; and its later ironclad composition with the flagship CSS Virginia II.
USS Alpha was a side wheel paddle steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Althea was a screw steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. The Union Navy used it as a tugboat, a torpedo boat, and a ship's tender in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

The Battle of Trent's Reach was one of the final major naval battles of the American Civil War. Beginning on January 23, 1865, a powerful flotilla of Confederate warships bombarded Fort Brady along the James River and engaged four Union Navy ships with the intention of breaking through the blockade to attack City Point, the base of General Ulysses S. Grant who was besieging Petersburg, Virginia. After two days of fighting, the rebels withdrew back up the river without completing their objectives.
CSS Arctic was a Confederate ironclad floating battery converted from USS Arctic at Wilmington, North Carolina in 1862. Confederate forces seized USS Arctic at the beginning of the war and converted into a receiving ship. Arctic was a 328-ton screw steamer built in Philadelphia in 1851 at the navy yard by Theodore Birely. The two-decked, three-masted steamer measured 121 feet (37 m) in length, 24 feet (7.3 m) in beam, 12 feet (3.7 m) in depth, and 125 tons.

Ebenezer Farrand was an American Commodore that served in the Confederate States Navy and was notable for his service at the Battle of Drewry's Bluff as well as his ship construction at Selma, Alabama.

The Squib class torpedo boats were built for the Confederate States Navy during the later stages of the American Civil War. After the torpedo boat CSS David attacked and damaged the ironclad USS New Ironsides, the Confederates continued building torpedo boats with hopes of breaking the Union blockade. Four vessels of the class – CSS Hornet, CSS Wasp, CSS Squib, and CSS Scorpion – were constructed in Richmond, Virginia, in 1864. All were armed with a single spar torpedo and were powered by steam engines. Squib damaged the gunboat USS Minnesota in an attack on April 9, 1864, and was later sent to Wilmington, North Carolina, where she was scuttled in February 1865. The other three vessels of the class were all part of the James River Squadron and participated in the Battle of Trent's Reach on the night of January 23 and 24, 1865. Scorpion ran aground during the battle, and was forced downriver and out of control after the tender CSS Drewry exploded on January 24. She was later captured by Union forces and may have been burned. Hornet was sunk in a collision with another vessel on January 27, and Wasp was scuttled on the night of April 2/3, as the Confederates were abandoning Richmond.














