
Oregon Hill is a historic working-class neighborhood in Richmond, Virginia. Oregon Hill overlooks the James River and Belle Isle, and provides access to Hollywood Cemetery. Due to the neighborhood's proximity to the Monroe Park Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University, the neighborhood is sometimes referred to as a student quarter because of its high college student population.

Lewis Ginter was a prominent businessman, financier, military officer, real estate developer, and philanthropist centered in Richmond, Virginia. A native of New York City, Ginter accumulated a considerable fortune throughout his numerous business ventures and became one of Richmond's wealthiest citizens despite his exceptionally modest demeanor. While the Jefferson Hotel and Ginter Park embody some of Ginter's major urban contributions to Richmond, many of his philanthropic gifts were given anonymously to charitable organizations and individuals in need. Ginter served in the Confederacy, attaining the rank of major and played a major role in bringing Richmond back from the ravages of the Civil War. His continued devotion to the city is captured in his famous remark, "I am for Richmond, first and last."

The Second White House of the Confederacy is a historic house located in the Court End neighborhood of Richmond, Virginia. Built in 1818, it served as the main executive residence of the sole President of the Confederate States of America, Jefferson Davis, from August 1861 until April 1865. It currently sits on the campus of Virginia Commonwealth University.
The Greater Richmond, Virginia area has many neighborhoods and districts.
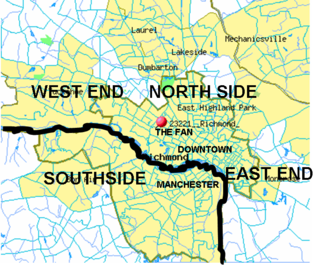
The Northside is an area composed of northern Richmond, Virginia and some parts of Henrico County, Virginia.

Hermitage Road Historic District (HRHD) is a Northside neighborhood in the independent city of Richmond, Virginia. The district is a Richmond Old and Historic District, as well as being listed on the Virginia Landmarks Register and the National Register of Historic Places.
The Ghent District is a historic neighborhood in Norfolk, Virginia. It comprises Ghent, West Ghent, and Ghent Square. Other portions of surrounding neighborhoods are often attributed to Ghent as an extension of its commerce including Chelsea, North Colley Avenue, and active gentrification into portions of Park Place to the north, labelled 'The Railroad District'.

Tree Hill near Richmond, Virginia, in Henrico County, Virginia, is a Greek Revival style plantation house overlooking the James River about two miles east of downtown Richmond near the intersection of the historic Osborne Turnpike and New Market Road. Currently still a private farm, but expected to become partly a park after housing and commercial development, it was once owned by Richmond distiller and landowner Franklin Stearns, a prominent Unionist during the American Civil War. Centuries earlier, it had been a Native American camp site, and the birthplace of powerful chief Powhatan (d.1618).

The Central National Bank building is a 23-story Art Deco skyscraper located in Richmond, Virginia. Completed in 1929, it was one of the first skyscrapers in the city of Richmond not in the heart of the financial district. According to architectural historian Richard Guy Wilson, it and the West Hospital building, are the only two skyscrapers in Richmond to have used the fashionable Art Deco ziggurat-inspired setback, and only a few others exist elsewhere in Virginia. When the bank later changed hands, it was known as the Central Fidelity Bank. It was used as a branch bank for Wachovia Corp. until that closed in 2000. After nearly fifteen years of vacancy, it was converted into apartments, and the first resident moved into the building in mid-2016. The redevelopment is called to "Deco at CNB," a 200-apartment development by Douglas Development Corp.

Barton Heights is a streetcar suburb neighborhood and former town in the Northside area of Richmond, Virginia. The area was primarily developed between 1890 and the 1920s.

The Chestnut Hill–Plateau Historic District is a historic area in the Highland Park neighborhood of Richmond, Virginia. It is also known as 'Highland Park Southern Tip' on city neighborhood maps.

Highland Park–Overlee Knolls, also known as Fostoria, is a national historic district located in Arlington County, Virginia. It is directly east of the Virginia Heights Historic District. It contains 681 contributing buildings, 3 contributing sites, and 1 contributing structure in a residential neighborhood in North Arlington. The first subdivision was platted in 1890 and known as Fostoria.
North End Historic District is a national historic district located at Newport News, Virginia. It encompasses 451 contributing buildings in a primarily residential section of Newport News. It is a compact, middle-class and upper middle-class residential neighborhood that arose during the period 1900–1935 in association with the nearby Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company. The neighborhood includes notable examples of the Victorian, Colonial Revival, and Bungalow styles. Notable buildings include the Walter A. Post House (1902), John Livesay House (1906), J. E. Warren House (1905), W. L. Shumate House (1915), and Willet House.

Hancock–Wirt–Caskie House, also known as The William Wirt House, is a historic home located in Richmond, Virginia. It was built in 1808–09, and is a two-story, seven-bay Federal-era brick dwelling with a hipped roof. The three bays on either side of the entrance are formed into octagonal-ended or three-sectioned bow front projections with a wooden, two-level porch arcade screening the central space. It has a central hall plan with an octagonal room on the south, a rectangular room behind and a larger single room across the hall. In 1816, William Wirt (1772–1834) purchased the house and lived there until 1818, when he moved to Washington as Attorney General of the United States under James Monroe. Diagonally across Main St, a mansion known as Moldavia was then acquired by the Randolphs, who, like Wirt, were among the oldest and most prestigious planter-aristocrat families of Virginia and were some of the founders of the United States. The Randolphs, however, had to sell one of their mansions in Richmond and sold Moldavia to a Spanish merchant named Joseph Gallego, who in turn sold it in 1825 to John Allan, a merchant of Scots origin who was the foster father of the author Edgar Allan Poe. It was in this house that Poe spent about a year before going away to the University of Virginia in 1826 at the age of 17. The sale of this house to merchants scandalized the planter-aristocracy, who expressed in letters written at the time their disdain for the fact that mere merchants were taking over their property and their world. Later serving as the headquarters of the Richmond Chapter of the American Red Cross, the house is now a private residence. The last business to occupy this house was the law firm of Bowles and Bowles. The house bears a strong resemblance to Point of Honor in Lynchburg, Virginia.

Scott House, also known as Frederic W. Scott House and Scott-Bocock House, is a historic home located in Richmond, Virginia and is owned by Virginia Commonwealth University as the University's alumni house. The first floor of the historic house is available for university, community and corporate events. Many affairs — including university and alumni receptions and retreats — have occurred at the Scott House since its doors opened in the fall of 2004.

The Laburnum Park Historic District is a national historic district located at Richmond, Virginia. The district encompasses 226 contributing buildings and 2 contributing structures located north of downtown Richmond. The primarily residential area developed starting in the early-20th century as one of the city's early "streetcar suburbs" and as home to several important local institutions. The buildings are in a variety of popular early-20th century architectural styles including Queen Anne and Colonial Revival. It was developed as neighborhood of middle-to-upper-class, single-family dwellings. Notable buildings include the Laburnum House (1908), Richmond Memorial Hospital (1954–1957), Richmond Memorial Hospital Nursing School (1960–1961), "The Hermitage" (1911), Laburnum Court (1919), Veritas School.

The Brookland Park Historic District is a national historic district located at Richmond, Virginia. The district encompasses 1,157 contributing buildings located north of downtown Richmond and Barton Heights.

The Scott's Addition Historic District is a national historic district located in Richmond, Virginia.

Grace Evelyn Arents was an heiress, Christian activist and philanthropist in Richmond, Virginia. She inherited $1.2 million from her uncle Lewis Ginter, a tobacco magnate, and she continued his philanthropic efforts in the Richmond area.

Sherwood Park is one of several historical neighborhoods that comprise the area known as Northside in the city of Richmond, Virginia.





















