Related Research Articles
Transport in Bolivia is mostly by road. The railways were historically important in Bolivia, but now play a relatively small part in the country's transport system. Because of the country's geography, aviation is also important.

The Armed Forces of Bolivia are the military of Bolivia. The Armed Forces of Bolivia are responsible for the defence, both of external and internal, of Bolivia and they are constituted by Bolivian Army, the Bolivian Air Force and the Bolivian Navy. All these institutions depend on the Ministry of Defence of this country.

The Bolivian gas conflict was a social confrontation in Bolivia reaching its peak in 2003, centering on the exploitation of the country's vast natural gas reserves. The expression can be extended to refer to the general conflict in Bolivia over the exploitation of gas resources, thus including the 2005 protests and the election of Evo Morales as president. Before these protests, Bolivia had seen a series of similar earlier protests during the Cochabamba protests of 2000, which were against the privatization of the municipal water supply.

Bolivia hosted the Copa América for the second time in its 38th edition. It was held from 11 to 29 June. It was organized by CONMEBOL, South America's football governing body.

Municipalities in Bolivia are administrative divisions of the entire national territory governed by local elections. Municipalities are the third level of administrative divisions, below departments and provinces. Some of the provinces consist of only one municipality. In these cases the municipalities are identical to the provinces they belong to.
The third tier of the Bolivian football league system consists of nine regional leagues ; the number of participants varies depending

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bolivia:
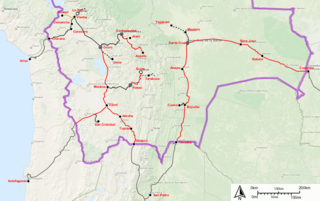
The Bolivian rail network has had a peculiar development throughout its history; owing to losses of land, prestige and credit rating due to the failure of the War of the Pacific, railway development came late to Bolivia. The demand for mineral wealth and communication to the inland city of La Paz, encouraged foreign investors, mainly British, to construct railways. However, into this mix came the experience of railway building in adjacent Peru, whereby overbuilding of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge line across the high Andes meant that Peru went bankrupt.

Xavier Moyano is an Argentine musician; producer, performer, composer, and educator. He began his career as a session guitarist in Tucuman in 1999. By 2003 was the guitarist for rock/pop band "AVe Cesar" until 2008, after that he became a solo rock instrumentalist. Between 2009 and 2011 he was guitarist and composer of metal band "Seliger" (Argentina/Brasil), between 2014 and 2019 he was guitarist and producer of "Cossas Novas", since 2018 he is guitarist and co-producer of "Rock Bro's" (ClassicRock). He is currently a solo guitarist, session musician and producer.

Bolivians are people identified with the country of Bolivia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Bolivians, several of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Bolivian.
The history of the Jews in Bolivia stretches from the colonial period of Bolivia in the 16th century to the end of the 19th century. In the 19th century, Jewish merchants came to Bolivia, most of them taking local women as wives and founding families that merged into the mainstream Catholic society. This was often the case in the eastern regions of Santa Cruz, Tarija, Beni and Pando, where these merchants came either from Brazil or Argentina.
The South American Youth Championship 1995 was held in Cochabamba, La Paz and Santa Cruz, Bolivia. It also served as qualification for the 1995 FIFA World Youth Championship.
The Battle of Montenegro, also called the Battle of Cuyambuyo, was fought on 24 June 1838 during the war between Argentina and the Peru–Bolivian Confederation.
Pukara means a ruin of the fortifications made by the natives of the central Andean cultures.

The history of rail transport in Bolivia began in the 1870s after almost three decades of failed efforts to build railroads to integrate the country, mining was the driving force for the construction of railways. The need to transport saltpeter to the coast triggered the first railway lines in Bolivia. It was the silver mining, however, that drove the construction of a railway from the Pacific coast to the high plateau during the nineteenth century. Later, at the beginning of the twentieth century, tin mining gave a new impetus to railway building, forming what is now known as the Andean or Western network. The eastern network, on the other hand, developed between the years 1940 and 1960 and is financed in exchange for oil through agreements with Argentina and Brazil. Bolivia being a landlocked country, the railways played a fundamental role and the history of its railroads is the history of the country's efforts to reach first ports on the Pacific coast and then the Atlantic.
The War between Argentina and Peru–Bolivian Confederation was an armed conflict that occurred between 1837 and 1839. Because it happened simultaneously when the Peru–Bolivian confederation was engaged in a parallel war against the Republic of Chile, in the so-called War of the Confederation, the first conflict referred here is often confused with the second. The war began on May 19, 1837, when the then in charge of managing foreign relations for the Argentine Confederation and governor of the Province of Buenos Aires, Juan Manuel de Rosas, declared war directly on President Andres de Santa Cruz, both for the Question of Tarija and its support for the Unitarian Party.
References
- 1 2 3 Welcome to Bolivia Altiplanic Rugby pt1 retrieved 8 July 2009