Related Research Articles

Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like Escherichia coli as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. S. cerevisiae cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding.
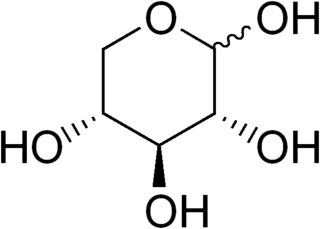
D-Xylose is a five-carbon aldose that can be catabolized or metabolized into useful products by a variety of organisms.
In enzymology, a methylglyoxal reductase (NADPH-dependent) (EC 1.1.1.283) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
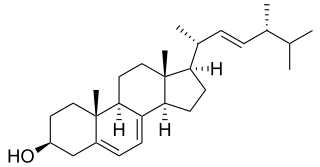
In enzymology, a sterol 14-demethylase (EC 1.14.13.70) is an enzyme of the Cytochrome P450 (CYP) superfamily. It is any member of the CYP51 family. It catalyzes a chemical reaction such as:

The enzyme holocytochrome-c synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.
In enzymology, a 2'-phosphotransferase (EC 2.7.1.160) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an initiation-specific alpha-1,6-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in which an alpha-D-mannosyl residue is transferred from GDP-mannose to a lipid-linked oligosaccharide, being linked by an alpha-1,6-D-mannosyl-D-mannose bond.
Diacetyl reductase ((R)-acetoin forming) (EC 1.1.1.303, (R)-acetoin dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (R)-acetoin:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Sphinganine C4-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.169, sphingolipid C4-hydroxylase, SUR2 (gene), SBH1 (gene), SBH2 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name sphinganine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (C4-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ditrans,polycis-polyprenyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (2E,6E)-farnesyl-diphosphate:isopentenyl-diphosphate cistransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aminopeptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Aminopeptidase Y is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Carboxypeptidase D can refer to one of several enzymes. A family of serine carboxypeptidases includes is an enzyme. This enzyme has an optimal pH of 4.5-6.0, is inhibited by diisopropyl fluorophosphate, and catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cerevisin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ulp1 peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Saccharopepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Barrierpepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Proteasome endopeptidase complex is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ERG5 or Sterol 22-desaturase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway of fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with the CYP Symbol CYP61A1. CYP61A1 is one of only three P450 enzyme found in baker's yeast, the other two are CYP51F1 and CYP56A1. The ortholog in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, was named CYP61A3 for historical reasons, and is only one of two P450 enzyme found with CYP51F1. ERG5 catalyzes the C22-C23 double bond formation on the sterol side chain of ergostatrienol to convert it into ergostatetraenol, then the C24 double bond of ergostatetrenol will be hydrogenation reduced into ergosterol by ERG4.
References
- ↑ Achstetter T, Ehmann C, Wolf DH (April 1985). "Proteinase yscD. Purification and characterization of a new yeast peptidase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (8): 4585–90. PMID 3886641.
- ↑ García-Alvarez N, Teichert U, Wolf DH (March 1987). "Proteinase yscD mutants of yeast. Isolation and characterization". European Journal of Biochemistry. 163 (2): 339–46. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10805.x. PMID 3545833.