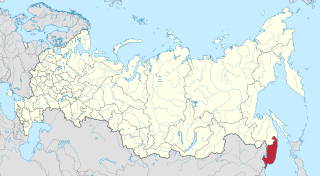
Primorsky Krai, informally known as Primorye, is a federal subject of Russia, part of the Far Eastern Federal District in the Russian Far East. The city of Vladivostok on the southern coast of the krai is its administrative center, and the second largest city in the Russian Far East, behind Khabarovsk in the neighbouring Khabarovsk Krai. Primorsky Krai has the largest economy among the federal subjects in the Russian Far East, and a population of 1,845,165 as of the 2021 Census.

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.

The Salicaceae are the willow family of flowering plants. The traditional family included the willows, poplars. Genetic studies summarized by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) have greatly expanded the circumscription of the family to contain 56 genera and about 1220 species, including the tropical Scyphostegiaceae and many of the former Flacourtiaceae.

Salix × fragilis, with the common names crack willow and brittle willow, is a hybrid species of willow native to Europe and Western Asia. It is native to riparian habitats, usually found growing beside rivers and streams, and in marshes and water meadow channels. It is a hybrid between Salix euxina and Salix alba, and is very variable, with forms linking both parents.

Salix babylonica is a species of willow native to dry areas of northern China, but cultivated for millennia elsewhere in Asia, being traded along the Silk Road to southwest Asia and Europe.

Salix arctica, the Arctic willow, is a tiny creeping willow. It is adapted to survive in Arctic conditions, specifically tundras.

Lycopus is a genus of herbaceous plants in the family Lamiaceae. The many species are known as water horehound, gypsywort, and bugleweed and are native to Europe, Asia, Australia, and North America. The species are most often found in wetlands, damp meadows, and stream banks. Some of the wetland species have become endangered.

Salix integra is a species of willow native to north-eastern China, Japan, Korea and the far south-eastern Russia.

Salix triandra, with the common names almond willow, almond-leaved willow or black maul willow, is a species of willow native to Europe and Western and Central Asia. It is found from south-eastern England east to Lake Baikal, and south to Spain and the Mediterranean east to the Caucasus, and the Alborz Mountains. It usually grows in riparian habitats, on river and stream banks, and in wetlands.

Lilium pensylvanicum is an Asian plant species of the family Liliaceae. Sometimes called the Siberian lily, it is native to a cold climate and needs frost in the winter. It is found in the wild form in Siberia, the Russian Far East, Mongolia, northeast China, Korea and Hokkaidō.

The Amur leopard is a leopard subspecies native to the Primorye region of southeastern Russia and northern China. It is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, as in 2007, only 19–26 wild leopards were estimated to survive in southeastern Russia and northeastern China.

Iris lactea is a species in the genus Iris. It is also in the subgenus Limniris and is the only species in the series Ensatae. The Japanese water iris, Iris ensata, is actually in series Laevigatae. It is a rhizomatous perennial, from central Asia, with pale blue or violet flowers. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions.

Gagea hiensis is a species of flowering plant in the lily family. It is native to Korea, Mongolia, China, and Far Eastern Russia.

Achillea alpina, commonly known as alpine yarrow, Chinese yarrow or Siberian yarrow, is an Asian and North American species of plant in the sunflower family. It is native to Siberia, the Russian Far East, China, Mongolia, Korea, Japan, Nepal, Canada, the northern United States.

Salix denticulata is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Salicaceae. It is a mountain species endemic to the Himalayan region.

Salix pierotii, the Korean willow, is a species of willow native to northeast China, far eastern Russia, the Korean peninsula and Japan. They are shrubs or trees reaching 8 m. Because their twisted wood is not good for timber or making tools, in Japan Salix pierotii trees are used to demarcate property lines between farms.
Salix caspica is a plant from the willow genus (Salix) within the willow family (Salicaceae). The natural range extends from eastern European Russia to far western China.

Aquilegia viridiflora, commonly known as the green columbine or green-flowered columbine, is a perennial flowering plant in the family Ranunculaceae, native to southern Siberia, northern China, Mongolia, and Japan.
The Yama is a river in Magadan Oblast, Russian Far East. It is 285 kilometres (177 mi) long, with a drainage basin of 12,500 square kilometres (4,800 sq mi).

Aquilegia parviflora is a species of flowering plant of the Aquilegia (columbine) genus in the family Ranunculaceae native to the Asian regions of Siberia, northern Mongolia, northern China, and Sakhalin. Its comparatively small blue-purple flowers give the plant its name and make it less popular with gardeners than other columbines.



















