Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the costamere or the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC). Many muscle proteins, such as α-dystrobrevin, syncoilin, synemin, sarcoglycan, dystroglycan, and sarcospan, colocalize with dystrophin at the costamere. It has a molecular weight of 427 kDa

Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UTRN gene. The name is a short form for ubiquitous dystrophin.
Dystrobrevin is a protein that binds to dystrophin in the costamere of skeletal muscle cells. In humans, there are at least two isoforms of dystrobrevin, dystrobrevin alpha and dystrobrevin beta.
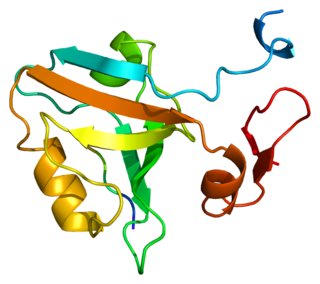
PSD-95 also known as SAP-90 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLG4 gene.

Disks large homolog 2 (DLG2) also known as channel-associated protein of synapse-110 (chapsyn-110) or postsynaptic density protein 93 (PSD-93) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLG2 gene.

Syntenin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDCBP gene.

The alpha-1B adrenergic receptor (α1B-adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRA1B, is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. The crystal structure of the α1B-adrenergic receptor has been determined in complex with the inverse agonist (+)-cyclazosin.

Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN1 gene.

Alpha-actinin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN4 gene.

GIPC PDZ domain containing family, member 1 (GIPC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GIPC1 gene. GIPC was originally identified as it binds specifically to the C terminus of RGS-GAIP, a protein involved in the regulation of G protein signaling. GIPC is an acronym for "GAIP Interacting Protein C-terminus". RGS proteins are "Regulators of G protein Signaling" and RGS-GAIP is a "GTPase Activator protein for Gαi/Gαq", which are two major subtypes of Gα proteins. The human GIPC1 molecule is 333 amino acids or about 36 kDa in molecular size and consists of a central PDZ domain, a compact protein module which mediates specific protein-protein interactions. The RGS-GAIP protein interacts with this domain and many other proteins interact here or at other parts of the GIPC1 molecule. As a result, GIPC1 was independently discovered by several other groups and has a variety of alternate names, including synectin, C19orf3, RGS19IP1 and others. The GIPC1 gene family in mammals consisting of three members, so the first discovered, originally named GIPC, is now generally called GIPC1, with the other two being named GIPC2 and GIPC3. The three human proteins are about 60% identical in protein sequence. GIPC1 has been shown to interact with a variety of other receptor and cytoskeletal proteins including the GLUT1 receptor, ACTN1, KIF1B, MYO6, PLEKHG5, SDC4/syndecan-4, SEMA4C/semaphorin-4 and HTLV-I Tax. The general function of GIPC family proteins therefore appears to be mediating specific interactions between proteins involved in G protein signaling and membrane translocation.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 4, also known as KCNJ4 or Kir2.3, is a human gene.

Beta-2-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTB2 gene.

Beta-1-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTB1 gene.

Microtubule-associated serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAST2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene controls TRAF6 and NF-kappaB activity.

Lin-7 homolog B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LIN7B gene.

Cysteine-rich PDZ-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRIPT gene.

Gamma-1-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTG1 gene.

Dystrobrevin alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DTNA gene.

Dystrobrevin beta is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DTNB gene.
Stanley C. Froehner is an American physiologist and biophysicist currently the UW Medicine Distinguished Professor at University of Washington and an Elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.