Dienes, trienes, and related ligands
Butadiene, cyclooctadiene, and norbornadiene are well-studied chelating agents. Trienes and even some tetraenes can bind to metals through several adjacent carbon centers. Common examples of such ligands are cycloheptatriene and cyclooctatetraene. The bonding is often denoted using the hapticity formalism. Keto-alkenes are tetrahapto ligands that stabilize highly unsaturated low valent metals as found in (benzylideneacetone)iron tricarbonyl and tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0).
- Metal alkene complexes.
- Bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0), a catalyst and source of "naked nickel."
- The first alkene complex, the anion in Zeise's salt.
- Chlorobis(cyclooctene)rhodium dimer, source of "RhCl".
- Crabtree's catalyst, a very active catalyst for hydrogenation.
- (Benzylideneacetone)iron tricarbonyl, source of "Fe(CO)3".
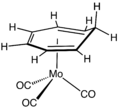
- Mo(C7H8)(CO)3, a complex of cycloheptatriene.
- Fe(C8H8)2, a complex of cyclooctatetraene
- (Norbornadiene)molybdenum tetracarbonyl, a source of "Mo(CO)4"
- (Xylylene)Fe(CO)3, illustrating the stabilization of a labile alkene by complexation