In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. As a type of active management, it stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of technical analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. It is distinguished from fundamental analysis, which considers a company's financial statements, health, and the overall state of the market and economy.
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength.
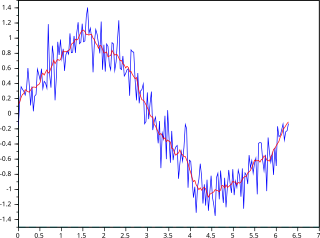
In statistics, a moving average is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different selections of the full data set. Variations include: simple, cumulative, or weighted forms.
In stock and securities market technical analysis, parabolic SAR is a method devised by J. Welles Wilder Jr., to find potential reversals in the market price direction of traded goods such as securities or currency exchanges such as forex. It is a trend-following (lagging) indicator and may be used to set a trailing stop loss or determine entry or exit points based on prices tending to stay within a parabolic curve during a strong trend.
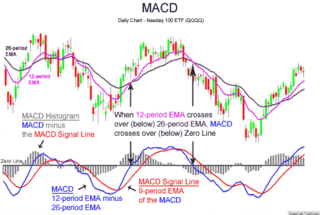
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.

Bollinger Bands are a type of statistical chart characterizing the prices and volatility over time of a financial instrument or commodity, using a formulaic method propounded by John Bollinger in the 1980s. Financial traders employ these charts as a methodical tool to inform trading decisions, control automated trading systems, or as a component of technical analysis. Bollinger Bands display a graphical band and volatility in one two-dimensional chart.
Exponential smoothing or exponential moving average (EMA) is a rule of thumb technique for smoothing time series data using the exponential window function. Whereas in the simple moving average the past observations are weighted equally, exponential functions are used to assign exponentially decreasing weights over time. It is an easily learned and easily applied procedure for making some determination based on prior assumptions by the user, such as seasonality. Exponential smoothing is often used for analysis of time-series data.

Trix is a technical analysis oscillator developed in the 1980s by Jack Hutson, editor of Technical Analysis of Stocks and Commodities magazine. It shows the slope of a triple-smoothed exponential moving average. The name Trix is from "triple exponential."
The commodity channel index (CCI) is an oscillator indicator that is used by traders and investors to help identify price reversals, price extremes and trend strength when using technical analysis to analyse financial markets.
Average true range (ATR) is a technical analysis volatility indicator originally developed by J. Welles Wilder, Jr. for commodities. The indicator does not provide an indication of price trend, simply the degree of price volatility. The average true range is an N-period smoothed moving average (SMMA) of the true range values. Wilder recommended a 14-period smoothing.

Keltner channel is a technical analysis indicator showing a central moving average line plus channel lines at a distance above and below. The indicator is named after Chester W. Keltner (1909–1998) who described it in his 1960 book How To Make Money in Commodities. This name was applied by those who heard about it from him, but Keltner called it the ten-day moving average trading rule and indeed made no claim to any originality for the idea.

The detrended price oscillator (DPO) is an indicator in technical analysis that attempts to eliminate the long-term trends in prices by using a displaced moving average so it does not react to the most current price action. This allows the indicator to show intermediate overbought and oversold levels effectively.
The mass index is an indicator, developed by Donald Dorsey, used in technical analysis to predict trend reversals. It is based on the notion that there is a tendency for reversal when the price range widens, and therefore compares previous trading ranges.
Stock market prediction is the act of trying to determine the future value of a company stock or other financial instrument traded on an exchange. The successful prediction of a stock's future price could yield significant profit. The efficient market hypothesis suggests that stock prices reflect all currently available information and any price changes that are not based on newly revealed information thus are inherently unpredictable. Others disagree and those with this viewpoint possess myriad methods and technologies which purportedly allow them to gain future price information.
In technical analysis of securities trading, the stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that uses support and resistance levels. George Lane developed this indicator in the late 1950s. The term stochastic refers to the point of a current price in relation to its price range over a period of time. This method attempts to predict price turning points by comparing the closing price of a security to its price range.
The average directional movement index (ADX) was developed in 1978 by J. Welles Wilder as an indicator of trend strength in a series of prices of a financial instrument. ADX has become a widely used indicator for technical analysts, and is provided as a standard in collections of indicators offered by various trading platforms.
The Vortex Indicator is a technical indicator invented by Etienne Botes and Douglas Siepman to identify the start of a new trend or the continuation of an existing trend within financial markets. It was published in the January 2010 edition of Technical Analysis of Stocks & Commodities.
The true strength index (TSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets that attempts to show both trend direction and overbought/oversold conditions. It was first published William Blau in 1991. The indicator uses moving averages of the underlying momentum of a financial instrument. Momentum is considered a leading indicator of price movements, and a moving average characteristically lags behind price. The TSI combines these characteristics to create an indication of price and direction more in sync with market turns than either momentum or moving average. The TSI is provided as part of the standard collection of indicators offered by various trading platforms.
The Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA) indicator was introduced in January 1994 by Patrick G. Mulloy, in an article in the "Technical Analysis of Stocks & Commodities" magazine: "Smoothing Data with Faster Moving Averages"
The zero lag exponential moving average (ZLEMA) is a technical indicator within technical analysis that aims is to eliminate the inherent lag associated to all trend following indicators which average a price over time. As is the case with the double exponential moving average (DEMA) and the triple exponential moving average (TEMA) this indicator aims to reduce the lag.






