Related Research Articles
Passive management is an investing strategy that tracks a market-weighted index or portfolio. Passive management is most common on the equity market, where index funds track a stock market index, but it is becoming more common in other investment types, including bonds, commodities and hedge funds.
A market trend is a perceived tendency of the financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as secular for long time-frames, primary for medium time-frames, and secondary for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time.
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. As a type of active management, it stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of technical analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. It is distinguished from fundamental analysis, which considers a company's financial statements, health, and the overall state of the market and economy.

Charles Henry Dow was an American journalist who co-founded Dow Jones & Company with Edward Jones and Charles Bergstresser.
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength.
Contrarian investing is an investment strategy that is characterized by purchasing and selling in contrast to the prevailing sentiment of the time.
In stock and securities market technical analysis, parabolic SAR is a method devised by J. Welles Wilder Jr., to find potential reversals in the market price direction of traded goods such as securities or currency exchanges such as forex. It is a trend-following (lagging) indicator and may be used to set a trailing stop loss or determine entry or exit points based on prices tending to stay within a parabolic curve during a strong trend.
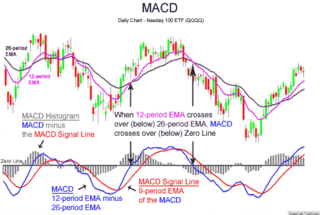
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.
Market timing is the strategy of making buying or selling decisions of financial assets by attempting to predict future market price movements. The prediction may be based on an outlook of market or economic conditions resulting from technical or fundamental analysis. This is an investment strategy based on the outlook for an aggregate market rather than for a particular financial asset.
In finance, an investment strategy is a set of rules, behaviors or procedures, designed to guide an investor's selection of an investment portfolio. Individuals have different profit objectives, and their individual skills make different tactics and strategies appropriate. Some choices involve a tradeoff between risk and return. Most investors fall somewhere in between, accepting some risk for the expectation of higher returns.
The Dogs of the Dow is an investment strategy popularized by Michael B. O'Higgins in a 1991 book and his Dogs of the Dow website.

Market sentiment, also known as investor attention, is the general prevailing attitude of investors as to anticipated price development in a market. This attitude is the accumulation of a variety of fundamental and technical factors, including price history, economic reports, seasonal factors, and national and world events. If investors expect upward price movement in the stock market, the sentiment is said to be bullish. On the contrary, if the market sentiment is bearish, most investors expect downward price movement. Market participants who maintain a static sentiment, regardless of market conditions, are described as permabulls and permabears respectively. Market sentiment is usually considered as a contrarian indicator: what most people expect is a good thing to bet against. Market sentiment is used because it is believed to be a good predictor of market moves, especially when it is more extreme. Very bearish sentiment is usually followed by the market going up more than normal, and vice versa. A bull market refers to a sustained period of either realized or expected price rises, whereas a bear market is used to describe when an index or stock has fallen 20% or more from a recent high for a sustained length of time.
Momentum investing is a system of buying stocks or other securities that have had high returns over the past three to twelve months, and selling those that have had poor returns over the same period.
The Negative Volume Index and Positive Volume Index are indicators to identify primary market trends and reversals when using technical analysis to study financial markets.
In finance, a calendar spread is a spread trade involving the simultaneous purchase of futures or options expiring on a particular date and the sale of the same instrument expiring on another date. These individual purchases, known as the legs of the spread, vary only in expiration date; they are based on the same underlying market and strike price.
Option strategies are the simultaneous, and often mixed, buying or selling of one or more options that differ in one or more of the options' variables. Call options, simply known as Calls, give the buyer a right to buy a particular stock at that option's strike price. Opposite to that are Put options, simply known as Puts, which give the buyer the right to sell a particular stock at the option's strike price. This is often done to gain exposure to a specific type of opportunity or risk while eliminating other risks as part of a trading strategy. A very straightforward strategy might simply be the buying or selling of a single option; however, option strategies often refer to a combination of simultaneous buying and or selling of options.
Bull–bear line is the index average line that indicates bull market or bear market in stock market.

William Peter Hamilton, a proponent of Dow Theory, was the fourth editor of the Wall Street Journal, serving in that capacity for more than 20 years.

Chaikin Analytics is a platform for stock trading ideas. Chaikin Analytics was established in September 2009 by Marc Chaikin. The centerpiece of Chaikin Analytics is the Chaikin Power Gauge stock rating. In 2016, it was named one of "Two Top Websites for Quantitative Analysis" by Barron's.

Volume Analysis is an example of a type of technical analysis that examines the volume of traded securities to confirm and predict price trends. Volume is a measure of the number of shares of an asset that are traded in a given period of time. As one of the oldest market indicators used for analysis, sudden changes in volume are often the result of news-related events. Commonly used by chartists and technical analysts, volume analysis is centered on the following ideas:
References
- ↑ ""More Proof For the Dow Theory", The New York Times, 9/6/98". Archived from the original on 2010-11-24. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Hulbert, Mark (6 September 1998). "VIEWPOINT; More Proof for the Dow Theory". The New York Times.
- 1 2 "The Dow Theory: William Peter Hamilton's Record Reconsidered". Archived from the original on 2010-10-27. Retrieved 2007-12-07.