
Tycho Brahe, generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope. Tycho Brahe has also been described as the greatest pre-telescopic astronomer.

1601 (MDCI) was a common year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 1601st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 601st year of the 2nd millennium, the 1st year of the 17th century, and the 2nd year of the 1600s decade. As of the start of 1601, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

Friday the 13th is considered an unlucky day in Western superstition. It occurs when the 13th day of the month in the Gregorian calendar falls on a Friday, which happens at least once every year but can occur up to three times in the same year. For example, 2015 had a Friday the 13th in February, March, and November, which will happen again in 2026. Leap years that begin on Sunday such as 2012 and 2040, also have three Friday the 13ths in January, April, and July. 2017 through 2020 had two Friday the 13ths, as did 2023; 2016, 2021, and 2022 had just one Friday the 13th, as will 2025, 2027, and 2028; 2024 will have two Friday the 13ths.
13 (thirteen) is the natural number following 12 and preceding 14.

The Swedish calendar or Swedish style was a calendar in use in Sweden and its possessions from 1 March 1700 until 30 February 1712. It was one day ahead of the Julian calendar and ten days behind the Gregorian calendar. Easter was calculated astronomically, with a minor exception, from 1740 to 1844.

Uraniborg was an astronomical observatory and alchemy laboratory established and operated by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe. It was the first custom-built observatory in modern Europe, and the last to be built without a telescope as its primary instrument.

Scanian is an East Scandinavian dialect spoken in the province of Scania in southern Sweden.

Scandinavism, also called Scandinavianism or pan-Scandinavianism, is an ideology that supports various degrees of cooperation among the Scandinavian countries. Scandinavism comprises the literary, linguistic and cultural movement that focuses on promoting a shared Scandinavian past, a shared cultural heritage, a common Scandinavian mythology and a common language or dialect continuum and which led to the formation of joint periodicals and societies in support of Scandinavian literature and languages. The movement was most popular among Danes and Swedes.

The Count's Feud, sometimes referred to as the Count's War, was a Danish war of succession occurring from 1534 to 1536, which gave rise to the Reformation in Denmark. In the broader international context, it was a part of the European wars of religion. The Count's Feud derives its name from the Protestant Count, Christopher of Oldenburg, who championed the claim to the throne of the deposed Catholic King, Christian II, rejecting Christian III's election. Christian III was a devoted Protestant who had already established Lutheranism as the state religion in Schleswig and Holstein by 1528.

Molslinjen is a Danish company that operates ferry services between Jutland and Zealand, and also services to Bornholm. In March 2017, the routes in the Kattegat were renamed to Molslinjen.

SophiaThott Lange, known by her maiden name, was a Danish noblewoman and horticulturalist with knowledge of astronomy, chemistry, and medicine. She worked alongside her brother Tycho Brahe in making astronomical observations.

Otte Brahe was a Danish (Scanian) nobleman and statesman, who served on the privy council. He was married to Beate Clausdatter Bille and was the father of astronomers Tycho and Sophia Brahe.

Babylonian astrology was the first known organized system of astrology, arising in the second millennium BC.
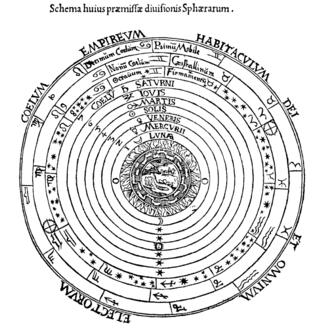
In astrology, certain stars are considered significant. Historically, all of the various heavenly bodies considered by astrologers were considered "stars", whether they were stars, planets, other stellar phenomena like novas and supernovas, or other solar system phenomena like comets and meteors.

Cosmonova is an IMAX Dome cinema and planetarium located in an annex of the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm, Sweden. Cosmonova premiered over three nights starting on 13 October 1992, with the first public showing on 16 October. It was the first ever dedicated IMAX installation in Sweden and is also the largest planetarium in Sweden.

Copenhagen Suborbitals is a crowd-funded human space program. It has flown six home-built rockets and capsules since 2011. The organization successfully launched its Nexø II rocket in the summer of 2018. Its stated goal is to have one of its members reach space on a sub-orbital spaceflight. The organization was founded by Kristian von Bengtson and Peter Madsen.
Auspicious wedding dates refer to auspicious, or lucky, times to get married, and is a common belief among many cultures.

Cyprianus is a name given in Scandinavian traditions of folk magic to the "black book" ("Svarteboken"): a grimoire or manuscript collection of spells; and by extension to the magical tradition that these spells form a part of. There is no standard text called "Cyprianus"; it was a general label given to a collection of spells.
The Bārûtu, the “art of the diviner,” is a monumental ancient Mesopotamian compendium of the science of extispicy or sacrificial omens stretching over around a hundred cuneiform tablets which was assembled in the Neo-Assyrian/Babylonian period based upon earlier recensions. At the Assyrian court, the term extended to encompass sacrificial prayers and rituals, commentaries and organ models. The ikribu was the name of collections of incantations to accompany the extispicy. The bārûtu's extant predecessors date back to Old Babylonian times with the liver models from Mari and where the order of the exta were largely fixed.
"Elveskud" or "Elverskud" is the Danish, and most widely used, name for one of the most popular ballads in Scandinavia.
















