
A semantic network, or frame network is a knowledge base that represents semantic relations between concepts in a network. This is often used as a form of knowledge representation. It is a directed or undirected graph consisting of vertices, which represent concepts, and edges, which represent semantic relations between concepts, mapping or connecting semantic fields. A semantic network may be instantiated as, for example, a graph database or a concept map. Typical standardized semantic networks are expressed as semantic triples.
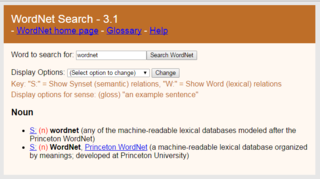
WordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words in more than 200 languages. WordNet links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into synsets with short definitions and usage examples. WordNet can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. While it is accessible to human users via a web browser, its primary use is in automatic text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. WordNet was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD style license and are freely available for download from that WordNet website.
EuroWordNet is a system of semantic networks for European languages, based on WordNet. Each language develops its own wordnet but they are interconnected with interlingual links stored in the Interlingual Index (ILI).
Polysemy is the capacity for a sign to have multiple related meanings. For example, a word can have several word senses.
Lexical semantics, as a subfield of linguistic semantics, is the study of word meanings. It includes the study of how words structure their meaning, how they act in grammar and compositionality, and the relationships between the distinct senses and uses of a word.
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science and uses Ferdinand de Saussure's notion of the sign. It uses a uniform formalism and is organized in a modular way which makes it attractive for natural language processing.
FrameNet is a research and resource development project based at the International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) in Berkeley, California, which has produced an electronic resource based on a theory of meaning called frame semantics. The data that FrameNet has analyzed show that the sentence "John sold a car to Mary" essentially describes the same basic situation as "Mary bought a car from John", just from a different perspective. A semantic frame is a conceptual structure describing an event, relation, or object along with its participants. The FrameNet lexical database contains over 1,200 semantic frames, 13,000 lexical units and 202,000 example sentences. Charles J. Fillmore, who developed the theory of frame semantics which serves as the theoretical the basis of FrameNet, founded the project in 1997 and continued to lead the effort until he died in 2014. Frame Semantic theory and FrameNet have been influential in linguistics and natural language processing, where it led to the task of automatic Semantic Role Labeling.

A semantic lexicon is a digital dictionary of words labeled with semantic classes so associations can be drawn between words that have not previously been encountered. Semantic lexicons are built upon semantic networks, which represent the semantic relations between words. The difference between a semantic lexicon and a semantic network is that a semantic lexicon has definitions for each word, or a "gloss".
The sequence between semantic related ordered words is classified as a lexical chain. A lexical chain is a sequence of related words in writing, spanning short or long distances. A chain is independent of the grammatical structure of the text and in effect it is a list of words that captures a portion of the cohesive structure of the text. A lexical chain can provide a context for the resolution of an ambiguous term and enable identification of the concept that the term represents.
PropBank is a corpus that is annotated with verbal propositions and their arguments—a "proposition bank". Although "PropBank" refers to a specific corpus produced by Martha Palmer et al., the term propbank is also coming to be used as a common noun referring to any corpus that has been annotated with propositions and their arguments.
Christiane D. Fellbaum is a Lecturer with Rank of Professor in the Program in Linguistics and the Computer Science Department at Princeton University. The co-developer of the WordNet project, she is also its current director.
Language resource management - Lexical markup framework, is the ISO International Organization for Standardization ISO/TC37 standard for natural language processing (NLP) and machine-readable dictionary (MRD) lexicons. The scope is standardization of principles and methods relating to language resources in the contexts of multilingual communication.
In natural language processing, semantic role labeling is the process that assigns labels to words or phrases in a sentence that indicates their semantic role in the sentence, such as that of an agent, goal, or result.
GermaNet is a semantic network for the German language. It relates nouns, verbs, and adjectives semantically by grouping lexical units that express the same concept into synsets and by defining semantic relations between these synsets. GermaNet is free for academic use, after signing a license. GermaNet has much in common with the English WordNet and can be viewed as an on-line thesaurus or a light-weight ontology. GermaNet has been developed and maintained at the University of Tübingen since 1997 within the research group for General and Computational Linguistics. It has been integrated into the EuroWordNet, a multilingual lexical-semantic database.
IndoWordNet is a linked lexical knowledge base of wordnets of 18 scheduled languages of India, viz., Assamese, Bangla, Bodo, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Meitei (Manipuri), Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.

BabelNet is a multilingual lexicalized semantic network and ontology developed at the NLP group of the Sapienza University of Rome. BabelNet was automatically created by linking Wikipedia to the most popular computational lexicon of the English language, WordNet. The integration is done using an automatic mapping and by filling in lexical gaps in resource-poor languages by using statistical machine translation. The result is an encyclopedic dictionary that provides concepts and named entities lexicalized in many languages and connected with large amounts of semantic relations. Additional lexicalizations and definitions are added by linking to free-license wordnets, OmegaWiki, the English Wiktionary, Wikidata, FrameNet, VerbNet and others. Similarly to WordNet, BabelNet groups words in different languages into sets of synonyms, called Babel synsets. For each Babel synset, BabelNet provides short definitions in many languages harvested from both WordNet and Wikipedia.
UBY-LMF is a format for standardizing lexical resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP). UBY-LMF conforms to the ISO standard for lexicons: LMF, designed within the ISO-TC37, and constitutes a so-called serialization of this abstract standard. In accordance with the LMF, all attributes and other linguistic terms introduced in UBY-LMF refer to standardized descriptions of their meaning in ISOCat.
plWordNet is a lexico-semantic database of the Polish language. It includes sets of synonymous lexical units (synsets) followed by short definitions. plWordNet serves as a thesaurus-dictionary where concepts (synsets) and individual word meanings are defined by their location in the network of mutual relations, reflecting the lexico-semantic system of the Polish language. plWordNet is also used as one of the basic resources for the construction of natural language processing tools for Polish.
UBY is a large-scale lexical-semantic resource for natural language processing (NLP) developed at the Ubiquitous Knowledge Processing Lab (UKP) in the department of Computer Science of the Technische Universität Darmstadt . UBY is based on the ISO standard Lexical Markup Framework (LMF) and combines information from several expert-constructed and collaboratively constructed resources for English and German.
Martha (Stone) Palmer is an American computer scientist. She is best known for her work on verb semantics, and for the creation of ontological resources such as PropBank and VerbNet.


