Related Research Articles
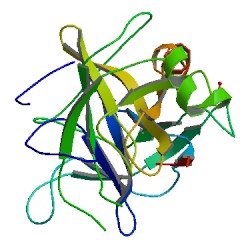
Chymotrypsin (EC 3.4.21.1, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly those containing leucine at the P1 position.
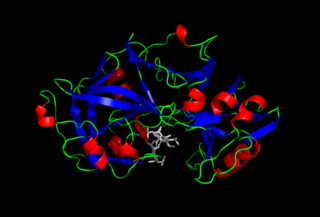
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site.
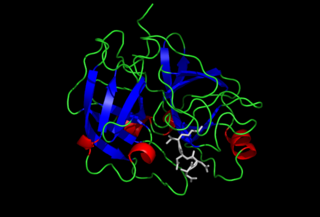
Enteropeptidase is an enzyme produced by cells of the duodenum and is involved in digestion in humans and other animals. Enteropeptidase converts trypsinogen into its active form trypsin, resulting in the subsequent activation of pancreatic digestive enzymes. Absence of enteropeptidase results in intestinal digestion impairment.
Aspergillopepsin I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as Clostridium. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of gas gangrene. They normally target the connective tissue in muscle cells and other body organs.
Microbial collagenase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N,N'-diacetylchitobiose phosphorylase is an enzyme with the systematic name N,N'-diacetylchitobiose:phosphate N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme was found in the genus Vibrio initially but has now been found to be taken up by Escherichia coli as well as many other bacteria. One study shows that Escherichia coli can replicate on a medium that is just composed of GlcNAc a product of phosphorylation of N,N'-diacetylchitobiose as the sole source of carbon. Because E. coli can go on this medium, the enzyme is present. The enzyme has also been found in multiple eukaryotic cells as well, especially in eukaryotes that make chitin and break chitin down. It is believed that N,N'-diacetylchitobiose phosphorylase is an integral part of the phosphoenolpyruvate:glucose phosphotransferase system (PTS). It is assumed that it is involved with Enzyme Complex II of the PTS and is involved with the synthesis of chitin. The enzyme is specific for N,N'-diacetylchitobiose.
Bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Peptidase Do is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Penicillopepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Endothiapepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Phytepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Yapsin 1 is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Serralysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Bacillolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Coccolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mycolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Deuterolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Snapalysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Holmquist B, Vallee BL (January 1976). "Esterase activity of zinc neutral proteases". Biochemistry. 15 (1): 101–7. doi:10.1021/bi00646a016. PMID 2276.
- ↑ Wilkes SH, Prescott JM (1976). Aeromonas neutral protease. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 45. pp. 404–15. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45036-x. PMID 1012006.
- ↑ Bayliss ME, Wilkes SH, Prescott JM (October 1980). "Aeromonas neutral protease: specificity toward extended substrates". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 204 (1): 214–9. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(80)90026-0. PMID 7000005.
- ↑ Wilkes SH, Bayliss ME, Prescott JM (February 1988). "Critical ionizing groups in Aeromonas neutral protease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (4): 1821–5. PMID 3123480.
- ↑ David VA, Deutch AH, Sloma A, Pawlyk D, Ally A, Durham DR (March 1992). "Cloning, sequencing and expression of the gene encoding the extracellular neutral protease, vibriolysin, of Vibrio proteolyticus". Gene. 112 (1): 107–12. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90310-l. PMID 1551587.