
Allopurinol, sold under the brand name Zyloprim among others, is a medication used to decrease high blood uric acid levels. It is specifically used to prevent gout, prevent specific types of kidney stones and for the high uric acid levels that can occur with chemotherapy. It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein.

Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (HHV-3), usually referred to as the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), is one of nine herpesviruses known to infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella), a disease most commonly affecting children, teens, and young adults, and shingles in adults; shingles is rare in children. VZV is a worldwide pathogen known by many names: chickenpox virus, varicella virus, and zoster virus. VZV infections are species-specific to humans, but can survive in external environments for a few hours, maybe a day or two.
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the dnaG gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers because they act as a starting point for DNA synthesis. DnaG catalyzes the synthesis of oligonucleotides that are 10 to 60 nucleotides long, however most of the oligonucleotides synthesized are 11 nucleotides. These RNA oligonucleotides serve as primers, or starting points, for DNA synthesis by bacterial DNA polymerase III. DnaG is important in bacterial DNA replication because DNA polymerase cannot initiate the synthesis of a DNA strand, but can only add nucleotides to a preexisting strand. DnaG synthesizes a single RNA primer at the origin of replication. This primer serves to prime leading strand DNA synthesis. For the other parental strand, the lagging strand, DnaG synthesizes an RNA primer every few kilobases (kb). These primers serve as substrates for the synthesis of Okazaki fragments.
ATC code J05Antivirals for systemic use is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup J05 is part of the anatomical group J Antiinfectives for systemic use.
ATC code S01Ophthalmologicals is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup S01 is part of the anatomical group S Sensory organs.

Vidarabine or 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ara-A) is an antiviral drug which is active against herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses.

Nucleoside analogues are nucleosides which contain a nucleic acid analogue and a sugar. Nucleotide analogs are nucleotides which contain a nucleic acid analogue, a sugar, and a phosphate groups with one to three phosphates.

Trifluridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug, used primarily on the eye. It was sold under the trade name Viroptic by Glaxo Wellcome, now merged into GlaxoSmithKline. The brand is now owned by Monarch Pharmaceuticals, which is wholly owned by King Pharmaceuticals.

Thymidine kinase from herpesvirus is a sub-family of thymidine kinases.

Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Other disorders caused by herpes simplex include: herpetic whitlow when it involves the fingers, herpes of the eye, herpes infection of the brain, and neonatal herpes when it affects a newborn, among others.
Neonatal herpes simplex is a rare but serious condition, usually caused by vertical transmission of herpes simplex virus from mother to newborn. Around 1 in every 3,500 babies in the United States contract the infection.
The molecular formula C10H13N5O4 may refer to:
The molecular formula C10H14N5O7P may refer to:

Neonatal meningitis is a serious medical condition in infants that is rapidly fatal if untreated. Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the central nervous system, is more common in the neonatal period than any other time in life, and is an important cause of morbidity and mortality globally. Mortality is roughly half in developing countries and ranges from 8%-12.5% in developed countries.
Tectitethya crypta is a species of demosponge belonging to the family Tethyidae. It is a massive, shallow-water sponge found in the Caribbean Sea. Oftentimes, it is covered in sand and algae.

Herpetic simplex keratitis is a form of keratitis caused by recurrent herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the cornea.
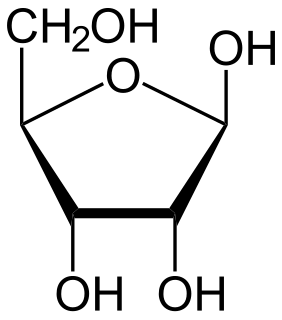
Arabinosyl nucleosides are derivatives of the nucleosides. They contain – in contrast to most nucleosides – instead of the β-D-Ribofuranose the β-D-Arabinofuranose. They are mostly used as cytostatics or virostatics.










