Borneo is the third-largest island in the world, with an area of 748,168 km2 (288,869 sq mi). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda Islands, located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra.

Kota Kinabalu, colloquially referred to as KK, is the state capital of Sabah, Malaysia. It is also the capital of the Kota Kinabalu District as well as the West Coast Division of Sabah. The city is located on the northwest coast of Borneo facing the South China Sea. The Tunku Abdul Rahman National Park lies to its west and Mount Kinabalu, which gave the city its name, is located to its east. Kota Kinabalu has a population of 452,058 according to the 2010 census; when the adjacent Penampang and Tuaran districts are included, the metro area has a combined population of 628,725. The 2020 Census revealed an increase in the municipal population to 500,421, while the wider area including the Penampang and Putatan districts had a population of 731,406.

North Borneo was a British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo,. The territory of North Borneo was originally established by concessions of the Sultanates of Brunei and Sulu in 1877 and 1878 to a German-born representative of Austria-Hungary, businessman and diplomat, Gustav Overbeck.

The North Borneo Chartered Company (NBCC), also known as the British North Borneo Company (BNBC) was a British chartered company formed on 1 November 1881 to administer and exploit the resources of North Borneo. The territory became a protectorate of the British Empire in 1888 but the company remained involved with the territory until 1946, when administration was fully assumed by the Crown colony government.

The Brunei revolt or the Brunei rebellion of 1962 was a December 1962 insurrection in the British protectorate of Brunei by opponents of its monarchy and its proposed inclusion in the Federation of Malaysia who wanted to establish a republic. The insurgents were members of the TNKU, a militia supplied by Indonesia and linked to the left-wing Brunei People's Party (BPP), which favoured a North Borneo Federation. The TNKU began co-ordinated attacks on the oil town of Seria, on police stations, and on government facilities around the protectorate. The revolt began to break down within hours, having failed to achieve key objectives such as the capture of Brunei Town and Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III. The revolt influenced the Sultan's 1963 decision not to join Malaysia. It is seen as one of the first stages of the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation.

The Interior Division is an administrative division of the state of Sabah, Malaysia. It occupies the southwest portion of Sabah, bordered by the neighbouring state of Sarawak on its west. With an area of 18,298 square kilometres, it covers 24.9% of Sabah's territory and is home to approximately 14.7% of Sabah's total population. The largest town in the Interior Division is Keningau. Other main towns in this division include Beaufort, Kuala Penyu, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom.

The Kedayan are an ethnic group residing in Brunei, Federal Territory of Labuan, southwest of Sabah, and north of Sarawak on the island of Borneo. According to the Language and Literature Bureau of Brunei, the Kedayan language is spoken by about 30,000 people in Brunei, and it has been claimed that there are a further 46,500 speakers in Sabah and 37,000 in Sarawak. In Sabah, the Kedayan mainly live in the southern districts of Sipitang and Beaufort, where they are counted as a part of the local Malay populace. Whilst in Sarawak, the Kedayans mostly reside in the towns of Lawas, Limbang and Miri.

The Battle of North Borneo took place during the Second World War between Allied and Japanese forces. Part of the wider Borneo campaign of the Pacific War, it was fought between 10 June and 15 August 1945 in North Borneo. The battle involved a series of amphibious landings by Australian forces on various points on the mainland around Brunei Bay and upon islands situated around the bay. Japanese opposition to the landings was sporadic initially, although as the campaign progressed a number of considerable clashes occurred and both sides suffered significant casualties, although major combat was largely restricted to Labuan and around Beaufort. On the mainland, while Allied conventional operations focused largely on the coastal areas around Brunei Bay, guerrilla forces consisting of Dayak tribesmen and small numbers of Allied personnel from the Services Reconnaissance Department fought an unconventional campaign in the interior. The Allies were successful in seizing control of the region. Nevertheless, many of the strategic gains that possession of North Borneo provided were ultimately negated by the sudden conclusion of the war in August 1945.
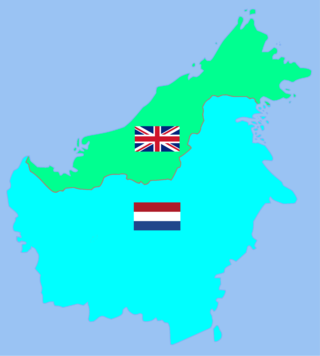
British Borneo comprised the four northern parts of the island of Borneo, which are now the country of Brunei, two Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak, and the Malaysian federal territory of Labuan. During the British colonial rule before World War II, Sarawak was known as the Raj of Sarawak (1841–1946), Sabah was known as North Borneo (1881–1946), and Labuan was known as the Crown Colony of Labuan (1848–1946). Between World War II and their independence from Britain, Sarawak became the Crown Colony of Sarawak (1946–1963) whereas Sabah and Labuan combined to form the Crown Colony of North Borneo (1946–1963). The Kingdom of Brunei (1888/1906–1984) was a protectorate of the United Kingdom since the 1888/1906 Protectorate Agreement, and was known as British Protectorate State of Brunei.

Before the outbreak of World War II in the Pacific, the island of Borneo was divided into five territories. Four of the territories were in the north and under British control – Sarawak, Brunei, Labuan, an island, and British North Borneo; while the remainder, and bulk, of the island, was under the jurisdiction of the Dutch East Indies.

The Jesselton revolt was a revolt by a resistance movement known as the Kinabalu Guerrillas, comprising local Chinese, indigenous peoples, Eurasian and Sikh Indians of Jesselton, North Borneo and led by Albert Kwok, against the Japanese occupying forces of North Borneo.

Albert Kwok, with the full name Albert Kwok Fen Nam was a leader of a resistance fighter known as the "Kinabalu Guerrillas" during the Japanese occupation of Borneo. He is regarded as the initiator of the so-called "Double Tenth Revolt" from 10 October 1943.

Arthur Joseph West was a British civil engineer. Under his leadership, the Labuan Coal Line and the North Borneo Railway from Beaufort to Weston and Melalap were built.

The Beaufort District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The population of Beaufort is composed mainly of Bisaya, Brunei Malays, Kadazan-Dusuns, Lun Bawang/Lun Dayeh, Muruts and Chinese.

The Keningau District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Keningau Town. The town comprises a majority native Dusun as well as Murut population with significant Chinese minorities.

The Kuala Penyu District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Kuala Penyu Town.

The Nabawan District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Nabawan Town.

The Sipitang District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which also includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Sipitang Town. The ecotourism village of Long Mio and Long Pasia is located in this district, while the small town of Sindumin serves as a gateway to the state of Sarawak.

The Tenom District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the Interior Division which includes the districts of Beaufort, Keningau, Kuala Penyu, Nabawan, Sipitang, Tambunan and Tenom. The capital of the district is in Tenom Town.Majority Tenom is Murut while Kadazandusun as well as Lundayeh are minorities in Tenom.

The Battle of Beaufort took place during the Second World War between Allied and Japanese forces. Part of the wider Borneo campaign of the Pacific War, it was fought between 26 and 28 June 1945 in North Borneo. The battle formed part of the Allied efforts to secure North Borneo in the final months of the war and saw two Australian infantry battalions attack the town, which was held by a force of around 800 – 1,000 Japanese. Over the course of several days heavy fighting took place before the Japanese began withdrawing on 29 June. While withdrawing, the Japanese were ambushed and suffered heavy casualties.