Related Research Articles

Hueco Tanks is an area of low mountains and historic site in El Paso County, Texas, in the United States. It is located in a high-altitude desert basin between the Franklin Mountains to the west and the Hueco Mountains to the east. Hueco is a Spanish word meaning hollows and refers to the many water-holding depressions in the boulders and rock faces throughout the region. Due to the unique concentration of historic artifacts, plants and wildlife, the site is under protection of Texas law; it is a crime to remove, alter, or destroy them.

Pictograph Cave is an area of three caves located 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Billings, Montana, United States, preserved and protected in the 23-acre (9.3 ha) Pictograph Cave State Park.

This is a list of properties and districts in Illinois that are on the National Register of Historic Places. There are over 1,800 in total. Of these, 85 are National Historic Landmarks. There are listings in all of the state's 102 counties.

This is a list of more than 1,100 properties and districts in Nebraska that are on the National Register of Historic Places. Of these, 20 are National Historic Landmarks. There are listings in 90 of the state's 93 counties.

The Abbott Farm Historic District is a National Historic Landmark archeological site in New Jersey. It is the largest known Middle Woodland village of its type on the East Coast of the United States. Significant evidence suggests that the Delaware River floodplain was occupied by Paleoindian people for a long period. It was inhabited between 500 BC and 500 AD. It has been a source of controversy and debate around early development.

Names Hill is a bluff located on the bank of the Green River in the U.S. state of Wyoming, where travelers on the Oregon and California trails carved their names into the rock. It is one of three notable "recording areas" along the emigrant trails in Wyoming along with Register Cliff and Independence Rock. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on April 16, 1969.

Cueva Lucero is a cave and archeological site in the Guayabal barrio of the Juana Díaz municipality, in Puerto Rico. The cave includes more than 100 petroglyphs and pictographs "making it one of the best examples of aboriginal rock art in the Antilles." It has been known to archeologists since at least the early 1900s. Most of its images are zoomorphic. The site is known to locals including rockclimbers and spelunkers and there is some modern graffiti.

Seminole State Park and Historic Site is located on US Route 90, east of the Pecos River High Bridge, 9 miles (14 km) west of Comstock in Val Verde County in the U.S. state of Texas. The park is conducive to camping, biking, bird watching, back packing and archeological study. Cave art and archeological artifacts date back to the earliest human habitation in the area. The park is part of the larger Seminole Canyon Archeological District on the National Register of Historic Places listings in Val Verde County, Texas.
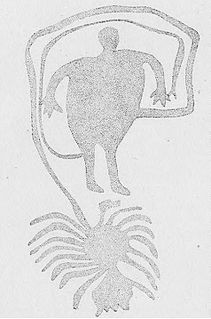
Spider Cave, also known as Burnt Bluff Cave or 20DE3, is an archaeological site located on the Garden Peninsula near Fayette, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971.
Archeological Site CA-INY-134, in Inyo County, California near Olancha, California, is an archeological site that is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). The site is located in the Coso Range 6 miles (9.7 km) northwest of Coso Hot Springs. It has also been known as Ayer's Rock Pictograph Site, as Bob Rabbit's Pictographs, as INY-134 and as INY-105. Prehistorically, it served as a camp and as a ceremonial site. The site includes three pictograph panels carved into a monolith. The pictographs are painted in a variety of colors and depict animal and human figures.
Brown Bluff is a rock art site in Washington County, Arkansas. The site consists of a prepared panel of sandstone extending some 80 metres (87 yd), on which have been painted pictographs in red. The site has been estimated to date to the Mississippian period, c. AD 1100–1600. The artwork is reminiscent of artwork found in the Arkansas River valley, and is one of the few places such artwork has been found in the western Ozark Mountains.

The Chugai' Pictograph Site is a prehistoric rock art site on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands. The rock art is located in a limestone cave on the southeastern side of the island, in the I'Chenchon Bird Sanctuary. It consists of a large panel, 185 feet (56 m) in length, of about 90 painted drawings, believed to be of late pre-contact origin. The site is accessed via a trail cut by the Japanese during the South Seas Mandate period.
The Unai Dangkulo Petroglyph Site is one of a small number of documented rock art sites in the Mariana Islands. Located on the northeastern shore of the island of Tinian in the Northern Marianas, it is the only such site composed exclusively of pictographs. It is also uncommon in that it is not found in a cave-like setting, which is where most of the other rock art sites in the region are found. The site is on a limestone outcrop that is sometimes covered by sand or cleared of sand by typhoons, and was discovered in 1998 after it was exposed by Typhoon Keith. It consists of about 50 figures, many of them anthropomorphic.
The Talagi Pictograph Cave is a rock art site on the island of Guam. It is located on property owned by the government of Guam within the bounds of Andersen Air Force Base on the northern part of the island near Tarague Beach. The cave contains thirteen pictographs representing human figures, and a places where limestone mortar was used that is of prehistoric origin. Based on the characteristics of the figures, it is believed that they were probably the work of a single individual. It is one of a small number known rock art sites on the island.
The Mahlac Pictograph Cave is a rock art site on the island of Guam. It is located high in the southern mountains of the island, and contains more than 40 images, rendered in paints that are white, red, brown, and black. The art was carefully analyzed in 2011, and a radiocarbon date of c. 600 CE was obtained from a paint sample. The meaning of the art is a subject of debate.
The Cooper's Bluff Site is a prehistoric panel of pictographs in Searcy County, Arkansas. Located under a sheltering overhang, it measures about 4.5 by 1.8 metres, and is accompanied by a scatter of prehistoric Native American artifacts. It is estimated to have been painted about 1500 CE.

The East Lake Abert Archeological District is an area in Lake County, Oregon, United States, that features numerous prehistoric camp sites and petroglyphs. It is located along the eastern shore of Lake Abert on land administered by the Bureau of Land Management and the Oregon Department of Transportation. The site includes stone-walled house pits and prehistoric rock art made by ancient Native Americans who occupied the site for approximately 11,000 years. Because of its unique archaeological and cultural significance, the East Lake Abert Archaeological District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.
The Edgemont Shelter, also designated by the Smithsonian trinomial 3VB6, is a prehistoric rock art site in Van Buren County, Arkansas. Located on a bluff overlooking Greers Ferry Lake, it consists of a panel extensively painted with petroglyphs. The site has been dated to about 1500.
Big Gyp Cave Pictograph site (14CM305) in Comanche County, Kansas, is an archeological site with pictographs in a cave. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.

Medicine Lodge State Archeological Site is a Wyoming state park that interprets the Medicine Lodge Creek Site, a prehistoric Native American archeological site near Hyattville, Wyoming. It is administered by the Wyoming Division of State Parks and Historic Sites. The site is at the base of a steep limestone outcropping near the point where the dry and running portions of Medicine Lodge Creek join. for a protected location with ready access to water. The site includes petroglyphs and pictographs on the rock face. Excavations starting in the 1970s have found twelve levels of habitation in 10.5 feet of stratum, ranging from historic times to 8300 years before the present. The site comprises a portion of the former Wickwire Ranch, which was purchased by the state in 1972 and became to Medicine Lodge Wildlife Habitat Management Area of 12,000 acres (4,900 ha). The archeological site was designated in 1973. The site is managed as a state park, with campgrounds and a visitor center. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on July 5, 1973.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ↑ Historic and Archeological Preservation. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Office of Environmental Policy. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ↑ "White Rock Bluff site (23TX001)".
| This article about a property in Texas County, Missouri on the National Register of Historic Places is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |