Biscayne National Park is an American national park located south of Miami, Florida in Miami-Dade County. The park preserves Biscayne Bay and its offshore barrier reefs. Ninety-five percent of the park is water, and the shore of the bay is the location of an extensive mangrove forest. The park covers 172,971 acres and includes Elliott Key, the park's largest island and northernmost of the true Florida Keys, formed from fossilized coral reef. The islands farther north in the park are transitional islands of coral and sand. The offshore portion of the park includes the northernmost region of the Florida Reef, one of the largest coral reefs in the world.

The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about 15 miles (24 km) south of Miami and extend in a gentle arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry Tortugas. The islands lie along the Florida Straits, dividing the Atlantic Ocean to the east from the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and defining one edge of Florida Bay. The southern part of Key West is 93 miles (150 km) from Cuba. The Keys are located between about 24.3 and 25.5 degrees North latitude.

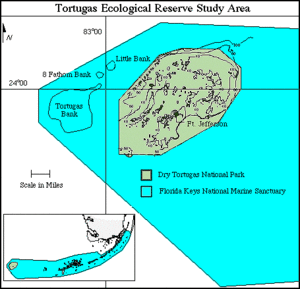
Dry Tortugas National Park is an American national park located about 68 miles (109 km) west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's coral reefs are the least disturbed of the Florida Keys reefs.

The Marquesas Keys form an uninhabited island group about 20 miles (32 km) west of Key West, four miles (6 km) in diameter, and largely covered by mangrove forest. They are an unincorporated area of Monroe County, Florida and belong to the Lower Keys Census County Division. They are protected as part of the Key West National Wildlife Refuge. The Marquesas were used for target practice by the military as recently as 1980.

Pulley Ridge is a mesophotic coral reef system off the shores of the continental United States. The reef rests on sunken barrier islands and lies 100 miles west of the Tortugas Ecological Reserve and stretches north about 60 miles at depths ranging from 60 to 80 meters. Pulley Ridge was originally discovered in 1950 during a dredging operation conducted by an academic group from Texas. While well known to fishermen, this remarkable habitat remained undiscovered by scientists until 1999 when the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and graduate students from the University of South Florida happened upon it. This reef system, like other mesophotic ecosystems, is inhabited by photosynthesizing corals and algae that are adapted to low-light environments. It is habitat for numerous species of bottom fish including Epinephelus morio spawning area.
Tortuga is the Spanish word for a turtle or tortoise. It may also refer to:
Pedro Bank is a large bank of sand and coral, partially covered with seagrass, about 80 km south and southwest of Jamaica, rising steeply from a seabed of 800 metres depth. It slopes gently from the Pedro Cays to the west and north with depths from 13 to 30 metres. The total area of the bank within the 100-metre (328-foot) isobath measures 8,040 square kilometres. The area of a depth to 40 metres is triangular, 70 kilometres long east-west, and 43 kilometres wide. 2,400 square kilometres are less than 20 metres deep. With its islets, cays and rocks, a total land area of 270,000 m2 (2,906,256 sq ft), it is the location of one of the two offshore island groups of Jamaica, the other one being the Morant Cays. The bank is centered at 17°06′N78°20′W.
Saba Bank in the Caribbean Netherlands is the largest submarine atoll in the Atlantic Ocean and has some of the richest diversity of marine life in the Caribbean Sea. In 2010 it was designated as "Saba Bank National Park", one of the National Parks of the Netherlands and was officially recognized as such in 2012.

The Atlantic Flyway is a major north-south flyway for migratory birds in North America. The route generally starts in Greenland, then follows the Atlantic coast of Canada, then south down the Atlantic Coast of the United States to the tropical areas of South America and the Caribbean. Every year, migratory birds travel up and down this route following food sources, heading to breeding grounds, or traveling to overwintering sites.
The Misteriosa Bank is a submerged bank or atoll in the Caribbean Sea, located at 18°48′N83°54′W – approximately equidistant from Mexico, Honduras and Cuba.
Cora Divh, also called Coradeeve or Little Bassas de Pedro Bank, is a submerged bank or sunken atoll belonging to the Amindivi Subgroup of islands of the Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. It has a distance of 1,733 km (1,077 mi) south of the city of Delhi.

Cay Sal Bank is the third largest and the westernmost of the Bahama Banks. It is located between 23º27'N - 24º10'N and 079º25'W – 080º35'W. In a geographical sense, it is separate from the Bahamas proper as it is much closer to Cuba than to the closest Bahamian island. It is separated by Santaren Channel from the Great Bahama Bank, the western rim of which is 50 km (31 mi) to the east. The Straits of Florida separate it from the United States mainland and the Florida Keys.

Poluwat, also Polowat, formerly Puluwat, is a coral atoll and a municipality of Chuuk state, Federated States of Micronesia.

The habitat of deep-water corals, also known as cold-water corals, extends to deeper, darker parts of the oceans than tropical corals, ranging from near the surface to the abyss, beyond 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) where water temperatures may be as cold as 4 °C (39 °F). Deep-water corals belong to the Phylum Cnidaria and are most often stony corals, but also include black and thorny corals and soft corals including the Gorgonians. Like tropical corals, they provide habitat to other species, but deep-water corals do not require zooxanthellae to survive.

The Florida Reef is the only living coral barrier reef in the continental United States. It lies a few miles seaward of the Florida Keys, is about 4 miles wide and extends 270 km (170 mi) from Fowey Rocks just east of Soldier Key to just south of the Marquesas Keys. The barrier reef tract forms a great arc, concentric with the Florida Keys, with the northern end, in Biscayne National Park, oriented north-south and the western end, south of the Marquesas Keys, oriented east-west. The rest of the reef outside Biscayne National Park lies within John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park and the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Isolated coral patch reefs occur northward from Biscayne National Park as far north as Stuart, in Martin County. Coral reefs are also found in Dry Tortugas National Park west of the Marquesas Keys. There are more than 6,000 individual reefs in the system. The reefs are 5,000 to 7,000 years old, having developed since sea levels rose following the Wisconsinan glaciation.
Carysfort is a coral reef located within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. It lies to the east of Key Largo, within the Key Largo Existing Management Area, which is immediately to the east of John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park. This reef is within a Sanctuary Preservation Area (SPA). The reef is northeast of The Elbow. The Carysfort Reef Light is near the center of the SPA.

Colpophyllia is a genus of stony corals in the family Mussidae. It is monotypic with a single species, Colpophyllia natans, commonly known as boulder brain coral or large-grooved brain coral. It inhabits the slopes and tops of reefs, to a maximum depth of fifty metres. It is characterised by large, domed colonies, which may be up to two metres across, and by the meandering network of ridges and valleys on its surface. The ridges are usually brown with a single groove, and the valleys may be tan, green, or white and are uniform in width, typically 2 centimetres. The polyps only extend their tentacles at night.

The Tizard Bank, 10°15′N114°30′E is a partially sunken atoll and one of the significant maritime features of the north-western part of the Spratly Islands. It is claimed by Vietnam, China, and Taiwan, and various parts of it are occupied by these states.

The Elbow Cays are uninhabited cays in the Cay Sal Bank, Bahamas. It is the most Western point in the Bahamas. They are part of a reef shelf located at the northwestern end of the bank about 80 km (50 mi) off the Cuban coast and 130 km (80 mi) southeast of Key West, Florida. These cays are an excellent scuba diving spot.

The Everglades & Dry Tortugas Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in Florida and the Gulf of Mexico. The 636,411 hectares (2,457.20 sq mi) reserve encompasses Everglades National Park and Dry Tortugas National Park, including historic Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands.