
Gram stain, is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884.

In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.

Rickettsia is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci, bacilli, or threads. The genus was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever.

The Actinomycetota are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, Actinomycetota are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, as fungi do, and the name of an important order of the phylum, Actinomycetales, reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus Mycobacterium, are important pathogens.

Mimivirus is a genus of giant viruses, in the family Mimiviridae. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses.
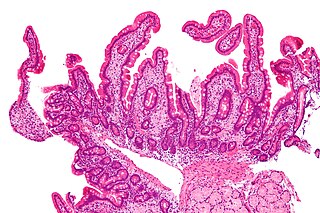
Whipple's disease is a rare systemic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Tropheryma whipplei. First described by George Hoyt Whipple in 1907 and commonly considered as a gastrointestinal disorder, Whipple's disease primarily causes malabsorption, but may affect any part of the human body, including the heart, brain, joints, skin, lungs and the eyes. Weight loss, diarrhea, joint pain, and arthritis are common presenting symptoms, but the presentation can be highly variable in certain individuals, and about 15% of patients do not have the standard signs and symptoms.
Rickettsia prowazekii is a species of gram-negative, alphaproteobacteria, obligate intracellular parasitic, aerobic bacillus bacteria that is the etiologic agent of epidemic typhus, transmitted in the feces of lice. In North America, the main reservoir for R. prowazekii is the flying squirrel. R. prowazekii is often surrounded by a protein microcapsular layer and slime layer; the natural life cycle of the bacterium generally involves a vertebrate and an invertebrate host, usually an arthropod, typically the human body louse. A form of R. prowazekii that exists in the feces of arthropods remains stably infective for months. R. prowazekii also appears to be the closest semi-free-living relative of mitochondria, based on genome sequencing.

Rickettsia rickettsii is a Gram-negative, intracellular, cocco-bacillus bacterium that was first discovered in 1902. Having a reduced genome, the bacterium harvests nutrients from its host cell to carry out respiration, making it an organo-heterotroph. Maintenance of its genome is carried out through vertical gene transfer where specialization of the bacterium allows it to shuttle host sugars directly into its TCA cycle.
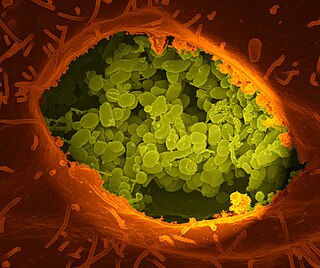
Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen, and is the causative agent of Q fever. The genus Coxiella is morphologically similar to Rickettsia, but with a variety of genetic and physiological differences. C. burnetii is a small Gram-negative, coccobacillary bacterium that is highly resistant to environmental stresses such as high temperature, osmotic pressure, and ultraviolet light. These characteristics are attributed to a small cell variant form of the organism that is part of a biphasic developmental cycle, including a more metabolically and replicatively active large cell variant form. It can survive standard disinfectants, and is resistant to many other environmental changes like those presented in the phagolysosome.

The bacterial capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases.
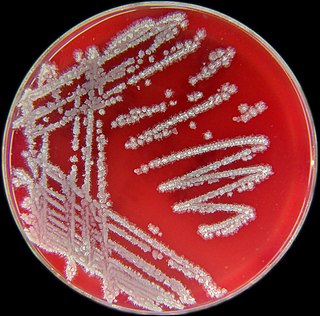
Bacillus licheniformis is a bacterium commonly found in the soil. It is found on bird feathers, especially chest and back plumage, and most often in ground-dwelling birds and aquatic species.

Bacteria are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. Most bacteria have not been characterised and there are many species that cannot be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.
A rickettsiosis is a disease caused by intracellular bacteria.

Rickettsia conorii is a Gram-negative, obligate intracellular bacterium of the genus Rickettsia that causes human disease called boutonneuse fever, Mediterranean spotted fever, Israeli tick typhus, Astrakhan spotted fever, Kenya tick typhus, Indian tick typhus, or other names that designate the locality of occurrence while having distinct clinical features. It is a member of the spotted fever group and the most geographically dispersed species in the group, recognized in most of the regions bordering on the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, Israel, Kenya, and other parts of North, Central, and South Africa, and India. The prevailing vector is the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. The bacterium was isolated by Emile Brumpt in 1932 and named after A. Conor, who in collaboration with A. Bruch, provided the first description of boutonneuse fever in Tunisia in 1910.

Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. Their direct examination under a light microscope enables the classification of these bacteria.
Rickettsia australis is a bacterium that causes a medical condition called Queensland tick typhus. The probable vectors are the tick species, Ixodes holocyclus and Ixodes tasmani. Small marsupials are suspected reservoirs of this bacterium.

Bacterial taxonomy is subfield of taxonomy devoted to the classification of bacteria specimens into taxonomic ranks.
Afipia birgiae is a species in the Afipia bacterial genus. It is a gram-negative, oxidase-positive rod in the alpha-2 subgroup of the class Proteobacteria. It is motile by means of a single flagellum. Its type strain is 34632T.
Peptidiphaga gingivicola is a Gram-positive, non-spore forming, coccus shaped bacterium. Coccus are spherical and generally round in shape. Coccus are differentiated by their groupings that can range from chains, groups, or grape-like clusters. Peptidiphaga gingivicola was observed to grow in groups of 2-5 cocci between 0.2-0.9 mm in diameter. Growth was observed when cultured under anaerobic conditions between 33 and 40 degrees celsius on Blood Brucella agar for 4 days. Peptidiphaga gingivicola has been cultured from patients with periodontal disease, primarily caused by bacterial plaque formation on the gum and teeth of the oral cavity. The microbe is known to break down peptides of the gum causing tissue damage and tooth decay, leading to serious implications for oral health.
Columbia Nalidixic Acid (CNA) agar is a growth medium used for the isolation and cultivation of bacteria from clinical and non-clinical specimens. CNA agar contains antibiotics that inhibit Gram-negative organisms, aiding in the selective isolation of Gram-positive bacteria. Gram-positive organisms that grow on the media can be differentiated on the basis of hemolysis.












