
The "Republican Revolution," "Revolution of '94," or "Gingrich Revolution" are political slogans that refer to the Republican Party (GOP) success in the 1994 U.S. mid-term elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of Representatives, and a pick-up of eight seats in the Senate. On November 9, 1994, the day after the election, Senator Richard Shelby of Alabama, a conservative Democrat, changed parties, becoming a Republican; on March 3, 1995, Colorado Senator Ben Nighthorse Campbell switched to the Republican side as well, increasing the GOP Senate majority.

John Hardy Isakson was an American businessman and politician who served as a United States Senator from Georgia from 2005 to 2019 as a member of the Republican Party. He represented Georgia's 6th congressional district in the United States House of Representatives from 1999 to 2005.

The 1920 United States House of Representatives elections were held, coinciding with the election of President Warren G. Harding, the first time that women in all states were allowed to vote in federal elections after the passage of the 19th Amendment.

The 1868 and 1869 United States House of Representatives elections coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant.
The 1860 and 1861 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from August 1860 to October 1861.

The 1822 and 1823 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states between July 1822 and August 1823 during President James Monroe's second term.

The 1812 and 1813 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states between April 1812 and August 1813 as James Madison was re-elected president.
The 1802 and 1803 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in each state, from April 26, 1802 to December 14, 1803 during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office. It was common in the early years of the United Congress for some states to elect representatives to a Congress after it had already convened. In the case of the 8th Congress, the representatives from New Jersey were only elected after its first meeting on October 17, 1803.

The 1792 and 1793 United States House of Representatives elections coincided with the re-election of President George Washington. While Washington ran for president as an independent, his followers formed the nation's first organized political party, the Federalist Party, whose members and sympathizers are identified as pro-Administration on this page. In response, followers of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison created the opposition Democratic-Republican Party, who are identified as anti-Administration on this page. The Federalists promoted urbanization, industrialization, mercantilism, centralized government, and a broad interpretation of the United States Constitution. In contrast, Democratic-Republicans supported the ideal of an agrarian republic made up of self-sufficient farmers and small, localized governments with limited power.

The 1978 United States elections were held on November 7, 1978, to elect the members of the 96th United States Congress. The election occurred in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. Democrats retained control of both houses of Congress. As of 2022, this is the most recent election in which the Democrats maintained a trifecta on the government.

The 1952 United States elections were held on November 4, 1952. The Republicans took control of the presidency and both chambers of Congress for the first time since the Great Depression. The election took place during the Korean War.

The 1946 United States elections were held on November 5, 1946, and elected the members of the 80th United States Congress. In the first election after the end of World War II, incumbent President Harry S. Truman and the Democratic Party suffered large losses. After having been in the minority of both chambers of Congress since 1932, Republicans took control of both the House and the Senate.

The 1930 United States elections were held on November 4, 1930, in the middle of Republican President Herbert Hoover's term. Taking place shortly after the start of the Great Depression, the Republican Party suffered substantial losses. The election was the last of the Fourth Party System, and marked the first time since 1918 that Democrats controlled either chamber of Congress.
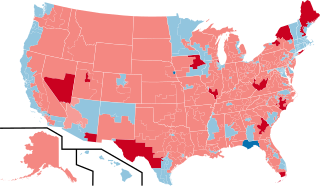
The 2014 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 4, 2014, in the middle of President Barack Obama's second term in office. Elections were held for all 435 seats of the House of Representatives, representing the 50 states. Elections were also held for the non-voting delegates from the District of Columbia and four of the five territories. The winners of these elections served in the 114th United States Congress, with seats apportioned among the states based on the 2010 United States Census.

The 2014 United States House of Representatives elections in Georgia were held on Tuesday, November 4, 2014, to elect the 14 U.S. representatives from the state of Georgia, one from each of the state's 14 congressional districts. The elections coincided with the elections of other federal and state offices, including Governor of Georgia and U.S. Senator.

The 2017 United States elections were held, in large part, on Tuesday, November 7, 2017. This off-year election featured gubernatorial elections in Virginia and New Jersey, as well as state legislative elections in both houses of the New Jersey Legislature and in the Virginia House of Delegates. Numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local elections also occurred. Special elections were also held for one seat of the U.S. Senate, representing Alabama, and six seats of the U.S. House of Representatives.

The 2018 Georgia House of Representatives elections took place as part of the biennial United States elections. Georgia voters elected state representatives in all 180 of the state house's districts. State representatives serve two-year terms in the Georgia House of Representatives.

The 2022 United States Senate election in Georgia will be held on November 8, 2022, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Georgia.

The 2020 United States state legislative elections were held on November 3, 2020 for 86 state legislative chambers in 44 states. Across the fifty states, approximately 65 percent of all upper house seats and 85 percent of all lower house seats were up for election. Nine legislative chambers in the five permanently-inhabited U.S. territories and the federal district of Washington, D.C. also held elections. The elections took place concurrently with several other federal, state, and local elections, including the presidential election, U.S. Senate elections, U.S. House elections, and gubernatorial elections.
The 2019 United States state legislative elections were held on November 5, 2019. Seven legislative chambers in four states held regularly-scheduled elections. These off-year elections coincided with other state and local elections, including gubernatorial elections in three states.


















