
The Whig Party was a mid-19th century political party in the United States. Alongside the Democratic Party, it was one of two major parties between the late 1830s and the early 1850s and part of the Second Party System. As well as four Whig presidents, other prominent members included Henry Clay, Daniel Webster, Rufus Choate, William Seward, John J. Crittenden, and John Quincy Adams. The Whig base of support was amongst entrepreneurs, professionals, Protestant Christians, the urban middle class, and nativists. It had much less backing from poor farmers and unskilled workers.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1852. Democratic nominee Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.
The Union Party, known as the Constitutional Union Party in the state of Georgia, was a political party organized in several slave states to support the Compromise of 1850. It was one of two major parties in the states of Alabama, Georgia, and Mississippi in the early 1850s, alongside the Southern Rights Party. While some figures, including notably Daniel Webster, predicted a sweeping political realignment in which the Union Party would unite all those in favor of the Compromise measures, no national organization ever emerged. The party bore no relation to the later Constitutional Union Party that supported John Bell in the 1860 United States presidential election, nor to unionist parties active in the loyal states during the American Civil War.
The Opposition Party was a third party in the South in the years just before the American Civil War.
Charles Dougherty was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician.

The American Party, known as the Native American Party before 1855 and colloquially referred to as the Know Nothings, or the Know Nothing Party, was an Old Stock nativist political movement in the United States in the 1850s. Members of the movement were required to say "I know nothing" whenever they were asked about its specifics by outsiders, providing the group with its colloquial name.

The 1836 United States presidential election in Georgia took place between November 3 and December 7, 1836, as part of the 1836 United States presidential election. Voters chose 11 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1854 Connecticut gubernatorial election was held on April 3, 1854. Former state legislator and Whig Party nominee Henry Dutton defeated former congressman and Democratic nominee Samuel Ingham and former congressman Charles Chapman with 31.89% of the vote.
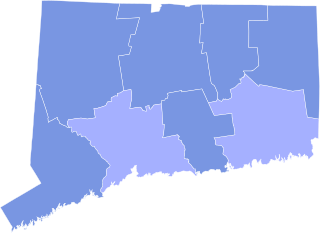
The 1853 Connecticut gubernatorial election was held on April 4, 1853. Incumbent governor and Democratic Party nominee Thomas H. Seymour defeated former state legislator and Whig nominee Henry Dutton and former state legislator and Free Soil nominee Francis Gillette with 51.01% of the vote.

The 1851 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 6, 1851, to elect the governor of Georgia. Howell Cobb, nominee for the newly formed Constitutional Union Party, defeated the Southern Rights Candidate, Charles McDonald.

The 1843 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 2, 1843, to elect the governor of Georgia. Whig candidate George W. Crawford defeated the Democratic challenger Mark A. Cooper and was elected Governor.

The 1841 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 4, 1841, to elect the governor of Georgia. Incumbent Democratic Governor Charles McDonald won re-election defeating Whig State Rights candidate William C. Dawson.

The 1839 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was held on April 17, 1839.

The 1841 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on September 7, 1841.

The 1842 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on September 6, 1842.

The 1827 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 1, 1827, to elect the governor of Georgia. Due to the death of the Democratic-Republican Clark candidate Matthew Talbot, Jacksonian Troup candidate John Forsyth won in a landslide against a divided opposition.

The 1833 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 7, 1833, to elect the governor of Georgia. Incumbent Democratic Union Governor Wilson Lumpkin narrowly defeated National Republican Troup nominee Joel Crawford

The 1835 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 5, 1835, to elect the governor of Georgia. Democratic Union Governor Wilson Lumpkin, first elected in the 1831 election, did not seek re-election to a second term, instead he became U.S. commissioner to the Cherokee Native Americans. Democratic Union candidate William Schley, U.S House rep for Georgia's 1st congressional district, narrowly defeated Whig State Rights candidate Charles Dougherty.

The 1837 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on October 2, 1837, to elect the governor of Georgia. In a major upset, thanks in part to the Panic of 1837, Whig State Rights candidate and Ex-Governor George R. Gilmer beat incumbent Democratic Union Governor Willam Schley.

The 1853 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on 3 October 1853 in order to elect the Governor of Georgia. Democratic nominee and former United States Senator from Georgia Herschel V. Johnson defeated Constitutional Union nominee and former Attorney General of Georgia Charles J. Jenkins by a slim margin.



















