The 470s decade ran from January 1, 470, to December 31, 479.
The 530s decade ran from January 1, 530, to December 31, 539.
The 500s decade ran from January 1, 500, to December 31, 509.
The 510s decade ran from January 1, 510, to December 31, 519.
The 520s decade ran from January 1, 520, to December 31, 529.
The 550s decade ran from January 1, 550, to December 31, 559.
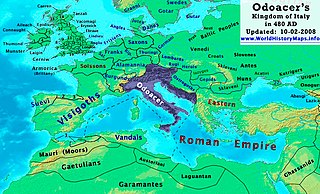
Year 480 (CDLXXX) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Basilius without colleague. The denomination 480 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 490s decade ran from January 1, 490, to December 31, 499.
The 480s decade ran from January 1, 480, to December 31, 489.
The 460s decade ran from January 1, 460, to December 31, 469.
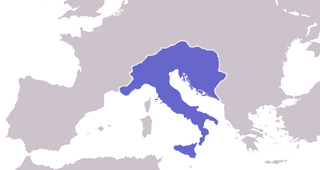
Year 493 (CDXCIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Albinus and Eusebius. The denomination 493 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 500 (D) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Patricius and Hypatius. The denomination 500 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. The year 500 AD is considered the beginning of the Middle Ages, approximately.

Year 507 (DVII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Anastasius and Venantius. The denomination 507 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 508 (DVIII) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Venantius and Celer. The denomination 508 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 522 (DXXII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Symmachus and Boethius. The denomination 522 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 524 (DXXIV) was a leap year starting on Monday on the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Iustinus and Opilio. The denomination 524 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 497 (CDXCVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Anastasius without colleague. The denomination 497 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 520 (DXX) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rusticus and Vitalianus. The denomination 520 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 530 (DXXX) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lampadius and Probus. The denomination 530 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy, was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ostrogoths killed Odoacer, a Germanic soldier and erstwhile leader of the foederati. Odoacer had previously become the de facto ruler of Italy following his deposition of Romulus Augustulus, the final emperor of the Western Roman Empire, in 476. Under Theodoric, the Ostrogothic kingdom reached its zenith, stretching from modern Southern France in the west to the modern western Serbia in the southeast. Most of the social institutions of the late Western Roman Empire were preserved during his rule. Theodoric called himself Gothorum Romanorumque rex 'King of the Goths and Romans', demonstrating his desire to be a leader for both peoples.










