
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages.

Charles Martel, Martel being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of the Franks from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesman Pepin of Herstal and a noblewoman named Alpaida. Charles successfully asserted his claims to power as successor to his father as the power behind the throne in Frankish politics. Continuing and building on his father's work, he restored centralized government in Francia and began the series of military campaigns that re-established the Franks as the undisputed masters of all Gaul. According to a near-contemporary source, the Liber Historiae Francorum, Charles was "a warrior who was uncommonly ... effective in battle".
The 790s decade ran from January 1, 790, to December 31, 799.
The 780s decade ran from January 1, 780, to December 31, 789.
The 760s decade ran from January 1, 760, to December 31, 769.
The 740s decade ran from January 1, 740, to December 31, 749.
The 710s decade ran from January 1, 710, to December 31, 719.
The 690s decade ran from January 1, 690, to December 31, 699.

Year 741 (DCCXLI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 741 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 740 (DCCXL) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 740th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 740th year of the 1st millennium, the 40th year of the 8th century, and the 1st year of the 740s decade. The denomination 740 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
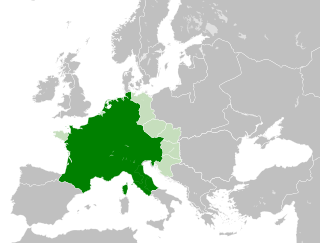
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the status of Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.

Carloman was the eldest son of Charles Martel, mayor of the palace and duke of the Franks, and his wife Chrotrud of Treves. On Charles's death (741), Carloman and his brother Pepin the Short succeeded to their father's legal positions, Carloman in Austrasia, and Pepin in Neustria. He was a member of the family later called the Carolingians and it can be argued that he was instrumental in consolidating their power at the expense of the ruling Merovingian kings of the Franks. He withdrew from public life in 747 to take up the monastic habit, "the first of a new type of saintly king", according to Norman Cantor, "more interested in religious devotion than royal power, who frequently appeared in the following three centuries and who was an indication of the growing impact of Christian piety on Germanic society".
The Carolingian dynasty was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and dux et princeps Francorum hereditary, and becoming the de facto rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Emperor of the Romans in the West in over three centuries. Nearly every monarch of France from Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious until the penultimate monarch of France Louis Philippe have been his descendants. His death in 814 began an extended period of fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and decline that would eventually lead to the evolution of the Kingdom of France and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Kingdom of the Franks, also known as the Frankish Kingdom, the Frankish Empire or Francia, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Frankish Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era.

Pepin or Pippin, was King of Italy from 781 until his death in 810. He was the third son of Charlemagne. Upon his baptism in 781, Carloman was renamed Pepin, where he was also crowned as king of the Lombard Kingdom his father had conquered. Pepin ruled the kingdom from a young age under Charlemagne, but predeceased his father. His son Bernard was named king of Italy after him, and his descendants were the longest-surviving direct male line of the Carolingian dynasty.
Charles the Younger was the son of the Frankish ruler Charlemagne and his wife Queen Hildegard. Charlemagne's second son, Charles gained favour over his older, possibly illegitimate half brother Pepin. Charles was entrusted with lands and important military commands by his father. In 800, Charlemagne was crowned emperor by Pope Leo III, and during this ceremony Charles was anointed a king. Charles was designated as the heir of the bulk of Charlemagne's lands but predeceased his father, leaving the empire to be inherited by his younger brother Louis the Pious.

Pepin the Short, was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
Waiofar, also spelled Waifar, Waifer or Waiffre, was the last independent Duke of Aquitaine from 745 to 768. He peacefully succeeded his father, Hunald I, after the latter entered a monastery. He also inherited the conflict with the rising Carolingian family and its leader, Pepin the Short, who was king of the Franks after 751 and thus Waiofar's nominal suzerain.
Hunald II, also spelled Hunold, Hunoald, Hunuald or Chunoald, was the Duke of Aquitaine from 768 until 769. He was probably the son of Duke Waiofar, who was assassinated on the orders of King Pippin the Short in 768. He laid claim to the duchy following Pippin's death later that year, but his revolt was crushed by Pippin's eldest son, Charlemagne. Hunald fled to the Duchy of Gascony, but he was handed over to Charlemagne and put into captivity. Nothing more is heard of him.
The siege of Toulouse was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortified town of Toulouse in the winter of 767 during the Aquitanian War. The Frankish army under King Pepin the Short conquered the town and accepted the surrender of nearby Albi and Gevaudan.









