
Alfonso II of Asturias, nicknamed the Chaste, was the king of Asturias during two different periods: first in the year 783 and later from 791 until his death in 842. Upon his death, Nepotian, a family member of undetermined relation, attempted to usurp the crown in place of the future Ramiro I.
The 800s decade ran from January 1, 800, to December 31, 809.
The 790s decade ran from January 1, 790, to December 31, 799.
The 780s decade ran from January 1, 780, to December 31, 789.
The 770s decade ran from January 1, 770, to December 31, 779.

Year 754 (DCCLIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 754th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 754th year of the 1st millennium, the 54th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 750s decade. The denomination 754 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 774 (DCCLXXIV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 774 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 778 (DCCLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 778th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 778th year of the 1st millennium, the 78th year of the 8th century, and the 9th year of the 770s decade. The denomination 778 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 780 (DCCLXXX) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 780th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 780th year of the 1st millennium, the 80th year of the 8th century, and the 1st year of the 780s decade. The denomination 780 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 782 (DCCLXXXII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 782nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 782nd year of the 1st millennium, the 82nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 780s decade. The denomination 782 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 785 (DCCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The article denomination 785 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It is still used today in this manner.

Year 789 (DCCLXXXIX) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 789 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 791 (DCCXCI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 791 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
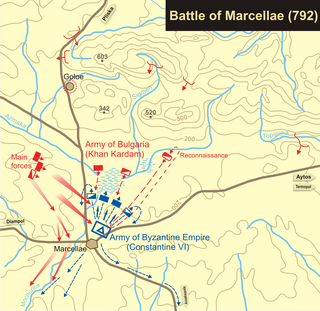
Year 792 (DCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 792nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 792nd year of the 1st millennium, the 92nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 790s decade. The denomination 792 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 793 (DCCXCIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 793 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 794 (DCCXCIV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 794th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 794th year of the 1st millennium, the 94th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 794 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 797 (DCCXCVII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 797 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 798 (DCCXCVIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 798th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 798th year of the 1st millennium, the 98th year of the 8th century, and the 9th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 798 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Alfonso I of Asturias, called the Catholic, was the third king of Asturias, reigning from 739 to his death in 757. His reign saw an extension of the Christian domain of Asturias, reconquering Galicia and León.
Adosinda was the queen of Asturias during the reign of her husband, Silo, from 774 to 783. She was a daughter of Alfonso I and Ermesinda, daughter of the first Asturian king, Pelayo. She was a sister of Fruela I.














