Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed, expressed as kilometres per hour (km/h) or miles per hour (mph) or both. Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of national or provincial governments and enforced by national or regional police and judicial authorities. Speed limits may also be variable, or in some places nonexistent, such as on most of the Autobahnen in Germany.

The Afsluitdijk is a major dam and causeway in the Netherlands. It was constructed between 1927 and 1932 and runs from Den Oever in North Holland province to the village of Zurich in Friesland province, over a length of 32 kilometres (20 mi) and a width of 90 metres (300 ft), at an initial height above Amsterdam Ordnance Datum of between 6.7 metres (22 ft) along the section at Friesland, and 7.4 metres (24 ft) where it crosses the deep channel of the Vlieter. The height at the greater sea depths west of Friesland was required to be a minimum of 7 metres everywhere when originally constructed.

The M50 motorway is a C-shaped orbital motorway in Dublin and the busiest motorway in Ireland. The current route was built in various sections over the course of 27 years, from 1983 to 2010. It begins at Dublin Port, running northward through the Dublin Port Tunnel and along a portion of the Airport Motorway. It then turns west at its junction with the M1, circling the northern, western and southern suburbs of Dublin, before merging with the M11 at Shankill in South East Dublin. The road forms part of European route E01.

A dual carriageway (BrE) or a divided highway (AmE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are designed to higher standards with controlled access are generally classed as motorways, freeways, etc., rather than dual carriageways.

A limited-access road, known by various terms worldwide, including limited-access highway, dual-carriageway, expressway, and partial controlled-access highway, is a highway or arterial road for high-speed traffic which has many or most characteristics of a controlled-access highway, including limited or no access to adjacent property, some degree of separation of opposing traffic flow, use of grade separated interchanges to some extent, prohibition of slow modes of transport, such as bicycles, horse-drawn vehicles or ridden horses, or self-propelled agricultural machines; and very few or no intersecting cross-streets or level crossings. The degree of isolation from local traffic allowed varies between countries and regions. The precise definition of these terms varies by jurisdiction.

The Autobahn is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official term is Bundesautobahn, which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word Bundesautobahn is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'.

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway or thruway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.

Bundesstraße, abbreviated B, is the denotation for German and Austrian national highways.

The A28 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. It is approximately 188 kilometers in length.
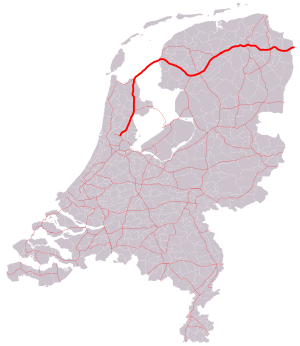
The A6 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. It is just over 100 kilometers in length and it connects the A1 motorway at interchange Muiderberg with the A7 motorway at interchange Joure.
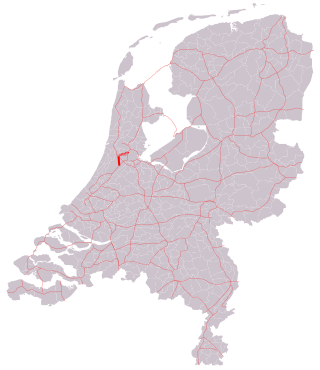
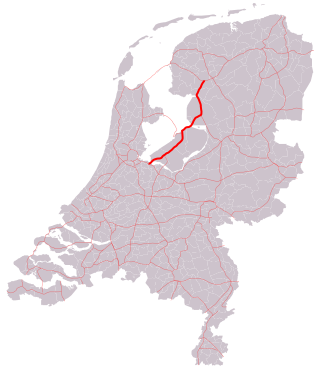
The A5 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. With a length of 17 kilometres (11 mi), it is one of the shortest motorways in the country.

The A2 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. It is one of the busiest highways in the Netherlands. The road connects the city of Amsterdam, near the Amstel interchange with the Belgian border, near Maastricht (NL) and Liège (B), and the Belgian A25 road.

The A16 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. It runs from the interchange Terbregseplein in the northeastern part of Rotterdam, towards the Belgian border near Hazeldonk. The motorway has 19 exits including 7 interchanges.
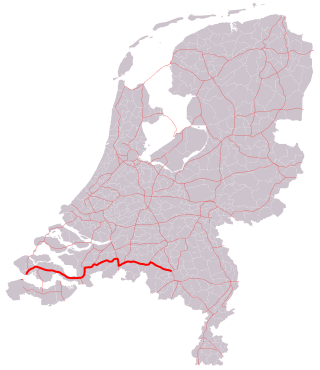
The A58 motorway is a motorway in the Netherlands. It is approximately 145 kilometres in length. The A58 is located in the Dutch provinces of North Brabant and Zeeland.

The A31 / N31 is a motorway and an expressway in the Netherlands. It connects the A7 near Zurich with the A7 near Drachten, passing close to Leeuwarden, the provincial capital of Friesland.
This article describes the highway systems available in selected countries.

Public roads in Hungary are ranked according to importance and traffic as follows:

Rijksstraatweg or simply Straatweg was the term for paved roads of interregional significance in the Netherlands in the 19th and early 20th centuries. These roads were built by the national government, and formed the country's first centrally planned highway network. They received route numbers, eventually resulting in a nationwide network of 82 highways. It formed the basis for today's system of nationally controlled roads, the Netherlands' main highway grid.

European route E 22 (E 22) is a west–east European route, running from Holyhead in the United Kingdom, through the Netherlands, Germany, Sweden and Latvia, to Ishim in Russia.