Related Research Articles
AD 68 (LXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Silius Italicus and Trachalus, or the start of the Year of the Four Emperors. The denomination AD 68 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. These are now used throughout the world.

The 30s decade ran from January 1, AD 30, to December 31, AD 39.
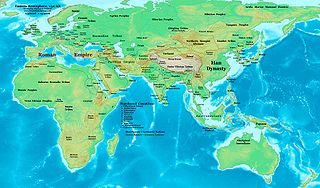
The 50s decade ran from January 1, 50, to December 31, 59. It was the sixth decade in the Anno Domini/Common Era, if the nine-year period from 1 AD to 9 AD is considered as a "decade".

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.

The 70s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 70, to December 31, AD 79.

The 110s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 110, to December 31, AD 119.

AD 50 (L) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time it was known in Europe as the Year of the Consulship of Vetus and Nerullinus. The denomination AD 50 for this year has been used since the Early Middle Ages, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 0s BC is the period between 9 BC and 1 BC, the last nine years of the before Christ era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s.
AD 62 (LXII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Afinius. The denomination AD 62 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 67 (LXVII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Julius Rufus and Fonteius Capito. The denomination AD 67 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 340s decade ran from January 1, 340, to December 31, 349.
The 250s was a decade that ran from January 1, 250, to December 31, 259.

Year 300 (CCC) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Constantius and Valerius. The denomination 300 for this year has been used since the early Middle Ages / Medieval period, when the Latin language term / abbreviation "Anno Domini" for the calendar era became the prevalent universal / worldwide method for naming and numbering years. First beginning in Europe at the end of the Roman Empire (after the split of the Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire in the early Middle Ages / Medieval period.
Year 252 (CCLII) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Trebonianus and Volusianus. The denomination 252 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The Year 345 (CCCXLV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Amantius and Albinus. The denomination 345 for this year has been used ever since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 320 (CCCXX) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.
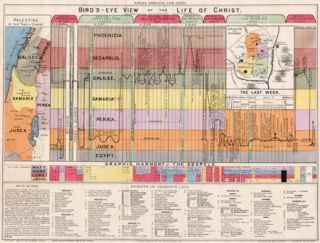
A chronology of Jesus aims to establish a timeline for the events of the life of Jesus. Scholars have correlated Jewish and Greco-Roman documents and astronomical calendars with the New Testament accounts to estimate dates for the major events in Jesus's life.
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the historical era of the Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Christianity spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish diaspora throughout the Eastern Mediterranean. The first followers of Christianity were Jews who had converted to the faith, i.e. Jewish Christians, as well as Phoenicians, i.e. Lebanese Christians. Early Christianity contains the Apostolic Age and is followed by, and substantially overlaps with, the Patristic era.

Aghjots Vank ; also known as the Saint Stephen Monastery of Goght, is a 13th-century monastery situated along a tributary of the Azat River Valley within the Khosrov State Reserve located half a mile walk from the hamlet of Mets Gilanlar, and near the villages of Goght and Garni in the Ararat Province of Armenia. Not far from this location and also within the reserve is the fortress of Kakavaberd and the monastic complex of Havuts Tar.

Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of various synagogues by his teachings. Accused of blasphemy at his trial, he made a speech denouncing the Jewish authorities who were sitting in judgment on him and was then stoned to death. Saul of Tarsus, later known as Paul the Apostle, a Pharisee and Roman citizen who would later become an apostle, participated in Stephen's execution.