The 790s decade ran from January 1, 790, to December 31, 799.
The 780s decade ran from January 1, 780, to December 31, 789.
The 770s decade ran from January 1, 770, to December 31, 779.

Year 795 (DCCXCV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 795 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 802 (DCCCII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 802nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 802nd year of the 1st millennium, the 2nd year of the 9th century, and the 3rd year of the 800s decade.
Year 801 (DCCCI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 801st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 801st year of the 1st millennium, the 1st year of the 9th century, and the 2nd year of the 800s decade.

Year 775 (DCCLXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 775 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 776 (DCCLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 776 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 778 (DCCLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 778th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 778th year of the 1st millennium, the 78th year of the 8th century, and the 9th year of the 770s decade. The denomination 778 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 779 (DCCLXXIX) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 779 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 780 (DCCLXXX) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 780th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 780th year of the 1st millennium, the 80th year of the 8th century, and the 1st year of the 780s decade. The denomination 780 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 782 (DCCLXXXII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 782nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 782nd year of the 1st millennium, the 82nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 780s decade. The denomination 782 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 783 (DCCLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 783 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 784 (DCCLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 784th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 784th year of the 1st millennium, the 84th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 780s decade. The denomination 784 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 785 (DCCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The article denomination 785 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It is still used today in this manner.
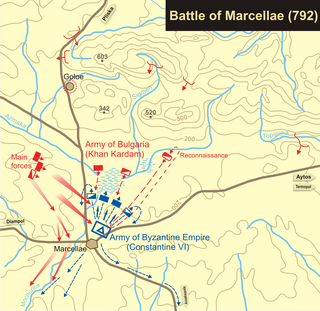
Year 792 (DCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 792nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 792nd year of the 1st millennium, the 92nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 790s decade. The denomination 792 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 794 (DCCXCIV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 794th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 794th year of the 1st millennium, the 94th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 794 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 796 (DCCXCVI) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 796th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 796th year of the 1st millennium, the 96th year of the 8th century, and the 7th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 796 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 797 (DCCXCVII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 797 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
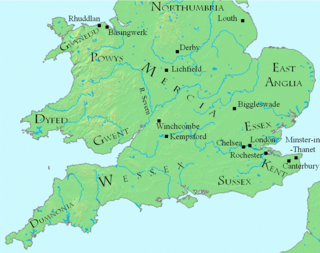
Year 798 (DCCXCVIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 798th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 798th year of the 1st millennium, the 98th year of the 8th century, and the 9th year of the 790s decade. The denomination 798 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.















