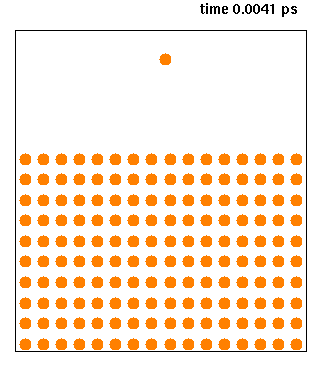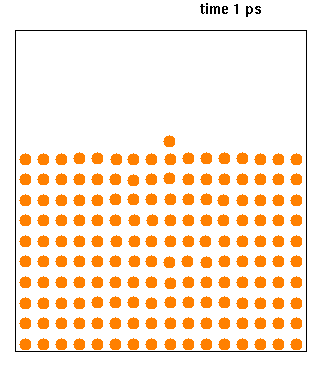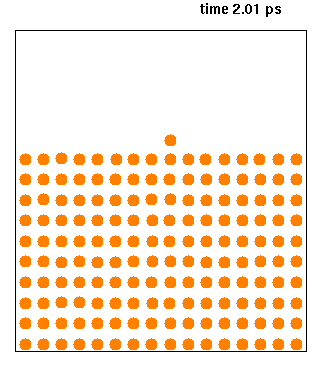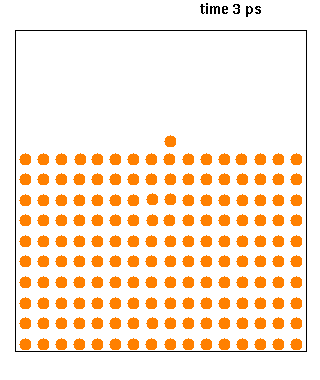
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics.
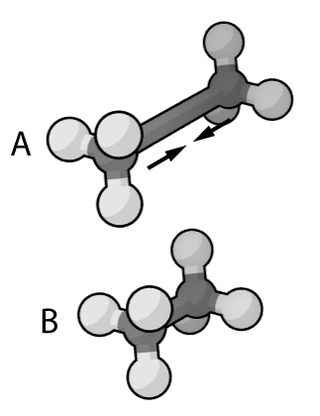
Assisted Model Building with Energy Refinement (AMBER) is the name of a widely-used molecular dynamics software package originally developed by Peter Kollman's group at the University of California, San Francisco. It has also, subsequently, come to designate a family of force fields for molecular dynamics of biomolecules that can be used both within the AMBER software suite and with many modern computational platforms.
Chemistry at Harvard Macromolecular Mechanics (CHARMM) is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics, and the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis computer software package associated with them. The CHARMM Development Project involves a worldwide network of developers working with Martin Karplus and his group at Harvard to develop and maintain the CHARMM program. Licenses for this software are available, for a fee, to people and groups working in academia.

Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms.
Global optimization is a branch of applied mathematics and numerical analysis that attempts to find the global minima or maxima of a function or a set of functions on a given set. It is usually described as a minimization problem because the maximization of the real-valued function is equivalent to the minimization of the function .
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit, or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons.

In the context of chemistry, molecular physics, physical chemistry, and molecular modelling, a force field is a computational model that is used to describe the forces between atoms within molecules or between molecules as well as in crystals. Force fields are a variety of interatomic potentials. More precisely, the force field refers to the functional form and parameter sets used to calculate the potential energy of a system on the atomistic level. Force fields are usually used in molecular dynamics or Monte Carlo simulations. The parameters for a chosen energy function may be derived from classical laboratory experiment data, calculations in quantum mechanics, or both. Force fields utilize the same concept as force fields in classical physics, with the main difference being that the force field parameters in chemistry describe the energy landscape on the atomistic level. From a force field, the acting forces on every particle are derived as a gradient of the potential energy with respect to the particle coordinates.
Tinker, previously stylized as TINKER, is a suite of computer software applications for molecular dynamics simulation. The codes provide a complete and general set of tools for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics, with some special features for biomolecules. The core of the software is a modular set of callable routines which allow manipulating coordinates and evaluating potential energy and derivatives via straightforward means.

In computational chemistry, a water model is used to simulate and thermodynamically calculate water clusters, liquid water, and aqueous solutions with explicit solvent. The models are determined from quantum mechanics, molecular mechanics, experimental results, and these combinations. To imitate a specific nature of molecules, many types of models have been developed. In general, these can be classified by the following three points; (i) the number of interaction points called site, (ii) whether the model is rigid or flexible, (iii) whether the model includes polarization effects.
This is a list of computer programs that are predominantly used for molecular mechanics calculations.
Molecular design software is notable software for molecular modeling, that provides special support for developing molecular models de novo.

Molecular modeling on GPU is the technique of using a graphics processing unit (GPU) for molecular simulations.

Molecular Dynamics of Mixtures (MDynaMix) is a computer software package for general purpose molecular dynamics to simulate mixtures of molecules, interacting by AMBER- and CHARMM-like force fields in periodic boundary conditions. Algorithms are included for NVE, NVT, NPT, anisotropic NPT ensembles, and Ewald summation to treat electrostatic interactions. The code was written in a mix of Fortran 77 and 90. The package runs on Unix and Unix-like (Linux) workstations, clusters of workstations, and on Windows in sequential mode.
Desmond is a software package developed at D. E. Shaw Research to perform high-speed molecular dynamics simulations of biological systems on conventional computer clusters. The code uses novel parallel algorithms and numerical methods to achieve high performance on platforms containing multiple processors, but may also be executed on a single computer.
This is a list of notable computer programs that are used for nucleic acids simulations.
Biochemical and Organic Simulation System (BOSS) is a general-purpose molecular modeling program that performs molecular mechanics calculations, Metropolis Monte Carlo statistical mechanics simulations, and semiempirical Austin Model 1 (AM1), PM3, and PDDG/PM3 quantum mechanics calculations. The molecular mechanics calculations cover energy minimizations, normal mode analysis and conformational searching with the Optimized Potentials for Liquid Simulations (OPLS) force fields. BOSS is developed by Prof. William L. Jorgensen at Yale University, and distributed commercially by Cemcomco, LLC and Schrödinger, Inc.

Ascalaph Designer is a computer program for general purpose molecular modelling for molecular design and simulations. It provides a graphical environment for the common programs of quantum and classical molecular modelling ORCA, NWChem, Firefly, CP2K and MDynaMix . The molecular mechanics calculations cover model building, energy optimizations and molecular dynamics. Firefly covers a wide range of quantum chemistry methods. Ascalaph Designer is free and open-source software, released under the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2).
MacroModel is a computer program for molecular modelling of organic compounds and biopolymers. It features various chemistry force fields, plus energy minimizing algorithms, to predict geometry and relative conformational energies of molecules. MacroModel is maintained by Schrödinger, LLC.