Related Research Articles

Kaiser-Wilhelmsland formed part of German New Guinea, the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago, the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea.
Tayap is an endangered Papuan language spoken by fewer than 50 people in Gapun village of Marienberg Rural LLG in East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. It is being replaced by the national language and lingua franca Tok Pisin.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western, Indonesian half of the island of New Guinea, granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.
The Border or Upper Tami languages are an independent family of Papuan languages in Malcolm Ross's version of the Trans–New Guinea proposal.

Porome, also known as Kibiri, is a Papuan language of southern Papua New Guinea.
Sogeram River is a river in Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. It empties into the Ramu River at 4.8°S 144.7333333°E.
May River Iwam, often simply referred to as Iwam, is a language of East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea.
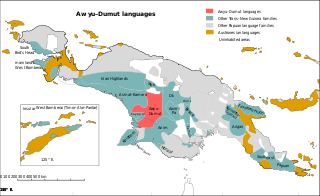
The Greater Awyu or Digul River languages, known in earlier classifications with more limited scope as Awyu–Dumut (Awyu–Ndumut), are a family of perhaps a dozen Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in eastern West Papua in the region of the Digul River. Six of the languages are sufficiently attested for a basic description; it is not clear how many of the additional names may be separate languages.
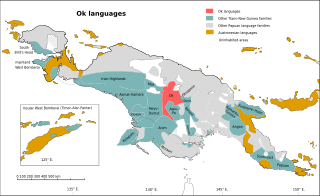
The Ok languages are a family of about a dozen related Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in a contiguous area of eastern Irian Jaya and western Papua New Guinea. The most numerous language is Ngalum, with some 20,000 speakers; the best known is probably Telefol.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

The Lower Sepik a.k.a. Nor–Pondo languages are a small language family of East Sepik Province in northern Papua New Guinea. They were identified as a family by K Laumann in 1951 under the name Nor–Pondo, and included in Donald Laycock's now-defunct 1973 Sepik–Ramu family.

The Sepik Hill languages form the largest and most ramified branch of the Sepik languages of northern Papua New Guinea. They are spoken along the southern margin of the Sepik floodplain in the foothills of Central Range of south-central East Sepik Province.
Guga River is a river of Papua New Guinea. It is part of the Wahgi River network.
Ipiko is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea, the most divergent of the Inland Gulf languages. Despite being spoken by only a few hundred people, language use is vigorous. It is spoken in Ipiko and Pakemuba villages, with Ipiko village being located in Amipoke ward, Baimuru Rural LLG, Kikori District, Gulf Province.
Kambota.k.a.Ap Ma, is a Keram language of Papua New Guinea. Compared to its nearest relative, Ambakich, Kambot drops the first segment from polysyllabic words.
Mbore a.k.a. Gamei (Gamai) is a Lower Ramu language of Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in the villages of Gamei and Boroi in Yawar Rural LLG, Bogia District, Madang Province.
Namia is a Sepik language spoken in Namea Rural LLG, Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea. It goes by various names, such as Edawapi, Lujere, Yellow River. Language use is "vigorous" (Ethnologue).
Marangis a.k.a. Watam is a Ramu language of Papua New Guinea. Like Bosmun, it shares a number of irregular plural markers with the Lower Sepik languages, supporting the proposal of a Ramu – Lower Sepik language family.
Foia Foia (Foyafoya), or Minanibai, is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea, spoken in an area near Omati River mouth in Ikobi Kairi and Goaribari Census districts.
Buna is a Torricelli language of Marienberg Rural LLG, East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea.
References
- ↑ "Abede River". GeoNames . Retrieved 1 January 2013.
- ↑ "Exploring Papua New Guinea". National Geographic Expeditions. 2014. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
7°13′31″S144°48′53″E / 7.22528°S 144.81472°E