Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.

In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation.

A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of body mass, sun damage, or temporarily, as the result of prolonged immersion in water. Age wrinkling in the skin is promoted by habitual facial expressions, aging, sun damage, smoking, poor hydration, and various other factors. In humans, it can also be prevented to some degree by avoiding excessive solar exposure and through diet.

The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix. It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, apocrine glands, lymphatic vessels, nerves and blood vessels are present in the dermis. Those blood vessels provide nourishment and waste removal for both dermal and epidermal cells.

Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELN gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes. It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the body to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin to return to its original position when it is poked or pinched. Elastin is also an important load-bearing tissue in the bodies of vertebrates and used in places where mechanical energy is required to be stored.

Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin. Actinic keratosis is a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes that is induced by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. These growths are more common in fair-skinned people and those who are frequently in the sun. They are believed to form when skin gets damaged by UV radiation from the sun or indoor tanning beds, usually over the course of decades. Given their pre-cancerous nature, if left untreated, they may turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated lesions have up to a 20% risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma, so treatment by a dermatologist is recommended.
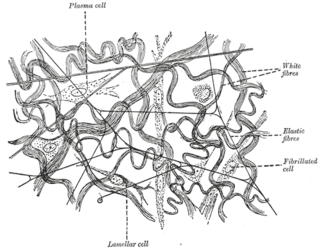
Elastic fibers are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan.

Stretch marks, also known as striae or striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. Over time they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Striae are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of rapid growth of the body, such as during puberty or pregnancy, in which they usually form during the last trimester. Usually on the stomach, these striae also commonly occur on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back, and buttocks. Pregnancy-related striae are known as striae gravidarum. Striae may also be influenced by the hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy. There is no evidence that creams used during pregnancy prevent stretch marks. Once they have formed there is no clearly effective treatment, though various methods have been attempted and studied.

Masson's trichrome is a three-colour staining procedure used in histology. The recipes evolved from Claude L. Pierre Masson's (1880–1959) original formulation have different specific applications, but all are suited for distinguishing cells from surrounding connective tissue.

A pinguecula is a common type of conjunctival stromal degeneration in the eye. It appears as an elevated yellow-white plaque in the bulbar conjunctiva near the limbus. Calcification may also seen occasionally.
Photorejuvenation is a skin treatment that uses lasers, intense pulsed light, or photodynamic therapy to treat skin conditions and remove effects of photoaging such as wrinkles, spots, and textures. The process induces controlled wounds to the skin. This prompts the skin to heal itself, by creating new cells. This process—to a certain extent—removes the signs of photoaging. The technique was invented by Thomas L Roberts, III using CO2 lasers in the 1990s. Observed complications have included scarring, hyperpigmentation, acne, and herpes.
Movat's stain is a pentachrome stain originally developed by Henry Zoltan Movat (1923–1995), a Hungarian-Canadian Pathologist in Toronto in 1955 to highlight the various constituents of connective tissue, especially cardiovascular tissue, by five colors in a single stained slide. In 1972, H. K. Russell, Jr. modified the technique so as to reduce the time for staining and to increase the consistency and reliability of the staining, creating the Russell–Movat stain.

Photoaging or photoageing is a term used for the characteristic changes to skin induced by chronic UVA and UVB exposure. Tretinoin is the best studied retinoid in the treatment of photoaging.
Intrinsic ageing and extrinsic ageing are terms used to describe cutaneous ageing of the skin and other parts of the integumentary system, which while having epidermal concomitants, seems to primarily involve the dermis. Intrinsic ageing is influenced by internal physiological factors alone, and extrinsic ageing by many external factors. Intrinsic ageing is also called chronologic ageing, and extrinsic ageing is most often referred to as photoageing.
Wrinkly skin syndrome(WSS) is a rare genetic condition characterized by sagging, wrinkled skin, low skin elasticity, and delayed fontanel (soft spot) closure along with a range of other symptoms. The disorder exhibits an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern with mutations in the ATP6V0A2 gene, leading to abnormal glycosylation events. There are only about 30 known cases of WSS as of 2010. Given its rarity and symptom overlap to other dermatological conditions, reaching an accurate diagnosis is difficult and requires specialized dermatological testing. Limited treatment options are available but long-term prognosis is variable from patient-to-patient, on the basis of individual case studies. Some skin symptoms recede with increasing age while progressive neurological advancement of the disorder causes seizures and mental deterioration later in life for some patients.
Elaunin is a component of elastic fibers formed from a deposition of elastin between oxytalan fibers. It is found in the periodontal ligament and in the connective tissue of the dermis, particularly in association with sweat glands.

Favre–Racouchot syndrome is a solar elastotic disorder consisting of multiple open comedones that occurs in skin damaged by sunlight, especially under and lateral of the eyes. The comedones are widened openings for hair follicles and sebaceous glands filled with material.
Role of skin in locomotion describes how the integumentary system is involved in locomotion. Typically the integumentary system can be thought of as skin, however the integumentary system also includes the segmented exoskeleton in arthropods and feathers of birds. The primary role of the integumentary system is to provide protection for the body. However, the structure of the skin has evolved to aid animals in their different modes of locomotion. Soft bodied animals such as starfish rely on the arrangement of the fibers in their tube feet for movement. Eels, snakes, and fish use their skin like an external tendon to generate the propulsive forces need for undulatory locomotion. Vertebrates that fly, glide, and parachute also have a characteristic fiber arrangements of their flight membranes that allows for the skin to maintain its structural integrity during the stress and strain experienced during flight.
Verhoeff's stain, also known as Verhoeff's elastic stain (VEG) or Verhoeff–Van Gieson stain (VVG), is a staining protocol used in histology, developed by American ophthalmic surgeon and pathologist Frederick Herman Verhoeff (1874–1968) in 1908. The formulation is used to demonstrate normal or pathologic elastic fibers.

Collagen is a protein that is an important part of connective tissues in the body. It is a rigid, non-soluble, fibrous protein that adds up to one-third of the proteins in the human body. Collagen is mostly made up of molecules packed together to form long and thin fibrils that support each other and ensure the skin is strong and elastic. various types of collagens have individual roles and structures. Most collagen belongs to types 1, 2, and 3. Collagen consists mainly of amino acids and can be mostly found in tendons, muscles, bones, skin, ligaments, and other fibrous tissues. It helps keep the skin strong and supple and sustains the renewal of skin cells and the replacement of damaged and dead body cells. The collagen tissues support the formation of bones, tendons, and cartilage that form depending on the level of mineralization. However, an individual can lose collagen components in the body due to exposure to ultraviolet light, tobacco, excessive intake of sugar, and aging. This loss of collagen can cause the skin to lose elasticity, reduction of the thickness of the epidermis, increase the formation of wrinkles and sagging and also make the skin vulnerable and easily damaged.