Related Research Articles
Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.

4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD), also known as α-ketoisocaproate dioxygenase, is an Fe(II)-containing non-heme oxygenase that catalyzes the second reaction in the catabolism of tyrosine - the conversion of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate into homogentisate. HPPD also catalyzes the conversion of phenylpyruvate to 2-hydroxyphenylacetate and the conversion of α-ketoisocaproate to β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate. HPPD is an enzyme that is found in nearly all aerobic forms of life.

Monoacylglycerol lipase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the MGLL gene. MAGL is a 33-kDa, membrane-associated member of the serine hydrolase superfamily and contains the classical GXSXG consensus sequence common to most serine hydrolases. The catalytic triad has been identified as Ser122, His269, and Asp239.
N4-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase (EC 3.5.1.26, aspartylglucosylamine deaspartylase, aspartylglucosylaminase, aspartylglucosaminidase, aspartylglycosylamine amidohydrolase, N-aspartyl-beta-glucosaminidase, glucosylamidase, beta-aspartylglucosylamine amidohydrolase, 4-N-(beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine amidohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name N4-(beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine amidohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine 1-acylhydrolase) encoded by the PLA1A gene is a phospholipase enzyme which removes the 1-acyl group:
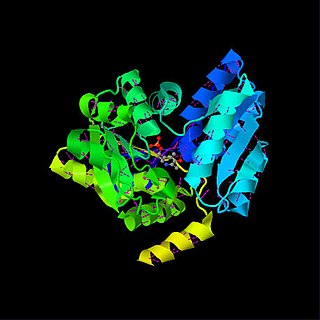
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
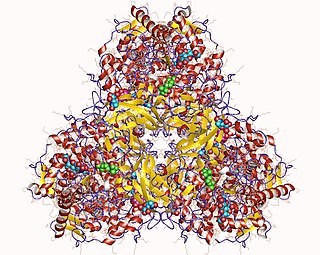
Glucan 1,4-α-glucosidase is an enzyme located on the brush border of the small intestine with systematic name 4-α-D-glucan glucohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
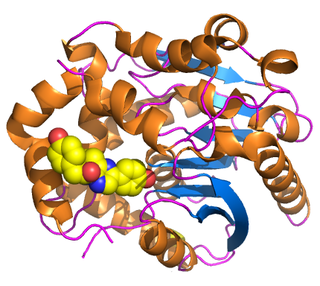
Renilla-luciferin 2-monooxygenase, Renilla luciferase, or RLuc, is a bioluminescent enzyme found in Renilla reniformis, belonging to a group of coelenterazine luciferases. Of this group of enzymes, the luciferase from Renilla reniformis has been the most extensively studied, and due to its bioluminescence requiring only molecular oxygen, has a wide range of applications, with uses as a reporter gene probe in cell culture, in vivo imaging, and various other areas of biological research. Recently, chimeras of RLuc have been developed and demonstrated to be the brightest luminescent proteins to date, and have proved effective in both noninvasive single-cell and whole body imaging.
In enzymology, a bis(5'-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase (asymmetrical) (EC 3.6.1.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme carboxylesterase (or carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1; systematic name carboxylic-ester hydrolase) catalyzes reactions of the following form:
Palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.2) is an enzyme in the family of hydrolases that specifically acts on thioester bonds. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of long chain fatty acyl thioesters of acyl carrier protein or coenzyme A to form free fatty acid and the corresponding thiol:
Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase (MOGS) (EC 3.2.1.106, processing α-glucosidase I,Glc3Man9NAc2 oligosaccharide glucosidase, trimming glucosidase I, GCS1) is an enzyme with systematic name mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucohydrolase. MOGS is a transmembrane protein found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells. Biologically, it functions within the N-glycosylation pathway.
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase (hydrolysing) (EC 3.2.1.183, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase, GNE (gene), siaA (gene), neuC (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine hydrolase (2-epimerising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aminopeptidase B is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methionyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Peptidyl-glycinamidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (EC 3.4.19.3, also known as Pyrrolidonyl peptidase, is an enzyme found in bacteria, plants and animals.
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-formylmethionyl-peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Tsunasawa S, Narita K, Ogata K (January 1975). "Purification and properties of acylamino acid-releasing enzyme from rat liver". Journal of Biochemistry. 77 (1?): 89–102. PMID 1137989.
- ↑ Unger T, Nagelschmidt M, Struck H (June 1979). "N-Acetylaminoacyl-p-nitranilidase from human placenta. Purification and some properties". European Journal of Biochemistry. 97 (1): 205–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13104.x . PMID 477668.
- ↑ Kobayashi K, Smith JA (August 1987). "Acyl-peptide hydrolase from rat liver. Characterization of enzyme reaction". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (24): 11435–45. PMID 3305492.